SIST IEC 60050(725):2005
(Main)International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 725: Space radiocommunications
International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 725: Space radiocommunications
It has the status of a horizontal standard in accordance with IEC Guide 108.
Vocabulaire Electrotechnique International - Chapitre 725: Radiocommunications spatiales
Elle a le statut d'une norme horizontale conformément au Guide 108 de la CEI.
Mednarodni elektrotehniški slovar – 725. poglavje: Vesoljske radiokomunikacije
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 31-Mar-2005
- Technical Committee
- TRM - Terminology
- Current Stage
- 6060 - National Implementation/Publication (Adopted Project)
- Start Date
- 01-Apr-2005
- Due Date
- 01-Apr-2005
- Completion Date
- 01-Apr-2005
Overview
ISO 80369-3:2016 - Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications - Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications (published 2016). Developed by ISO in collaboration with IEC/SC 62D, this standard specifies the design dimensions, material and functional requirements, and performance tests for small-bore connectors used on enteral medical devices and accessories. The goal is to reduce hazardous misconnections (e.g., enteral feed delivered intravenously or into the airway) by making enteral connectors dimensionally incompatible with connectors from other medical application categories.
Key topics and technical requirements
- Scope: Applies to connectors for enteral feeding sets, enteral drainage sets, enteral syringes, access ports and patient interface devices. It does not cover device-specific requirements or certain enteral-related items (e.g., gastric suction-only, oral-only devices, rectal devices, gastrointestinal endoscopy, skin-level gastrostomy, or balloon inflation ports).
- Design and dimensions: Detailed dimensional drawings and tolerances for enteral small-bore connectors are provided (see normative Annex B and C for reference connectors).
- Materials: Guidance and requirements on materials suitable for enteral connectors to ensure biocompatibility and mechanical integrity.
- Performance requirements and tests (aligned with ISO 80369-1 and ISO 80369-20):
- Fluid leakage (pressure-decay and positive-pressure leakage tests)
- Stress cracking resistance
- Resistance to separation from axial loads, unscrewing, and overriding
- Controlled disconnection behavior
- Usability and risk management: Informative annexes (D–G) summarize usability requirements, design assessment, and rationale. Risk management referencing ISO 14971 is required.
- Non-interconnectability: Connectors are designed so they cannot mate with connectors intended for other clinical applications, reducing misconnection risk.
Applications
- Use when designing, manufacturing, testing, or procuring components of enteral feeding systems and accessories:
- Enteral feeding sets and tubing
- Enteral syringes and administration devices
- Patient access ports and enteral connectors on devices
- Helps hospitals and procurement teams choose safer connectors to mitigate misconnection incidents.
- Useful for regulatory submissions, quality systems, and conformity assessment for enteral device connectors.
Who should use this standard
- Medical device designers and manufacturers
- Regulatory and quality managers (compliance with device standards)
- Clinical engineers, procurement officers, and hospital safety officers
- Test labs performing connector performance and compatibility testing
Related standards
- ISO 80369-1 (General requirements)
- ISO 80369-20 (Common test methods)
- Other ISO 80369 parts (e.g., Part 2, Part 6, Part 7)
- ISO 14971 (Risk management)
- ISO 18250-3 (enteral reservoir connectors)
Keywords: ISO 80369-3:2016, small-bore connectors, enteral connectors, enteral feeding, misconnection prevention, connector dimensions, medical device standards.
ISO 80369-3:2016 - Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications -- Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications
ISO 80369-3:2016 - Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé - Partie 3: Raccords destinés à des applications entérales Released:7/1/2016
Frequently Asked Questions
SIST IEC 60050(725):2005 is a standard published by the Slovenian Institute for Standardization (SIST). Its full title is "International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 725: Space radiocommunications". This standard covers: It has the status of a horizontal standard in accordance with IEC Guide 108.
It has the status of a horizontal standard in accordance with IEC Guide 108.
SIST IEC 60050(725):2005 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 01.040.33 - Telecommunications. Audio and video engineering (Vocabularies); 29.020 - Electrical engineering in general; 33.060.30 - Radio relay and fixed satellite communications systems. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
SIST IEC 60050(725):2005 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL ISO
STANDARD 80369-3
First edition
2016-07-01
Small-bore connectors for liquids and
gases in healthcare applications —
Part 3:
Connectors for enteral applications
Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine
de la santé —
Partie 3: Raccords destinés à des applications entérales
Reference number
©
ISO 2016
© ISO 2016, Published in Switzerland
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized otherwise in any form
or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, or posting on the internet or an intranet, without prior
written permission. Permission can be requested from either ISO at the address below or ISO’s member body in the country of
the requester.
ISO copyright office
Ch. de Blandonnet 8 • CP 401
CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland
Tel. +41 22 749 01 11
Fax +41 22 749 09 47
copyright@iso.org
www.iso.org
ii © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
Contents Page
Foreword .iv
Introduction .v
1 * Scope . 1
2 Normative references . 1
3 Terms and definitions . 2
4 General requirements . 3
4.1 General requirements for the enteral application. 3
4.2 Material used for enteral small-bore connectors . 3
4.3 Type tests . 4
5 Dimensional requirements for enteral small-bore connectors .4
6 Performance requirements . 4
6.1 Fluid leakage . 4
6.1.1 Fluid leakage requirement . 4
6.1.2 Leakage by pressure decay . 4
6.1.3 Positive pressure liquid leakage . 4
6.2 Stress cracking . 4
6.3 Resistance to separation from axial load. 4
6.4 Resistance to separation from unscrewing . 5
6.5 Resistance to overriding . 5
6.6 Disconnection by unscrewing . 5
Annex A (informative) Rationale and guidance . 6
Annex B (normative) Enteral small-bore connectors .10
Annex C (normative) Reference connectors .16
Annex D (informative) Assessment of medical devices and their attributes with
connections within this application .21
Annex E (informative) Summary of the usability requirements for small-bore connectors
for enteral applications .22
Annex F (informative) Summary of small-bore connector criteria and requirements for
enteral applications .27
Annex G (informative) Summary of assessment of the design of the connectors for
enteral applications .30
Annex H (informative) Reference to the essential principles .36
Annex I (informative) Terminology — Alphabetized index of defined terms .38
Bibliography .39
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards
bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out
through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical
committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International
organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of
electrotechnical standardization.
The procedures used to develop this document and those intended for its further maintenance are
described in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1. In particular the different approval criteria needed for the
different types of ISO documents should be noted. This document was drafted in accordance with the
editorial rules of the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2 (see www.iso.org/directives).
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of
patent rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights. Details of
any patent rights identified during the development of the document will be in the Introduction and/or
on the ISO list of patent declarations received (see www.iso.org/patents).
Any trade name used in this document is information given for the convenience of users and does not
constitute an endorsement.
For an explanation on the meaning of ISO specific terms and expressions related to conformity
assessment, as well as information about ISO’s adherence to the WTO principles in the Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) see the following URL: Foreword - Supplementary information
The committee responsible for this document is ISO/TC 210, Quality management and corresponding
general aspects for medical devices, and IEC/SC 62D, Electromedical equipment. The draft was circulated
for voting to the national bodies of both ISO and IEC.
ISO 80369 consists of the following parts, under the general title Small-bore connectors for liquids and
gases in healthcare applications:
— Part 1: General requirements
— Part 2: Connectors for breathing systems and driving gases applications
— Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications
— Part 5: Connectors for limb cuff inflation applications
— Part 6: Connectors for neuraxial applications
— Part 7: Connectors with 6 % (Luer) taper for intravascular or hypodermic applications
— Part 20: Common test methods
An additional part on connectors for urethral and urinary applications is planned.
iv © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
Introduction
This part of ISO 80369 was developed because of several incidents, with catastrophic consequences,
resulting from firstly, the administration of inappropriate medication into the alimentary canal and
secondly, from enteral solutions being administered via incorrect routes, including intravenously and
into the airway. Many incidents were reported leading to international recognition of the importance of
these issues, and a need was identified to develop specific connectors for medical devices and their
accessories used to deliver feed via the enteral route.
The ISO 80369 series has been developed to prevent misconnection between small-bore connectors
used in different applications. ISO 80369-1 specifies the requirements necessary to verify the designs
of small-bore connectors to ensure that
a) they do not misconnect with other small-bore connectors, and
b) they safely and securely connect with their mating half.
ISO 80369-20 contains the common test methods to support the performance requirements for
small-bore connectors.
This part of ISO 80369 specifies the design, the dimensions, and the drawings of small-bore
connectors intended to be used in enteral applications. Annex D to Annex G describe the methods
by which this design has been assessed. Other parts of ISO 80369 include requirements for small-bore
connectors used in different application categories.
Connectors manufactured to the dimensions set out within this part of ISO 80369 are dimensionally
incompatible with any of the other connectors for applications identified in the ISO 80369 series
for small-bore connectors, except as indicated in G.2. If fitted to the relevant medical devices
and accessories, these connectors are to reduce the risk of medication and liquid nutritional
formula intended for enteral administration from being delivered via an alternative route, such as
intravenously or via an airway device.
During the development of this International Standard, the committee decided to cover the whole
enteral system but to have a separate International Standard for reservoir connectors. ISO 18250-3
specifies the requirements for enteral reservoir connectors. This part of ISO 80369 includes the
interface dimensions for small-bore connectors for access ports and patient interfaces on enteral
feeding sets and enteral syringes.
In this part of ISO 80369, the following print types are used:
— requirements and definitions: roman type;
— informative material appearing outside of tables, such as notes, examples and references: in smaller
type. Normative text of tables is also in a smaller type;
— terms defined in Clause 3 or as noted: small capitals.
In this part of ISO 80369, the conjunctive “or” is used as an “inclusive or” so a statement is true if any
combination of the conditions is true.
The verbal forms used in this International Standard conform to usage described in ISO/IEC Directives,
Part 2, Annex H. For the purposes of this part of ISO 80369, the auxiliary verb
— “shall” means that compliance with a requirement or a test is mandatory for compliance with this
part of ISO 80369,
— “should” means that compliance with a requirement or a test is recommended but is not mandatory
for compliance with this part of ISO 80369, and
— “may” is used to describe a permissible way to achieve compliance with a requirement or test.
An asterisk (*) as the first character of a title or at the beginning of a paragraph or table title indicates
that there is guidance or rationale related to that item in Annex A.
vi © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 80369-3:2016(E)
Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare
applications —
Part 3:
Connectors for enteral applications
1 * Scope
This part of ISO 80369 specifies the dimensions and requirements for the design and functional
performance of small-bore connectors intended to be used for connections on enteral medical
devices and accessories.
NOTE 1 Enteral medical devices include enteral feeding sets, enteral drainage sets, enteral syringes,
and patient interface devices including access ports.
This part of ISO 80369 does not specify the dimensions and requirements for the medical devices
or accessories that use these connectors. Such requirements are given in particular International
Standards for specific medical devices or accessories.
This part of ISO 80369 does not specify requirements for small-bore connectors that are used for the
following:
— gastric suction-only medical devices;
— oral-only medical devices;
EXAMPLE An oral tip syringe that is not intended to connect to another medical device. It is intended
to administer directly to the patient’s mouth.
— pressurizing and depressurizing the retention mechanism (e.g. balloon) used to hold invasive
enteral medical devices in place;
— medical devices for rectal drainage, rectal administration of medicines or fluid, and any other
rectal access medical device;
— gastrointestinal endoscopy equipment;
— skin level gastrostomy medical devices.
NOTE 2 Manufacturers are encouraged to incorporate the small-bore connectors specified in this part
of ISO 80369 into enteral medical devices or accessories, even if currently not required by the relevant
particular medical device standards. It is expected that when the relevant particular medical device standards
are revised, requirements for small-bore connectors, as specified in ISO 80369, will be included.
2 Normative references
The following documents, in whole or in part, are normatively referenced in this document and are
indispensable for its application. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 14971:2007, Medical devices — Application of risk management to medical devices
ISO 80369-1:2010, Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 1: General
requirements
ISO 80369-6:2016, Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 6:
Connectors for neuraxial applications
1)
ISO 80369-7:— , Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 7:
Connectors with 6% (Luer) taper for intravascular or hypodermic applications
ISO 80369-20:2015, Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 20:
Common test methods
ASTM D638-10, Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics
ASTM D790-10, Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and
electrical insulating materials
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 80369-1, ISO 80369-7,
ISO 80369-20, and ISO 14971 and the following apply.
NOTE For convenience, the sources of all defined terms used in this part of ISO 80369 are given in Annex I.
3.1
enteral
pertaining to the gastrointestinal tract
3.2
normal use
operation, including routine inspection and adjustments by any user, and stand-by, according to the
instructions for use
Note 1 to entry: Normal use should not be confused with intended use. While both include the concept of use as
intended by the manufacturer, intended use focuses on the medical purpose while normal use incorporates
not only the medical purpose, but maintenance, service, transport, etc. as well
[SOURCE: IEC 60601-1:2005+A1:2012, 3.71, modified—replaced “operator” with “user”.]
3.3
rated
term referring to a value assigned by the manufacturer for a specified operating condition
[SOURCE: IEC 60601-1:2005, 3.97]
3.4
user
person interacting with (i.e. operating or handling) the medical device
Note 1 to entry: This includes, but is not limited to, cleaners, maintainers and installers
Note 2 to entry: Patients or other laypersons can be users
[SOURCE: IEC 62366-1:2015, 3.24]
3.5
user profile
summary of the mental, physical, and demographic traits of an intended user population, as well as any
special characteristics that can have a bearing on design decisions, such as occupational skills and job
requirements
[SOURCE: IEC 62366-1:2015, 3.29]
1) To be published.
2 © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
4 General requirements
4.1 General requirements for the enteral application
Small-bore connectors of medical devices or accessories intended for use in enteral applications
made in compliance with this part of ISO 80369 comply with ISO 80369-1 unless otherwise indicated in
this part of ISO 80369.
The sealing surface of female E1 connector may contact the thread surfaces of the N female
connector, as specified in ISO 80369-6 in LMC conditions when evaluating the non-interconnectable
characteristics tests of ISO 80369-1:2010, Annex B. Additional information is provided in G.2.
Because the following connectors are inadequately specified, small-bore connectors for use in
enteral applications should not, but may connect with the following:
— the cones and sockets of ISO 5356-1:2004, ISO 5356-1:2015, ISO 5356-2:2006 and ISO 5356-2:2012;
— the temperature sensor and mating ports made in compliance with ISO 8185:2007, Annex DD;
— the nipples of EN 13544-2:2002 and EN 13544-2:2002+A1:2009.
The reference connectors for evaluation of the non-interconnectable characteristics are described
in Annex C.
Where the design of the small-bore connector of this part of ISO 80369 relies on dimensions or
features of the medical device or accessory to ensure non-interconnectable characteristics, the
non-interconnectable characteristics shall be verified.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-1:2010, 5.1, and ISO 80369-1:2010, Annex B.
Compliance also may be shown by applying a computer aided design (CAD) analysis of the dimensions
of all of the ISO 80369 series small bore connectors and the small bore connector under test, in
conjunction with physical testing of the small bore connector per Annex B where the CAD analysis
does not demonstrate the non-interconnectable characteristics. When necessary, the small-bore
connector may be installed on the medical device or accessory to demonstrate compliance with the
non-interconnectable characteristics test requirements of ISO 80369-1:2010, Annex B.
NOTE 1 Medical devices using the small-bore connectors of this part of ISO 80369 that do not rely on the
dimensions or features of the medical device or accessory to ensure non-interconnectable characteristics
are presumed to comply with the non-interconnectable characteristics test requirements of this part of
ISO 80369.
NOTE 2 The summary of medical devices and their attributes with connections within this application is
provided in Annex D.
NOTE 3 The summary of the usability requirements for enteral small-bore connectors is provided in
Annex E.
NOTE 4 The summary of enteral small-bore connectors criteria and requirements is provided in Annex F.
NOTE 5 The summary of assessment of the design of enteral small-bore connectors according to
ISO 80369-1:2010, Clause 7, is contained in Annex G.
4.2 Material used for enteral small-bore connectors
In addition to the requirements of ISO 80369-1:2010, Clause 4, enteral small-bore connectors shall
be made of materials with a nominal modulus of elasticity either in flexure or in tension greater than
700 MPa.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ASTM D638-10 or ASTM D790-10.
4.3 Type tests
Compliance with the requirements of this part of ISO 80369 shall be determined by type tests.
5 Dimensional requirements for enteral small-bore connectors
Enteral small-bore connectors shall comply with the relevant dimensions and tolerances as given in
— Figure B.1 and Table B.1 for a male E1 connector, and
— Figure B.2 and Table B.2 for a female E1 connector.
Check compliance by verifying the dimensions and tolerances specified in Annex B, as appropriate.
6 Performance requirements
6.1 Fluid leakage
6.1.1 Fluid leakage requirement
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for leakage using either the leakage by pressure
decay test method or the positive pressure liquid leakage test method.
6.1.2 Leakage by pressure decay
Enteral small-bore connectors evaluated for fluid leakage performance with the leakage by
pressure decay test method shall not leak by more than 0,005 Pa·m /s while being subjected to an
applied pressure of between 300 kPa and 330 kPa over a hold period between 15 s and 20 s using air as
the medium. Manufacturers may use a greater applied pressure.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex B, while using the leakage
reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.1.3 Positive pressure liquid leakage
Enteral small-bore connectors evaluated for fluid leakage performance with the positive pressure
liquid leakage test method shall show no signs of leakage, sufficient to form a falling drop of water,
over a hold period of 30 s to 35 s while being subjected to an applied pressure of between 300 kPa and
330 kPa. Manufacturers may use a greater applied pressure or a longer hold period.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex C, while using the leakage
reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.2 Stress cracking
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for stress cracking. enteral small-bore
connectors shall meet the requirements of 6.1.1 after being subjected to stresses of ISO 80369-20:2015,
Annex E.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex E, while using the stress cracking
reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.3 Resistance to separation from axial load
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for separation from axial load. enteral small-
bore connectors shall not separate from the reference connector over a hold period between
4 © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
10 s and 15 s while being subjected to a disconnection applied axial force between 32 N and 35 N.
Manufacturers may use a greater disconnection applied axial force or a longer hold period.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex F, while using the separation from
axial load reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.4 Resistance to separation from unscrewing
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for separation from unscrewing. Enteral
small-bore connectors shall not separate from the reference connector for a hold period between
10 s and 15 s while being subjected to an unscrewing torque of between 0,019 8 N·m to 0,020 0 N·m.
Manufacturers may use a greater applied unscrewing torque or a longer hold period.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex G, while using the separation from
unscrewing reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.5 Resistance to overriding
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for resistance to overriding. enteral small-
bore connectors shall not override the threads or lugs of the reference connector while being
subjected to an applied torque of between 0,15 N·m to 0,17 N·m over a hold period between 5 s and 10 s.
Manufacturers may use a greater applied torque or a longer hold period.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex H, while using the resistance to
overriding reference connector specified in Annex C.
6.6 Disconnection by unscrewing
Enteral small-bore connectors shall be evaluated for disconnection by unscrewing. enteral
small-bore connectors shall separate from the reference connector with an applied unscrewing
torque of no greater than 0,35 N·m.
Check compliance by applying the tests of ISO 80369-20:2015, Annex I, while using the disconnection
by unscrewing reference connector specified in Annex C.
Annex A
(informative)
Rationale and guidance
A.1 General guidance
A.1.1 Guidance
This Annex provides a rationale for some requirements of this part of ISO 80369 and is intended for
those who are familiar with the subject of this part of ISO 80369 but who have not participated in its
development. An understanding of the rationale underlying these requirements is considered to be
essential for their proper use. Furthermore, as clinical practice and technology change, it is believed
that a rationale will facilitate any revision of this part of ISO 80369 necessitated by those developments.
A.1.2 Connector selection
It is understood that small bore connector systems cannot be designed to overcome all chances of
misconnection or to eliminate deliberate misuse. However, a number of steps that would improve the
current situation and lead to greater patient safety can be taken.
The patient connector needs to be one that is intended to be non-interconnectable with
connectors in the patient care area. Care should be taken to ensure misconnection testing and
associated risk analysis is performed to ensure safety and efficacy of the system.
A.1.3 Colour coding
Relative to this part of ISO 80369, it is not considered appropriate to specify a colour because this is
a connector standard as opposed to a medical device standard. The connectors specified will be
physically unable to fit into a non-enteral connector and a designation of colour is deemed insufficient
to signal, and ineffective in preventing, a misconnection. Other applications such as intravascular
medical devices and suction catheters might use colour, and these colours are not standardized across
applications and countries. Identification of enteral with any specific colour (e.g. purple, orange,
yellow) could contribute to additional instances of medical device misconnection.
A.2 Rationale for particular clauses and subclauses
The clauses and subclauses in this Annex have been numbered to correspond to the numbering of the
clauses and subclauses of this part of ISO 80369 to which they refer. The numbering is, therefore, not
consecutive.
Clause 1 Scope
In 2000, a Task Group of the European standards organization, CEN, proposed a strategy to
reduce incidents of accidental misconnection of patient therapy lines by the use of a series
of non-interconnectable connectors, differentiated by design, for use in different medical
[12]
applications. The strategy reserves the use of luer connectors solely for use in medical devices
used to access the vascular system or for hypodermic syringes so that they can achieve their intended
function.
Exclusion of gastric suction-only medical devices:
The committee determined that medical devices and accessories intended for gastric suction-
only use would be excluded from the scope of this part of ISO 80369. Many gastric suction-only uses
6 © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
require an inner diameter larger than 8,5 mm, the defined maximum inner diameter for a small-bore
connector, therefore falling outside of the scope of ISO 80369-1.
Exclusion of oral-only medical devices:
The committee determined that delivery of fluids orally to the gastrointestinal tract would be excluded
from the scope of this part of ISO 80369. The delivery of fluids orally does not require a connection
to be made as defined in this part of ISO 80369; therefore, it is considered to be out of the scope of this
part of ISO 80369.
The connectors detailed in this part of ISO 80369 are specifically intended to be used as a connection
system (i.e. female connector mating to a male connector). If a connector that is not intended to be
used exclusively as part of this connection system is incorporated into an enteral medical device
or accessory, then the medical device manufacturer needs to evaluate and control the associated
risks as appropriate.
Orientation of connection:
This part of ISO 80369 does not specify the orientation of the E1 connectors, allowing each jurisdiction
to designate the direction of flow they see most appropriate because the connectors specified in
this part of ISO 80369 have been designed with non-interconnectable characteristics preventing
misconnection with any other male and female connectors of the ISO 80369 series. Individual
jurisdictions or manufacturers should consider the potential risks associated with orientation, such
as contamination and ease of cleaning prior to implementation.
User studies for misconnection were performed on the E1 connector with a specified orientation in
which the indwelling enteral medical device incorporated the male connector, and the connecting
medical devices (syringe, feed sets, etc.) incorporated the female design. Misconnection analysis using
CAD modelling and associated risk analyses have been performed to identify risk of misconnection
regardless of orientation.
Subpopulations within the enteral clinical application:
Concerns have been raised about the possible risks of delivering inaccurate doses of medicines in
certain clinical practices across high risk subpopulations (e.g. neonatal patients) if using a reversed
connection system (female to male). This orientation can introduce inadvertent displacement of
fluid originally contained within the female small-bore connector. This displacement occurs
when fluid is drawn up into the syringe without the use of an adaptor or drawing-up accessory that
is then administered through a connection being made to a feeding tube. Laboratory testing has
demonstrated that the majority of this fluid is displaced into the male small-bore connector and the
medical device behind it.
Laboratory testing also shows a mid-tolerance E1 connector pair in a female to male orientation
displaces a mean average of 0,148 ml (min 0,089 ml and max 0,179 ml with an n = 32) of fluid. For
comparative purposes, a reverse luer connector (EN 1615) tested in similar conditions displaced a
mean average 0,103 ml (min 0,074 ml and max 0,122 ml with an n = 64). To date, risks associated with
dose accuracy in medical devices designed with a reversed orientation have not been fully evaluated,
and therefore, there is no proven need to explicitly exclude any subpopulations within the enteral
clinical application. It is therefore recommended that the E1 small-bore connector be used for all
patients to reduce the risks of misconnection. Manufacturers incorporating the E1 small-bore
connector in medical devices intended for use with high risk subpopulations (e.g. neonatal patients)
should evaluate any risk associated with this potential displacement and, if objective evidence indicates
such a potential risk exists, should make the user aware of the potential for fluid displacement.
The fluid that could be delivered into a male E1 connector, due to the insertion of the cone of male
connector into the female connector filled with fluid, is the over delivered volume (displaced fluid
volume delivered in excess of the intended dose). When highly accurate dose delivery is required using
the E1 connection in a female to male orientation, the use of draw up adapters (e.g. a draw up straw)
is recommended. Preliminary data suggests that with the correct use of a draw up adapter, the volume
of fluid delivered (the overdose amount) has been shown to be 0,003 ml. Manufacturers of devices
incorporating the ISO 80369-3 connector will need to conduct validation studies to ensure dose
accuracy meets the requirements of the device.
Displaced delivered volume should not be confused with the volume between the female port and male
cone surfaces once connected, which is often referred to as dead space.
Manufacturers and responsible organizations are encouraged to report their experience with the
small-bore connectors specified in this part of ISO 80369 to the Secretariat of ISO/TC 210, so that it
can consider this feedback during the revision of the relevant part of the ISO 80369 series.
Table B.1 Male E1 small-bore connector dimensions
The design of the enteral connectors incorporate features for which functionality might not be
readily apparent. Many of those reasons affect either the non-interconnectable characterizes or the
performance requirements of these connectors.
c Projection of the tip of the connector from thread collar
This feature provides a visual cue for the user to ease alignment during assembly. A rotatable, internally
threaded lock fitting is permitted, but dimension c is required to be maintained.
e Length of male taper (Ød to Øg)
The taper length is specified to define the taper angle with a transition to a lesser angle. The taper
length defines a minimum length necessary for sealing. The angle beyond the taper is permitted to be
as large as 0,5° (1° included angle) or the area beyond the taper is permitted to be smaller than the end
of the taper (Øg) at the discretion of the manufacturer.
Øg Outside diameter of the larger end of the male taper at e from the tip (small end) of the
male taper
The maximum size of the nozzle is limited in order to provide non-interconnectable characteristics
with the inside diameter of the male cone of the 8,5 mm connector as defined by ISO 5356-1.
s3 Length of nozzle from end of collar
The maximum thread length is not specified but is required to provide clearance and support for the
thread of the female enteral connector when both connectors are at least material condition (LMC).
x3 Chord length of thread minor diameter (Øj) at thread start
This feature performs two functions. The minimum dimension provides two edges on Øj to provide
non-interconnectable characteristics for other small-bore connectors as determined by the
misconnection evaluation. The maximum dimension creates a blunt thread and was incorporated to
reduce the likelihood of inadvertent cross threading when mating male and female E1 connectors
during non-axial insertion.
Øw Diameter of the smallest cylinder that encompasses the outside surfaces of external
features at the open end of the collar
The dimensions specified for the diameter of the smallest cylinder that encompasses the outside
surfaces of external features at the open end of the collar (Øw) have been demonstrated to exhibit non-
interconnectable characteristics. Manufacturers are permitted to deviate from these dimensions
(Øw for depth s3), but then the medical device incorporating the enteral connector needs to
demonstrate non-interconnectable characteristics using ISO 80369-1:2010, Annex B to ensure that
misconnections cannot occur.
When the male connector is used as a source of flow (e.g. on an administration set, syringe, or other
similar medical device) a collar, wings, or other feature with a minimum diameter of Øw is required
for the purpose of preventing misconnection with the unspecified inside diameter of most 15 mm
connectors as defined by ISO 5356-1.
8 © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
When the male connector is not used as a source of flow (e.g. on a patient access medical device), a
collar or wings with the dimensions specified for the diameter Øw have been demonstrated to exhibit
non-interconnectable characteristics.
z3 Face angle at thread start
This feature was incorporated to reduce the likelihood of inadvertent cross threading when mating
male and female E1 connectors during non-axial insertion.
Table B.2 Female E1 small-bore connector dimensions
The design of the enteral connectors incorporate features for which functionality might not be
readily apparent. Many of those reasons affect either the non-interconnectable characteristics or the
performance requirements of these connectors.
R3 Length of clearance for male connector collar and threads, and
ØW Diameter of the smallest cylinder that encompasses the outside surfaces of the external
features at R3
When the female connector is used as a source of flow (e.g. on an administration set, syringe, or other
similar medical device) a ring, wings, or other feature is required by this part of ISO 80369 behind the
thread with a minimum diameter of ØW located within the range of dimension R3 for the purpose of
preventing misconnection with the unspecified inside diameter of most 15 mm connectors as defined
by ISO 5356-1.
When the female connector is not used as a source of flow (e.g. on a patient access medical device)
a ring, wings or other feature are not required by this part of ISO 80369. A ring or wings behind the
thread are at the discretion of the manufacturer and are permitted by this part of ISO 80369 to be a
feature of the medical device.
Manufacturers are permitted to deviate from these dimensions (R3 and ØW), but then the
medical device incorporating the enteral small-bore connector needs to demonstrate non-
interconnectable characteristics using ISO 80369-1:2010, Annex B to ensure that misconnections
cannot occur.
X3 Chord length of thread major diameter (ØH) at thread start
This feature performs two functions. The minimum dimension provides two edges on ØH to provide
non-interconnectable characteristics for other small-bore connector as determined by the
misconnection evaluation. The maximum dimension creates a blunt thread and was incorporated to
reduce the likelihood of inadvertent cross threading when mating male and female E1 connectors
during non-axial insertion.
Y Chord length at extremity of thread in a plane at a right angle to axis of the connector
This feature can be achieved in many ways, such as a lug thread as shown or a full thread continuing to
some other feature. This is at the discretion of the manufacturer as long as the final design meets the
performance requirements of Clause 6.
Z3 Face angle at thread start
This feature was incorporated to reduce the likelihood of inadvertent cross threading when mating
male and female E1 connectors during non-axial insertion.
Annex B
(normative)
Enteral small-bore connectors
NOTE Table B.1 contains the dimensions for Figure B.1.
Figure B.1 — Male E1 small-bore connector
10 © ISO 2016 – All rights reserved
In Figure B.1, the male enteral small-bore connector may utilize a rotatable collar. The requirements
for dimension c shall be maintained.
Table B.1 — Male E1 small-bore connector dimensions
Dimensions in millimetres unless otherwise indicated
Male E1 small-bore connector
Dimension
Reference Designation
Minimum Nominal Maximum
Angle of taper (6 % taper nominal)
(a) — (3,44°) —
(degrees, reference)
Projection of the tip of the connector from
* c 1,00 1,10 1,20
thread collar
Ød Outside diameter at the tip of the male taper 5,36 5,41 5,46
a
* e Length of male taper (Ød to Øg) 3,72 3,82 3,92
Øf Inside diameter at the tip of the male taper 0,0 2,90 2,95
Outside diameter of the larger end of the male
a
* Øg taper at e from the tip (small end) of the male 5,59 5,64 5,69
a b
taper
Major inside thread diameter
Øh 10,13 10,23 10,33
(diameter at thread root)
Minor inside thread diameter
Øj 8,55 8,65 8,75
(diameter at thread crest)
Length of engagement (reference)
(L) (3,00) (4,67) (6,33)
(see Figure B.3)
Width of the thread groove at the root
m3 1,05 1,15 1,25
(symmetrical with n3)
Width of the thread groove at the crest
n3 1,80 1,90 2,00
(symmetrical with m3)
Pitch of double-start, right-hand thread
p 2,45 2,50 2,55
(reference 5 mm lead)
a a b
* s3 Length of nozzle from end of collar 6,82 — —
Angle of projection of nozzle from end of collar
t3 40° 45° 50°
(degrees)
Diameter of the smallest cylinder that encom-
c
* Øw passes the outside surfaces of external features 13,30 — —
d
of the collar
a
Region of male taper between dimensions e and s3 defined by Øg may have draft in the direction of pull no greater
than 1,0° inclusive (0,5°/side).
b
This dimension is required to provide clearance for the inside diameter at the open end of the female taper (Ød) and
face of female connector. Maximum thread profile length is not specified but shall provide clearance for the thread of the
male connector. The geometry defined by Ød is flush to the face of the collar.
c
This dimension is only required where the male connector is a source of fluid flow.
d
The minimum value of w shall be maintained for the length of 1,00 mm, and the maximum value shall be maintained
for the length of e. This dimension may be achieved by either the connector or the medical device which incorporates
this connector. Alternatively, non-interconnectable characteristics may be demonstrated using ISO 80369-1:2010,
Annex B.
e
This dimension is only required where the male connector is not a source of fluid flow.
f
Other geometries that begin and end at the limits of the specified angle line may be used.
Table B.1 (continued)
Male E1 small-bore connector
Dimension
Reference Designation
Minimum Nominal Maximum
Diameter of the smallest cylinder that encom-
e
* Øw passes the outside surfaces of external features 12,00 12,20 —
d
of the collar
Chord length of thread minor diameter (Øj) at
* x3 0,25 0,50 1,50
thread start
f
* z3 Face angle at thread start (degrees) — — 40°
a
Region of male taper between dimensions e and s3 defined by Øg may have draft in the direction of pull no greater
than 1,0° inclusive (0,5°/side).
b
This dimension is required to provide clearance for the inside diameter at the open end of the female taper (Ød) and
face of female connector. Maximum thread profile length is not specified but shall provide clearance for the thread of the
male connector. The geometry defined by Ød is flush to the face of the collar.
c
This dimension is only required where the male connector is a source of fluid flow.
d
The minimum value of w shall be maintained for the length of 1,00 mm, and the maximum value shall be maintained
for the length of e. This dimension may be achieved by either the connector or the medical devi
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 80369-3
Première édition
2016-07-01
Raccords de petite taille pour
liquides et gaz utilisés dans le
domaine de la santé —
Partie 3:
Raccords destinés à des applications
entérales
Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare
applications —
Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications
Numéro de référence
©
ISO 2016
DOCUMENT PROTÉGÉ PAR COPYRIGHT
© ISO 2016, Publié en Suisse
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf indication contraire, aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée
sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie, l’affichage sur
l’internet ou sur un Intranet, sans autorisation écrite préalable. Les demandes d’autorisation peuvent être adressées à l’ISO à
l’adresse ci-après ou au comité membre de l’ISO dans le pays du demandeur.
ISO copyright office
Ch. de Blandonnet 8 • CP 401
CH-1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland
Tel. +41 22 749 01 11
Fax +41 22 749 09 47
copyright@iso.org
www.iso.org
ii © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
Sommaire Page
Avant-propos .iv
Introduction .v
1 * Domaine d’application . 1
2 Références normatives . 1
3 Termes et définitions . 2
4 Exigences générales . 3
4.1 Exigences générales relatives aux applications entérales . 3
4.2 Matériaux utilisés pour la fabrication des raccords de petite taille à usage entéral . 4
4.3 Essais de type . 4
5 Exigences dimensionnelles relatives aux raccords de petite taille à usage entéral .4
6 Exigences de performance . 4
6.1 Fuite de fluide . 4
6.1.1 Exigence relative à la fuite de fluide . 4
6.1.2 Fuite par baisse de pression . 4
6.1.3 Fuite de liquide sous pression positive . 4
6.2 Formation de craquelures sous contrainte . 5
6.3 Résistance à la séparation sous l’effet d’une force axiale . 5
6.4 Résistance à la séparation par dévissage . 5
6.5 Résistance à l’arrachement des filets. 5
6.6 Désolidarisation par dévissage . 5
Annexe A (informative) Exposé des motifs et préconisations . 7
Annexe B (normative) Raccords de petite taille à usage entéral .12
Annexe C (normative) raccords de référence .18
Annexe D (informative) Évaluation des dispositifs médicaux présentant des
raccordements dans le cadre de cette application et de leurs propriétés .23
Annexe E (informative) Récapitulatif des exigences d’aptitude à l’utilisation des raccords
de petite taille destinés à des applications entérales .24
Annexe F (informative) Récapitulatif des critères et exigences relatifs aux raccords de
petite taille destinés à des applications entérales .30
Annexe G (informative) Récapitulatif de l’évaluation du modèle des raccords destinés à
des applications entérales .33
Annexe H (informative) Référence aux principes essentiels .40
Annexe I (informative) Terminologie — Index alphabétique des termes définis .42
Bibliographie .43
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale d’organismes
nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de l’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est
en général confiée aux comités techniques de l’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude
a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales,
gouvernementales et non gouvernementales, en liaison avec l’ISO participent également aux travaux.
L’ISO collabore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (IEC) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les procédures utilisées pour élaborer le présent document et celles destinées à sa mise à jour sont
décrites dans les Directives ISO/IEC, Partie 1. Il convient, en particulier de prendre note des différents
critères d’approbation requis pour les différents types de documents ISO. Le présent document a été
rédigé conformément aux règles de rédaction données dans les Directives ISO/IEC, Partie 2 (voir www.
iso.org/directives).
L’attention est appelée sur le fait que certains des éléments du présent document peuvent faire l’objet de
droits de propriété intellectuelle ou de droits analogues. L’ISO ne saurait être tenue pour responsable
de ne pas avoir identifié de tels droits de propriété et averti de leur existence. Les détails concernant
les références aux droits de propriété intellectuelle ou autres droits analogues identifiés lors de
l’élaboration du document sont indiqués dans l’Introduction et/ou dans la liste des déclarations de
brevets reçues par l’ISO (voir www.iso.org/brevets).
Les appellations commerciales éventuellement mentionnées dans le présent document sont données
pour information, par souci de commodité, à l’intention des utilisateurs et ne sauraient constituer un
engagement.
Pour une explication de la signification des termes et expressions spécifiques de l’ISO liés à
l’évaluation de la conformité, ou pour toute information au sujet de l’adhésion de l’ISO aux principes
de l’OMC concernant les obstacles techniques au commerce (OTC), voir le lien suivant: Avant-propos —
Informations supplémentaires.
Le comité chargé de l’élaboration du présent document est l’ISO/TC 210, Management de la qualité et
aspects généraux correspondants des dispositifs médicaux, en collaboration avec l’IEC/SC 62D, Appareils
électromédicaux. Ce projet a été soumis aux organismes nationaux de l’ISO et de l’IEC pour vote.
L’ISO 80369 comprend les parties suivantes, présentées sous le titre général Raccords de petite taille
pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé:
— Partie 1: Exigences générales
— Partie 2: Raccords destinés à des systèmes respiratoires et applications aux gaz d’entraînement
— Partie 3: Raccords destinés à des applications entérales
— Partie 5: Raccords destinés à des applications de gonflage autour des membres
— Partie 6: Raccords destinés à des applications en contact avec le système nerveux (neuraxiales)
— Partie 7: Raccords à 6 % (Luer) destinés aux applications intravasculaires ou hypodermiques
— Partie 20: Méthodes d’essai communes
Une partie supplémentaire relative aux raccords destinés à des applications urétrales et urinaires
est prévue.
iv © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
Introduction
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 a été élaborée suite à plusieurs incidents, qui ont eu des conséquences
catastrophiques et qui résultent, en premier lieu, de l’administration de médicaments inappropriés
dans le canal alimentaire et, en second lieu, de l’administration de solutions entérales par une
voie incorrecte, notamment par voie intraveineuse ou par voie aérienne. Le signalement d’un grand
nombre d’incidents a conduit à une reconnaissance internationale de l’importance de ces problèmes
et à l’identification du besoin de développer des raccords propres aux dispositifs médicaux et aux
accessoires associés utilisés pour la nutrition par voie entérale.
La série ISO 80369 a été élaborée pour éviter les erreurs de raccordement entre des raccords de
petite taille destinés à des applications différentes. L’ISO 80369-1 spécifie les exigences requises
pour la vérification des modèles des raccords de petite taille afin de s’assurer:
a) qu’ils ne risquent pas d’être raccordés par erreur à d’autres raccords de petite taille; et
b) qu’ils permettent de raccorder les différents éléments de manière fiable et sûre.
L’ISO 80369-20 décrit les méthodes d’essai communes qui permettent de valider les exigences de
performance relatives aux raccords de petite taille.
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 spécifie la conception et les dimensions et comprend les schémas
des raccords de petite taille destinés à être utilisés dans des applications entérales. Les
Annexes D à G décrivent les méthodes selon lesquelles cette conception a été évaluée. Les autres parties
de l’ISO 80369 incluent les exigences relatives aux raccords de petite taille utilisés dans d’autres
catégories d’applications.
Les raccords fabriqués aux dimensions spécifiées dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 possèdent
des dimensions incompatibles avec celles de tout autre raccord destiné à des applications identifiées
dans la série ISO 80369 relative aux raccords de petite taille, hormis l’exception identifiée en G.2.
S’ils sont raccordés aux dispositifs médicaux et accessoires appropriés, ces raccords sont destinés
à réduire le risque d’administration par une autre voie, par exemple par voie intraveineuse ou par
un appareil respiratoire, de médicaments et de produits de nutrition liquides prévus pour la voie
entérale.
Au cours de l’élaboration de la présente Norme internationale, le comité a décidé de couvrir l’ensemble
du système d’administration par voie entérale, mais de développer une Norme internationale distincte
pour les raccords des poches de nutrition. L’ISO 18250-3 spécifie les exigences relatives aux raccords
des poches de nutrition entérale. La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 comprend les dimensions de
l’interface des raccords de petite taille avec les voies d’abord et les interfaces avec le patient des
tubulures de nutrition entérale et des seringues entérales.
Dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369, les polices et caractères suivants sont employés:
— exigences et définitions: police de caractères romains;
— éléments informatifs situés hors des tableaux, tels que notes, exemples et références: petits
caractères. Le texte normatif des tableaux apparaît également en petits caractères;
— termes définis à l’Article 3 de la présente norme ou comme indiqué: petites majuscules.
Dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369, la conjonction «ou» est utilisée comme «ou inclusif»; une
affirmation est donc vraie si une combinaison quelconque des conditions est vraie.
Les formes verbales utilisées dans la présente Norme internationale sont conformes à l’usage décrit
dans l’Annexe H des Directives ISO/IEC, Partie 2. Pour les besoins de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369,
la forme verbale:
— «doit» signifie que la conformité à une exigence ou à un essai est obligatoire pour la conformité à la
présente partie de l’ISO 80369;
— «il convient que/de» signifie que la conformité à une exigence ou à un essai est recommandée, mais
n’est pas obligatoire pour la conformité à la présente partie de l’ISO 80369; et
— «peut» est utilisée pour décrire une manière autorisée d’obtenir la conformité à une exigence ou à
un essai.
Un astérisque (*) utilisé comme premier caractère d’un titre ou au début d’un paragraphe ou d’un titre
de tableau indique qu’il y a des préconisations ou un exposé des motifs concernant cet élément dans
l’Annexe A.
vi © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 80369-3:2016(F)
Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans
le domaine de la santé —
Partie 3:
Raccords destinés à des applications entérales
1 * Domaine d’application
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 spécifie les dimensions et exigences relatives à la conception et aux
performances fonctionnelles des raccords de petite taille destinés à être utilisés pour effectuer des
raccordements à des dispositifs médicaux et des accessoires à usage entéral.
NOTE 1 Les dispositifs médicaux à usage entéral incluent les tubulures de nutrition entérale, les
tubulures de drainage entéral, les seringues entérales et les dispositifs d’interface avec le patient, y compris
les voies d’abord.
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 ne spécifie pas les dimensions et exigences relatives aux dispositifs
médicaux ou aux accessoires sur lesquels ces raccords sont utilisés. Ces exigences figurent dans des
Normes internationales spécifiques traitant de dispositifs médicaux ou d’accessoires particuliers.
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 ne spécifie pas d’exigences relatives aux raccords de petite taille
utilisés pour:
— les dispositifs médicaux réservés à l’aspiration digestive;
— les dispositifs médicaux réservés à un usage oral;
EXEMPLE Une seringue à embout buccal qui n’est pas destinée à être raccordée à un autre dispositif
médical. Elle est prévue pour que son contenu soit directement administré dans la bouche du patient.
— la mise sous pression et la dépressurisation du mécanisme de rétention (par exemple, ballonnet)
utilisé pour maintenir les dispositifs médicaux entéraux invasifs en place;
— les dispositifs médicaux destinés au lavage rectal, à l’administration rectale de médicaments ou de
liquides, ainsi que tout autre dispositif médical permettant l’accès au rectum;
— l’équipement d’endoscopie gastro-intestinale;
— les dispositifs médicaux de type boutons de gastrostomie.
NOTE 2 Les fabricants sont incités à intégrer les raccords de petite taille spécifiés dans la présente
partie de l’ISO 80369 dans les dispositifs médicaux ou accessoires à usage entéral, même si cela n’est pas
actuellement requis par les normes appropriées, spécifiques de ces dispositifs médicaux. Il est prévu d’inclure
des exigences relatives aux raccords de petite taille, tels que spécifiés dans l’ISO 80369, lors de la révision des
normes appropriées spécifiques de ces dispositifs médicaux.
2 Références normatives
Les documents ci-après, dans leur intégralité ou non, sont des références normatives indispensables à
l’application du présent document. Pour les références datées, seule l’édition citée s’applique. Pour les
références non datées, la dernière édition du document de référence s’applique (y compris les éventuels
amendements).
ISO 14971:2007, Dispositifs médicaux — Application de la gestion des risques aux dispositifs médicaux
ISO 80369-1:2010, Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé —
Partie 1: Exigences générales
ISO 80369-6:2016, Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé —
Partie 6: Raccords destinés à des applications en contact avec le système nerveux (neuraxiales)
1)
ISO 80369-7:— , Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé —
Partie 7: Raccords à 6 % (Luer) destinés aux applications intravasculaires ou hypodermiques
ISO 80369-20:2015, Raccords de petite taille pour liquides et gaz utilisés dans le domaine de la santé —
Partie 20: Méthodes d’essai communes
ASTM D638-10, Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics
ASTM D790-10, Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and
electrical insulating materials
3 Termes et définitions
Pour les besoins du présent document, les termes et définitions donnés dans l’ISO 80369-1, l’ISO 80369-7,
l’ISO 80369-20 et l’ISO 14971 ainsi que les termes et définitions suivants s’appliquent.
NOTE Pour des raisons pratiques, les sources de tous les termes définis utilisés dans la présente partie de
l’ISO 80369 sont données à l’Annexe I.
3.1
entéral
relatif au tractus gastro-intestinal
3.2
utilisation normale
fonctionnement, y compris lors des vérifications périodiques et des réglages faits par un utilisateur,
ainsi que dans l’état en attente, selon les instructions d’utilisation
Note 1 à l’article: Il convient de ne pas confondre utilisation prévue et utilisation normale. Si les deux
expressions intègrent le concept de l’utilisation telle qu’elle est prévue par le fabricant, l’utilisation prévue
se concentre sur le but médical tandis que l’utilisation normale ne se limite pas au but médical mais englobe
aussi la maintenance, l’entretien, le transport, etc.
[SOURCE: IEC 60601-1:2005+A1:2012, définition 3.71 modifiée: remplacement d’« opérateur » par
«utilisateur».]
3.3
assignée
terme qui fait référence à une valeur attribuée par le fabricant pour une condition de fonctionnement
spécifiée
[SOURCE: IEC 60601-1:2005, 3.97]
3.4
utilisateur
personne en interaction (c’est-à-dire exploitant ou manipulant) avec le dispositif médical
Note 1 à l’article: Cela inclut, sans toutefois s’y limiter, les personnes chargées du nettoyage et de la maintenance,
ainsi que les installateurs.
Note 2 à l’article: Les patients ou autres non-spécialistes peuvent être des utilisateurs.
[SOURCE: IEC 62366-1:2015, 3.24]
1) À publier.
2 © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
3.5
profil de l’utilisateur
synthèse des caractères mentaux, physiques et démographiques d’une population d’utilisateurs
prévue, ainsi que toute caractéristique particulière qui peut avoir une influence sur les décisions de
conception, comme les aptitudes professionnelles et les exigences de travail
[SOURCE: IEC 62366-1:2015, 3.29]
4 Exigences générales
4.1 Exigences générales relatives aux applications entérales
Les raccords de petite taille pour dispositifs médicaux ou accessoires destinés à être utilisés
dans des applications entérales, fabriqués conformément à la présente partie de l’ISO 80369, sont
conformes à l’ISO 80369-1, sauf indication contraire dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369.
Le plan de joint du raccord E1 femelle peut entrer en contact avec les surfaces filetées du raccord
femelle N tel que spécifié dans l’ISO 80369-6 dans les conditions de minimum de matière, lors des
essais des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité de l’Annexe B de l’ISO 80369-1:2010. De plus amples
informations sont fournies en G.2.
Il convient de ne pas assembler les raccords de petite taille destinés à des applications entérales
avec les raccords suivants; ces derniers n’étant pas spécifiés de manière appropriée, les raccords de
petite taille destinés à des applications entérales peuvent toutefois se raccorder:
— aux raccords mâles et femelles de l’ISO 5356-1:2004, l’ISO 5356-1:2015, l’ISO 5356-2:2006 et
l’ISO 5356-2:2012;
— aux capteurs de température et aux orifices de raccordement fabriqués conformément à l’Annexe DD
de l’ISO 8185:2007;
— aux embouts de l’EN 13544-2:2002 et de l’EN 13544-2:2002+A1:2009.
Les raccords de référence pour l’évaluation des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité sont décrits
à l’Annexe C.
Lorsque la conception du raccord de petite taille de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 repose sur
des dimensions ou des caractéristiques du dispositif médical ou de l’accessoire pour garantir les
caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité, les caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité doivent être
vérifiées.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais du 5.1 et de l’Annexe B de l’ISO 80369-1:2010. La
conformité peut également être démontrée en ayant recours à une analyse avec conception assistée
par ordinateur (CAO) des dimensions de tous les raccords de petite taille de la série ISO 80369 et du
raccord de petite taille soumis à essai, associée à des essais physiques du raccord de petite taille
selon l’Annexe B lorsque l’analyse CAO ne démontre pas les caractéristiques de non raccordabilité. Si
nécessaire, le raccord de petite taille peut être installé sur le dispositif médical ou l’accessoire
pour démontrer la conformité aux exigences de l’essai des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité de
l’Annexe B de l’ISO 80369-1:2010.
NOTE 1 Les dispositifs médicaux sur lesquels les raccords de petite taille de la présente partie de
l’ISO 80369 sont employés et qui ne reposent pas sur des dimensions ou des caractéristiques du dispositif
médical ou de l’accessoire pour garantir les caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité sont supposés conformes
aux exigences de l’essai des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369.
NOTE 2 Un récapitulatif des dispositifs médicaux présentant des raccordements entrant dans le cadre de
cette application et de leurs propriétés est fourni dans l’Annexe D.
NOTE 3 Un récapitulatif des exigences d’aptitude à l’utilisation des raccords de petite taille à usage
entéral est fourni dans l’Annexe E.
NOTE 4 Un récapitulatif des critères et exigences relatifs aux raccords de petite taille à usage entéral
est fourni dans l’Annexe F.
NOTE 5 Un récapitulatif de l’évaluation du modèle des raccords de petite taille à usage entéral
conformément à l’Article 7 de l’ISO 80369-1:2010 est fourni dans l’Annexe G.
4.2 Matériaux utilisés pour la fabrication des raccords de petite taille à usage entéral
Outre les exigences de l’Article 4 de l’ISO 80369-1:2010, les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral
doivent être fabriqués dans des matériaux dont le module d’élasticité nominal, en flexion ou en traction,
est supérieur à 700 MPa.
Vérifier la conformité en effectuant les essais de l’ASTM D638-10 ou de l’ASTM D790-10.
4.3 Essais de type
La conformité aux exigences de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 doit être déterminée par des essais
de type.
5 Exigences dimensionnelles relatives aux raccords de petite taille à usage
entéral
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être conformes aux dimensions et aux
tolérances appropriées, telles qu’indiquées:
— à la Figure B.1 et dans le Tableau B.1 pour un raccord E1 mâle; et
— à la Figure B.2 et dans le Tableau B.2 pour un raccord E1 femelle.
Vérifier la conformité en contrôlant les dimensions et tolérances spécifiées dans l’Annexe B, le cas
échéant.
6 Exigences de performance
6.1 Fuite de fluide
6.1.1 Exigence relative à la fuite de fluide
L’étanchéité des raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doit être évaluée, soit en utilisant la
méthode d’essai de fuite par baisse de pression, soit en employant la méthode d’essai de fuite de
liquide sous pression positive.
6.1.2 Fuite par baisse de pression
S’agissant de l’évaluation de la performance pour la fuite de fluide à l’aide de la méthode d’essai de
fuite par baisse de pression, la fuite ne doit pas être supérieure à 0,005 Pa·m /s lorsque les raccords
de petite taille à usage entéral sont soumis à une pression d’application comprise entre 300 kPa et
330 kPa, sur une période de maintien de 15 s à 20 s, le milieu utilisé étant l’air. Les fabricants peuvent
utiliser une pression d’application supérieure.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe B de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour les essais d’étanchéité spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6.1.3 Fuite de liquide sous pression positive
S’agissant de l’évaluation de la performance pour la fuite de fluide à l’aide de la méthode d’essai de
fuite de liquide sous pression positive, les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral ne doivent
4 © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
présenter aucun signe de fuite suffisamment importante pour former une goutte d’eau se détachant,
sur une période de maintien de 30 s à 35 s, lorsqu’ils sont soumis à une pression d’application comprise
entre 300 kPa et 330 kPa. Les fabricants peuvent utiliser une pression d’application supérieure ou
une période de maintien plus longue.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe C de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour les essais d’étanchéité spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6.2 Formation de craquelures sous contrainte
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être soumis à une évaluation de la formation
de craquelures sous contrainte. Ils doivent satisfaire aux exigences de 6.1.1 après avoir été soumis aux
contraintes spécifiées dans l’Annexe E de l’ISO 80369-20:2015.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe E de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour l’essai de formation de craquelures sous contrainte spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6.3 Résistance à la séparation sous l’effet d’une force axiale
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être soumis à une évaluation de leur
résistance à la séparation sous l’effet d’une force axiale. Ils ne doivent pas se désolidariser du raccord
de référence, sur une période de maintien de 10 s à 15 s, lorsqu’ils sont soumis à une force axiale
d’application visant à les séparer comprise entre 32 N et 35 N. Les fabricants peuvent utiliser pour
l’essai de séparation une force axiale d’application supérieure ou une période de maintien plus longue.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe F de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour l’essai de résistance à la séparation sous l’effet d’une force axiale spécifié à
l’Annexe C.
6.4 Résistance à la séparation par dévissage
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être soumis à une évaluation de leur
résistance à la séparation par dévissage. Ils ne doivent pas se désolidariser du raccord de référence,
sur une période de maintien de 10 s à 15 s, lorsqu’ils sont soumis à un couple de dévissage compris
entre 0,019 8 N·m et 0,020 0 N·m. Les fabricants peuvent utiliser un couple de dévissage d’application
supérieur ou une période de maintien plus longue.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe G de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour l’essai de résistance à la séparation par dévissage spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6.5 Résistance à l’arrachement des filets
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être soumis à une évaluation de leur résistance
à l’arrachement des filets. Les filets ou les ailettes des raccords de petite taille à usage entéral
ne doivent pas dépasser les limites des filets ou des ailettes du raccord de référence, lorsqu’ils sont
soumis à un couple d’application compris entre 0,15 N·m et 0,17 N·m, sur une période de maintien de 5 s
à 10 s. Les fabricants peuvent utiliser un couple d’application supérieur ou une période de maintien
plus longue.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe H de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour l’essai de résistance à l’arrachement des filets spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6.6 Désolidarisation par dévissage
Les raccords de petite taille à usage entéral doivent être soumis à une évaluation de leur aptitude
à la désolidarisation par dévissage. Ils doivent se désolidariser du raccord de référence lorsqu’ils sont
soumis à un couple de dévissage d’application de 0,35 N·m au maximum.
Vérifier la conformité en réalisant les essais de l’Annexe I de l’ISO 80369-20:2015 et en utilisant le
raccord de référence pour l’essai de désolidarisation par dévissage spécifié à l’Annexe C.
6 © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
Annexe A
(informative)
Exposé des motifs et préconisations
A.1 Préconisations d’ordre général
A.1.1 Préconisations
La présente annexe fournit un exposé des motifs de certaines des exigences de la présente partie
de l’ISO 80369. Elle est destinée à ceux qui sont familiarisés avec l’objet de la présente partie de
l’ISO 80369, mais qui n’ont pas participé à son élaboration. La compréhension des motifs qui sous-
tendent ces exigences est considérée comme essentielle pour l’application correcte de ces dernières. En
outre, comme les pratiques cliniques et la technologie évoluent, on considère qu’un exposé des motifs
facilitera une révision éventuelle de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 en fonction de ces changements.
A.1.2 Sélection du raccord
Il est compréhensible que les systèmes de raccords de petite taille ne peuvent pas être conçus
pour passer outre toutes les chances d’erreurs de raccordement ou éliminer une mauvaise utilisation
intentionnelle. Cependant, un nombre d’étapes qui améliorerait la situation actuelle et mènerait vers
une sécurité du patient accrue peut être pris en compte.
Le raccord cote patient a besoin d’être de type non raccordable avec des raccords dans la zone de
soins du patient. Il est recommandé de prendre soin de s’assurer de l’essai de la mauvaise connexion et
que l’analyse du risque associée soit réalisée pour assurer la sécurité et l’efficacité du système.
A.1.3 Code couleur
Concernant la présente partie de l’ISO 80369, la spécification d’une couleur n’est pas considérée comme
appropriée, car il s’agit d’une norme relative à un raccord, et non d’une norme relative à un dispositif
médical. Il sera physiquement impossible de raccorder les raccords spécifiés à un raccord non
destiné à un usage entéral. En outre, l’attribution d’une couleur est jugée insuffisante pour signaler
une erreur de raccordement et inefficace pour l’éviter. D’autres applications telles que les dispositifs
médicaux intravasculaires et les sondes d’aspiration peuvent utiliser une couleur, mais ces couleurs
ne sont pas normalisées pour toutes les applications et dans tous les pays. L’association de l’usage
entéral et d’une couleur particulière (par exemple, pourpre, orange, jaune) pourrait contribuer à
d’autres cas d’erreurs de raccordement de dispositifs médicaux.
A.2 Exposé des motifs d’articles et de paragraphes particuliers
Les articles et paragraphes de la présente annexe ont été numérotés de façon à correspondre aux
numéros des articles et des paragraphes de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 auxquels ils font référence.
Leur numérotation n’est donc pas consécutive.
Article 1 Domaine d’application
En l’an 2000, un groupe de travail du CEN, le Comité européen de normalisation, a proposé une approche
permettant de réduire les incidents dus aux erreurs de raccordement accidentelles des lignes pour le
traitement des patients en utilisant une série de raccords non raccordables, qui se distinguent
sur le plan de la conception et sont destinés à être utilisés dans différentes applications médicales.
[12]
Cette approche limite l’utilisation des raccords Luer exclusivement aux dispositifs médicaux
destinés à être raccordés au système vasculaire ou à des seringues hypodermiques, de sorte qu’ils
puissent remplir leur fonction prévue.
Exclusion des dispositifs médicaux réservés à l’aspiration digestive:
Le comité a établi que les dispositifs médicaux et les accessoires réservés à l’aspiration digestive
seraient exclus du domaine d’application de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369. De nombreuses
applications d’aspiration digestive exclusives nécessitent un diamètre intérieur supérieur à 8,5 mm,
c’est-à-dire au diamètre intérieur maximal défini d’un raccord de petite taille. Elles ne relèvent
donc pas du domaine d’application de l’ISO 80369-1.
Exclusion des dispositifs médicaux réservés à un usage oral:
Le comité a établi que l’administration orale de fluides dans le tractus gastro-intestinal serait exclue
du domaine d’application de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369. L’administration de fluides par voie orale
ne requiert pas de raccordement tel que défini dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369. Elle est donc
considérée comme ne relevant pas du domaine d’application de la présente partie de l’ISO 80369.
Les raccords décrits dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 sont spécialement destinés à être utilisés
comme système de raccordement (c’est-à-dire raccord femelle se couplant à un raccord mâle). Si un
raccord non destiné à être utilisé exclusivement dans le cadre de ce système de raccordement est
intégré à un dispositif médical ou à un accessoire à usage entéral, alors le fabricant du dispositif
médical doit évaluer et maîtriser les risques associés, le cas échéant.
Sens du raccordement:
La présente partie de l’ISO 80369 ne spécifie pas le sens de raccordement des raccords E1, laissant le
soin à chaque autorité compétente de définir le sens d’écoulement qu’elle estime le plus approprié, car
les raccords spécifiés dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 ont été conçus avec des caractéristiques
de non-raccordabilité, qui empêchent les erreurs de raccordement avec tout autre raccord mâle ou
femelle de la série ISO 80369. Il convient que les autorités ou fabricants individuels examinent les
risques potentiels liés au sens de raccordement, notamment la contamination et la facilité de nettoyage
avant utilisation.
Des études auprès des utilisateurs, des erreurs de raccordement ont été réalisées afin de préciser
un sens de raccordement pour le raccord E1 pour lequel le dispositif médical à usage entéral à
demeure incluait le raccord mâle et les dispositifs médicaux qui s’y raccordent (seringue, tubulures
de nutrition, etc.) incluaient la conception femelle. L’analyse de l’erreur de raccordement utilisant un
modèle CAO et les analyses de risque associées ont été réalisées pour identifier le risque d’erreur de
raccordement sans tenir compte du sens.
Sous-populations de l’application clinique entérale:
Des inquiétudes ont été exprimées concernant les risques potentiels en cas d’administration de doses
imprécises de médicaments dans le cadre de certaines pratiques cliniques qui concernent des sous-
populations à haut risque (par exemple, les nouveau-nés), si le sens de raccordement du système est
inversé (femelle à mâle). Cette inversion du sens peut entraîner un déplacement involontaire du fluide
contenu à l’origine dans le raccord de petite taille femelle. Ce déplacement se produit lorsque le
fluide est aspiré dans la seringue sans utiliser un adaptateur ou un accessoire d’aspiration et est
ensuite administré via un raccordement vers une sonde de nutrition. Des essais en laboratoire ont
démontré que la majeure partie de ce fluide est déplacée dans le raccord de petite taille mâle et le
dispositif médical installé en aval de ce raccord.
Des essais en laboratoire montrent également qu’une paire de raccords E1 de tolérance moyenne
raccordée dans le sens femelle à mâle déplace un volume moyen de 0,148 ml (au minimum 0,089 ml
et au maximum 0,179 ml avec n = 32) de fluide. À titre de comparaison, un raccordement inversé de
raccords Luer (EN 1615) soumis à essai dans des conditions similaires a déplacé un volume moyen de
0,103 ml (au minimum 0,074 ml et au maximum 0,122 ml avec n = 64). À ce jour, les risques associés à
l’exactitude de la dose administrée dans les dispositifs médicaux conçus avec un sens de raccordement
inversé n’ont pas été entièrement évalués et il n’y a donc pas de nécessité avérée d’exclure explicitement
une sous-population quelconque de l’application clinique entérale. Il est donc recommandé
8 © ISO 2016 – Tous droits réservés
d’utiliser le raccord de petite taille E1 sur tous les patients afin de réduire les risques d’erreur
de raccordement. Il convient que les fabricants qui intègrent le raccord de petite taille E1 à des
dispositifs médicaux destinés à être utilisés sur des sous-populations à haut risque (par exemple,
nouveau-nés) évaluent tout risque associé à un déplacement potentiel et, si des éléments objectifs
indiquent que ce risque potentiel existe, il convient qu’ils informent les utilisateurs de ce risque de
déplacement de fluide.
Le fluide qui pourrait être administré dans un raccord E1 mâle en raison de l’insertion du cône du
raccord mâle dans le raccord femelle rempli de fluide est le volume sur-administré (volume de fluide
déplacé administré en plus de la dose prévue). Lorsque l’administration d’une dose très précise est
exigée via le raccordement E1 dans le sens femelle à mâle, l’utilisation d’adaptateurs d’aspiration (par
exemple d’une pipette d’aspiration) est recommandée. Des données préliminaires suggèrent qu’en cas
d’utilisation correcte d’un adaptateur d’aspiration, le volume de fluide administré (quantité surdosée)
est de 0,003 ml. Les fabricants de dispositifs incluant le raccord ISO 80369-3 auront besoin de mener
des études de validation pour s’assurer que l’exactitude de la dose satisfasse aux exigences du dispositif.
Il convient de ne pas confondre le volume déplacé administré et le volume entre les surfaces de l’orifice
femelle et du cône mâle après raccordement, qui est souvent appelé espace mort.
Les fabricants et les organismes responsables sont incités à faire part de leur expérience concernant
les raccords de petite taille spécifiés dans la présente partie de l’ISO 80369 au secrétariat de
l’ISO/TC 210, de sorte que leurs commentaires puissent être pris en compte lors de la révision de la
partie appropriée de la série ISO 80369.
Tableau B.1 Dimensions du raccord de petite taille E1 mâle
La conception des raccords à usage entéral inclut des caractéristiques dont la fonction peut ne pas
être immédiatement évidente. Un grand nombre d’entre elles influent soit sur les caractéristiques de
non-raccordabilité, soit sur les exigences de performance de ces raccords.
c Projection de l’extrémité du raccord depuis le collier fileté
Cette caractéristique fournit un signal visuel à l’utilisateur pour faciliter l’alignement pendant
l’assemblage. Un assemblage verrouillé rotatif à filetage interne est autorisé, mais la dimension c doit
être respectée.
e Longueur du cône mâle (Ød à Øg)
La longueur du cône est spécifiée pour définir l’angle du cône par rapport à une transition vers un angle
inférieur. La longueur du cône définit une longueur minimale nécessaire pour assurer l’étanchéité. Il est
permis que l’angle au-delà du cône soit égal à 0,5° (angle total de 1°) ou que la zone au-delà du cône soit
plus petite que l’extrémité du cône (Øg), le choix étant laissé à la discrétion du fabricant.
Øg Diamètre extérieur de l’extrémité plus large du cône mâle à une distance e de l’extrémité
(petite extrémité) du cône mâle
La dimension maximale de l’embout est limitée afin de garantir les caractéristiques de non-
raccordabilité avec le diamètre intérieur du cône mâle du raccord de 8,5 mm, tel que défini dans
l’ISO 5356-1.
s3 Longueur de l’embout à partir de l’extrémité du collier fileté
La longueur maximale du filetage n’est pas spécifiée, mais elle doit fournir l’espace et le support requis
pour l’emboîtement du filetage du raccord à usage entéral femelle lorsque les deux raccords
correspondent aux conditions de minimum de matière (LMC).
x3 Longueur de la corde sous-tendue par le plus petit diamètre du filetage (Øj) au niveau du
départ du filetage
Cette caractéristique remplit deux fonctions. La dimension minimale fournit deux bords sur Øj, pour
garantir les caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité avec d’autres raccords de petite taille,
comme déterminé lors de l’évaluation des erreurs de raccordement. La dimension maximale génère un
filetage émoussé et a été ajoutée pour réduire le risque de fausser involontairement des filets lors de
l’assemblage des raccords E1 mâle et femelle, si l’insertion n’est pas effectuée dans le plan axial.
Øw Diamètre du plus petit cylindre qui contient les surfaces extérieures des parties externes
au niveau de l’extrémité ouverte du collier fileté
Il a été démontré que les dimensions définies pour le diamètre du plus petit cylindre qui contient
les surfaces extérieures des parties externes au niveau de l’extrémité ouverte du collier fileté (Øw)
présentent des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité. Les fabricants peuvent utiliser des
dimensions qui s’écartent de ces valeurs (Øw pour la profondeur s3), mais il faut alors démontrer
les caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité du dispositif médical sur lequel le raccord à usage
entéral est fixé, à l’aide de l’Annexe B de l’ISO 80369-1:2010, afin de garantir l’absence de risque
d’erreur de raccordement.
Lorsque le raccord mâle est utilisé comme une source de débit (par exemple, sur une tubulure
d’administration, une seringue ou un autre dispositif médical similaire), un collier, des ailettes
ou une autre caractéristique de diamètre minimal Øw est/sont requis(es) pour éviter les erreurs de
raccordement avec le diamètre intérieur non spécifié de la plupart des raccords de 15 mm définis dans
l’ISO 5356-1.
Lorsque le raccord mâle n’est pas utilisé comme une source de débit (par exemple, sur un dispositif
médical d’accès au patient), il a été démontré qu’un collier ou des ailettes possédant les dimensions
spécifiées pour le diamètre Øw présente(nt) des caractéristiques de non-raccordabilité.
z3 Angle d’attaque au niveau du départ du filetage
Cette caractéristique a été ajoutée pour réduire le risque de fausser involontairement des filets lors de
l’assemblage des raccords E1 mâle et femelle, si l’insertion n’est pas effectuée dans le plan axi
...
SLOVENSKI STANDARD
SIST IEC 60050(725)
april 2005
Mednarodni elektrotehniški slovar – 725. poglavje: Vesoljske
radiokomunikacije
International Electrotechnical Vocabulary – Chapter 725: Space
radiocommunications
Vocabulaire Electrotechnique International – Chapitre 725: Radiocommunications
spatiales
Internationales Elektrotechnisches Wörterbuch – Kapitel 725:
Weltraumradiokommunikations
Ta slovenski standard je enakovreden z IEC 60050(725):1994.
Referenčna oznaka
ICS 33.160.30, 33.160.40 SIST IEC 60050(725):2005 (sl)
Nadaljevanje na straneh od 2 do 47
© 2005-04. Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
NACIONALNI UVOD
Standard SIST IEC 60050(725) (sl), Mednarodni elektrotehniški slovar – Poglavje 725: Vesoljske
radiokomunikacije, 2005, ima status slovenskega standarda in je enakovreden mednarodnemu
standardu IEC 60050(725) (en), International Electrotechnical Vocabulary – Chapter 725: Space
radiocommunication, 1994.
NACIONALNI PREDGOVOR
Mednarodni standard IEC 60050(725):1994 je pripravil tehnični odbor Mednarodne elektrotehniške
komisije IEC/TC 1 Terminologija.
Slovenski standard SIST IEC 60050(725):2005 je prevod mednarodnega standarda
IEC 60050(725):1994. V primeru spora glede besedila slovenskega prevoda v tem standardu je
odločilen izvirni mednarodni standard v angleškem jeziku. Slovensko izdajo standarda je pripravil
tehnični odbor USM/TC OMS Oprema za mobilne in satelitske telekomunikacijske sisteme.
Odločitev za prevzem tega standarda po metodi prevoda je dne 1998-11-17 sprejel tehnični odbor
USM/TC Oprema za mobilne in satelitske telekomunikacijske sisteme.
OSNOVA ZA IZDAJO STANDARDA
– Prevzem standarda IEC 60050(725):1994
OPOMBA
– Uvod in nacionalni predgovor nista sestavni del standarda.
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
VSEBINA Stran
Podpoglavje 725-11: Sateliti, vesoljska plovila in orbite.4
Podpoglavje 725-12: Vesoljski radiokomunikacijski sistemi. 14
Podpoglavje 725-13: Antene in antenski snopi (žarki) . 25
Podpoglavje 725-14: Prenos . 28
Abecedni seznam slovenskih izrazov. 34
Abecedni seznam angleških izrazov . 37
Abecedni seznam francoskih izrazov. 40
Abecedni seznam nemških izrazov. 43
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Poglavje 725: Vesoljske radiokomunikacije
Podpoglavje 725-11: Sateliti, vesoljska plovila in orbite
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-01 − vesoljsko plovilo Vozilo, ki ga je izdelal človek in je namenjeno
− spacecraft potovanju zunaj zemeljske atmosfere.
− engin spatial; spationef
− Weltraumfahrzeug
725-11-02 − globoko vesolje Prostor na razdalji od Zemlje (po konvenciji),
− deep space enaki ali večji od 2 x 10 kilometrov.
− espace lointain
− ferner Weltraum; Tiefraum
725-11-03 − vesoljska sonda Vesoljsko plovilo, izdelano za opazovanje
− space probe vesolja ali izvajanje meritev v vesolju.
− sonde spatiale
− Weltraumsonde
725-11-04 − sonda za globoko vesolje Vesoljska sonda, namenjena raziskovanju v
− deep space probe globokem vesolju.
− sonde spatiale lointaine
− Tiefraumsonde
725-11-05 − satelit Telo, ki se giblje okrog drugega telesa z večjo
− satellite maso, njegovo gibanje pa je predvsem in stalno
− satellite določeno s privlačno silo tega drugega telesa.
− Satellit
OPOMBI: 1. Tako opredeljeno telo, ki se giblje okoli
Sonca, se imenuje planet ali planetoid.
2. Satelit je lahko naravno telo ali vesoljsko
plovilo.
725-11-06 − osnovno telo (v odnosu do Telo, ki privlači satelit in določa osnovno
satelita) gibanje satelita.
− primary body (in relation to a
satellite)
− corps principal (pour un satellite)
− Zentralkörper (in bezug auf einen
satelliten)
725-11-07 − orbita; tirnica 1) Pot (glede na določen referenčni sistem), ki
− orbit jo opisuje masno središče satelita ali
− orbite drugega objekta v prostoru, katerega
− Umlaufbahn; Orbit gibanje je izključno posledica sil naravnega
izvora, pretežno gravitacijske sile.
2) Širše je to pot, ki opisuje gibanje masnega
središča objekta v prostoru zaradi vpliva
naravnih sil in občasnih umetnih
korekcijskih sil. Slednje povzroča pogonska
naprava, ki ohranja želeno smer.
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-08 − nemotena orbita (satelita) Satelitova orbita v idealnih pogojih, v katerih
− unperturbed orbit (of a satellite) na satelit vpliva le privlačna sila osnovnega
− orbite non perturbée (d’un satellite) telesa, osredotočena na njegov masni center.
− ungestörte Umlaufbahn (eines
OPOMBA: V referenčnem sistemu, katerega središče
Satelliten)
je masno središče osnovnega telesa in
katerega osi imajo stalne smeri glede na
zvezde, ima nemotena orbita obliko elipse.
725-11-09 − (osnovna) referenčna ravnina (za Ravnina, ki se uporablja pri določanju orbitnih
telo v vesolju) elementov telesa v vesolju.
− (principal) reference plane (for a
OPOMBA: Osnovna referenčna ravnina je v splošnem
body in space); (basic) reference
v eliptični ali ekvatorialni ravnini osnovnega
plane (for a body in space)
telesa; za umetni zemeljski satelit je
− plan fondamental (d’un objet dans
osnovna referenčna ravnina zemeljska
ekvatorialna ravnina.
l’espace); plan principal de référence
(d’un objet dans l’espace)
− (Haupt-)Bezugsebene (eines
Weltraumkörpers)
725-11-10 − orbitni elementi; elementi orbite Parametri, po katerih se lahko oblika, mere in
− orbital elements položaj orbite telesa v vesolju določijo glede
− éléments orbitaux na posamezni referenčni sistem.
− Bestimmungsgrößen der
OPOMBE: 1. Da je kadarkoli mogoče določiti položaj
Umlaufbahn
telesa v vesolju, je treba za dani primer
poleg njegovih orbitnih elementov poznati
tudi položaj njegovega masnega središča v
orbiti.
2. Uporabljen referenčni sistem je ponavadi
pravilen pravokotni koordinatni sistem
OXYZ, katerega začetek je v masnem
središču osnovnega telesa in je tretja os
OZ pravokotna na osnovno referenčno
ravnino.
3. Za umetni zemeljski satelit je osnovna
referenčna ravnina zemeljska ekvatorialna
ravnina in tretja os OZ je v smeri sever-jug.
Ravnina, ki vsebuje masno središče osnovnega
725-11-11 − orbitna ravnina (satelita)
− orbital plane (of a satellite) telesa in vektor hitrosti satelita; referenčni
− plan de l’orbite (d’un satellite) sistem je enak tistemu, ki je specificiran za
− Orbitebene (eines Satelliten) ugotavljanje orbitnih elementov.
OPOMBA: Pri nemoteni orbiti je orbitna ravnina stalna
v referenčnem sistemu, katerega središče
je masno središče osnovnega telesa in
katerega osi imajo stalne smeri glede na
zvezde.
725-11-12 − direktna orbita (satelita) Takšna satelitova orbita, da se projekcija
− direct orbit (of a satellite) masnega središča satelita v osnovni
− orbite directe (de satellite) referenčni ravnini giblje okrog osi osnovnega
− voreilender Umlauf (eines Satelliten) telesa v isti smeri kot tista, v kateri se vrti
osnovno telo.
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-13 − retrogradna orbita (satelita); Takšna satelitova orbita, da se projekcija
(nasprotna) orbita (satelita) masnega središča satelita v osnovni
− retrograde orbit (of a satellite) referenčni ravnini giblje okrog osi osnovnega
− orbite rétrograde (de satellite) telesa v obratni (nasprotni) smeri, kakor se vrti
− nacheilender Umlauf (eines osnovno telo.
Satelliten)
725-11-14 − krožna orbita (satelita) Satelitova orbita, v kateri je razdalja med
− circular orbit (of a satellite) masnima središčema satelita in osnovnega
− orbite circulaire (de satellite) telesa stalna.
− kreisförmige Umlaufbahn (eines
Satelliten)
725-11-15 − eliptična orbita (satelita) Nemotena orbita satelita, v kateri razdalja med
− elliptical orbit (of a satellite) masnima središčema satelita in osnovnega
− orbite elliptique (de satellite) telesa ni stalna.
− elliptische Umlaufbahn (eines
OPOMBA: Orbita je elipsa v referenčnem sistemu,
Satelliten)
katerega središče je masno središče
osnovnega telesa in katerega osi imajo
stalne smeri glede na zvezde.
725-11-16 − ekvatorialna orbita (satelita) Satelitova orbita, katere ravnina se ujema z
− equatorial orbit (of a satellite) ekvatorialno ravnino osnovnega telesa.
− orbite équatoriale (de satellite)
− äquatoriale Umlaufbahn (eines
Satelliten)
725-11-17 − polarna orbita (satelita) Satelitova orbita, katere ravnina vsebuje
− polar orbit (of a satellite) polarne osi osnovnega telesa.
− orbite polaire (de satellite)
− polare Umlaufbahn (eines Satelliten)
725-11-18 − nagnjena orbita (satelita) Satelitova orbita, ki ni ne ekvatorialna in ne
− inclined orbit (of a satellite) polarna.
− orbite inclinée (de satellite)
− geneigte Umlaufbahn (eines
Satelliten)
725-11-19 − parkirna orbita Orbita, ki je ponavadi blizu osnovnemu telesu
− parking orbit in v kateri je vesoljsko plovilo začasno pred
− orbite d’attente prehodom v svojo delovno orbito.
− Parkbahn
Orbita, v katero se vesoljsko plovilo lahko
725-11-20 − vmesna (začasna) orbita
− transfer orbit začasno umesti med prehodom iz svoje
− orbite de transfert začetne orbite ali lansirne trajektorije v drugo
− Transferbahn; Übergangsbahn orbito.
OPOMBA: Vmesna orbita je ponavadi eliptična orbita
med dvema krožnima orbitama.
725-11-21 − nagib (nagnjenost) (satelitove Kot med orbitno ravnino satelita in osnovno
orbite) referenčno ravnino.
− inclination (of a satellite orbit)
OPOMBA: Po dogovoru je nagib direktne orbite ostri
− inclinaison (d’une orbite de satellite)
kot in nagib retrogradne orbite topi kot.
− Neigung (einer
Satellitenumlaufbahn)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-22 − rastoče sečišče (točka) (satelita) Točka, v kateri satelitova orbita seka osnovno
− asscending node (of a satellite) referenčno ravnino, tretja satelitova koordinata
− noeud ascendant (d’un satellite) pa pri prehodu skozi to točko narašča.
− aufsteigender Knoten (eines
Satelliten)
725-11-23 − padajoče sečišče (satelita) Točka, v kateri satelitova orbita seka osnovno
− descending node (of a satellite) referenčno ravnino, tretja satelitova koordinata
− noeud descendant (d’ un satellite) pa pri prehodu skozi to točko upada.
− absteigender Knoten (eines
Satelliten)
Črta sečišč satelitove orbitne ravnine in
725-11-24 − sečiščna črta (satelita)
− line of nodes (of a satellite) osnovne referenčne ravnine.
− ligne des noeuds (d’un satellite)
− Knotenlinie (eines Satelliten)
725-11-25 − dolžina rastočega sečišča Kot, merjen proti vzhodu, med črto iz središča
(zemeljskega satelita) Zemlje do spomladanskega ekvinokcija in črto
− longitude of the ascending node (of iz središča Zemlje do rastočega sečišča
an earth satellite) zemeljskega satelita.
− longitude (céleste) du noeud
OPOMBA: Spomladanski ekvinokcij je rastoče sečišče
ascendant (d’un satellite de la Terre)
Sonca v zemeljski ekvatorialni ravnini. V
− Länge des aufsteigenden Knotens
angleščini se včasih imenuje “the First
(eines Erdsatelliten)
Point of Aries” (prva točka Ovna).
725-11-26 − precesija (orbite satelita) Sprememba dolžine značilne točke v satelitovi
− precession (of the orbit of a satellite) orbiti, kakor je rastoče sečišče, merjena v okviru
− précession (de l’orbite d’un satellite) referenc, ki jih določajo osnovno telo in zvezde.
− Präzession (der Umlaufbahn eines
OPOMBI: 1. Precesija satelitove orbite povzroča motnje
Satelliten)
pri njegovem gibanju po orbiti, ki se
pojavljajo zaradi npr. neenakomerne
porazdelitve mase osnovnega telesa.
2. Precesija satelitove orbite naj se ne
zamenjuje s precesijo vrtečega se telesa.
725-11-27 − apoapsida Točka v orbiti satelita ali planeta, ki je najdlje
− apoapsis od masnega središča osnovnega telesa.
− apoastre; apside supérieur;
apoapside
− Apoapside
725-11-28 − periapsida Točka v orbiti satelita ali planeta, ki je najbližje
− periapsis masnemu središču osnovnega telesa.
− périastre; apside inférieure;
périapside
− Periapside
725-11-29 − črta apsid; apsidna črta Črta, ki povezuje periapside in apoapside
− line of the apsides satelitove orbite.
− ligne des apsides
− Apsidenlinie
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-30 − argument periapside Kot ob masnem središču osnovnega telesa
− argument of periapsis med rastočim sečiščem in smerjo periapside
− élongation nodale du périastre; satelitove orbite.
argument de latitude du périastre
− Argument der Periapside
725-11-31 − apogej Točka v orbiti zemeljskega satelita, ki je
− apogee najdlje od središča Zemlje.
− apogée
OPOMBA: Apogej je apoapsida zemeljskega satelita.
− Apogäum
725-11-32 − perigej Točka v orbiti zemeljskega satelita, ki je
− perigee najbližje središču Zemlje.
− périgée
OPOMBA: Perigej je periapsida zemeljskega satelita.
− Perigäum
725-11-33 − višina apogeja Višina apogeja nad določeno referenčno
− altitude of the apogee površino, ki predstavlja površino Zemlje.
− altitude de l’apogée
− Apogäumshöhe
725-11-34 − višina perigeja Višina perigeja nad določeno referenčno
− altitude of the perigee površino, ki predstavlja površino Zemlje.
− altitude du périgée
− Perigäumshöhe
725-11-35 − perioda kroženja (satelita); Čas med dvema zaporednima prehodoma
obhodni čas (satelita) satelita skozi značilno točko v njegovi orbiti.
− period of revolution (of a satellite);
OPOMBA: Če ni dodatnih informacij, se "perioda
orbital period (of a satellite)
kroženja" razume kot "anomalistična
− période de révolution (d’un satellite)
perioda". Glej tudi izraza "perioda sečišča"
− Umlaufzeit (eines Satelliten)
in "zvezdna (siderična) perioda kroženja
(satelita).
725-11-36 − anomalistična perioda Čas med dvema zaporednima prehodoma
− anomalistic period satelita skozi periapsido.
− période anomalistique
− anomalistische Umlaufzeit
725-11-37 − perioda sečišča Čas med dvema zaporednima prehodoma
− nodal period satelita skozi rastoče sečišče njegove orbite.
− période nodale
− Knotenumlaufzeit
725-11-38 − zvezdna (siderična) perioda Čas med dvema zaporednima križanjema
kroženja (satelita) projekcije satelita na referenčno ravnino, ki gre
− sidereal period of revolution (of a skozi masno središče osnovnega telesa, s črto v
satellite) tisti ravnini, ki se razteza od masnega središča
− période de révolution sidérale (d’un do neskončnosti, od normalne do referenčne
satellite) ravnine in smeri črte, ki sta obe stalni glede na
− siderische Umlaufzeit (eines zvezde.
Satelliten)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-39 − korekturni pogon (vesoljskega Naprava, ki z izmetavanjem snovi omogoča
plovila) majhne popravke vesoljskega plovila za
− thruster (of a spacecraft) popravljanje lege, smeri kroženja ali orbite,
− micropropulseur (d’un engin spatial) vključno položaja v orbiti.
− Korrekturdüse (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-40 − vrtilna os (vesoljskega plovila) Prva iz nabora treh ortogonalnih koordinatnih
− roll axis (of a spacecraft) osi, imenovanih vrtilna, prečna in sučna os, ki
− axe de roulis (d’un engin spatial) so določene s konvencijo o vesoljskih plovilih
− Rollachse (eines in uporabljene kot referenca za postavljanje
Weltraumfahrzeugs) elementov vesoljskega plovila, opisovanje
vrtenja vesoljskega plovila in za ugotavljanje
položaja vesoljskega plovila glede na sistem
zunanjih koordinat.
OPOMBA: Za geostacionarni satelit je vrtilna os
ponavadi približno tangenta na orbito.
725-11-41 − vrtenje (vesoljskega plovila) Gibanje vesoljskega plovila okrog njegove
− roll (of a spacecraft) vrtilne osi.
− roulis (d’un engin spatial)
− Rollbewegung (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-42 − vrtilni kot (vesoljskega plovila) Kotni premik vesoljskega plovila okrog
− roll (angle) (of a spacecraft) njegove vrtilne osi glede na sistem zunanjih
− angle de roulis (d’un engin spatial) koordinat, merjen v odvisnosti od neke
− Rollwinkel (eines začetne usmeritve vesoljskega plovila.
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-43 − hitrost vrtenja (vesoljskega Kotna hitrost kroženja okrog vrtilne osi glede
plovila) na sistem zunanjih koordinat.
− roll rate (of a spacecraft)
− vitesse de roulis (d’un engin spatial)
− Rollgeschwindigkeit (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-44 − prečna os (vesoljskega plovila) Druga iz nabora treh ortogonalnih koordinatnih
− pitch axis (of a spacecraft) osi, imenovanih vrtilna, prečna in sučna os, ki
− axe de tangage (d’un engin spatial) so določene s konvencijo o vesoljskih plovilih
− Nickachse (eines in uporabljene kot referenca za postavljanje
Weltraumfahrzeugs) elementov vesoljskega plovila, opisovanje
vrtenja vesoljskega plovila in za ugotavljanje
položaja vesoljskega plovila glede na sistem
zunanjih koordinat.
OPOMBA: Za geostacionarni satelit je prečna os
ponavadi približno vzporedna zemeljski
polarni osi.
725-11-45 − prečenje (vesoljskega plovila) Gibanje vesoljskega plovila okrog njegove
− pitch (of a spacecraft) prečne osi.
− tangage (d’un engin spatial)
− Nickbewegung (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-46 − prečni kot (vesoljskega plovila) Kotni premik vesoljskega plovila okrog
− pitch (angle) (of a spacecraft) njegove prečne osi glede na sistem zunanjih
− angle de tangage (d’un engin koordinat, merjen v odvisnosti od neke
spatial) začetne usmerjenosti vesoljskega plovila.
− Nickwinkel (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-47 − prečna hitrost (vesoljskega Kotna hitrost kroženja okrog prečne osi glede
plovila) na sistem zunanjih koordinat.
− pitch rate (of a spacecraft)
− vitesse de tangage (d’un engin
spatial)
− Nickgeschwindigkeit (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-48 − sučna os; os sukanja (vesoljskega Tretja iz nabora treh ortogonalnih koordinatnih
osi, imenovanih vrtilna, prečna in sučna os, ki
plovila)
− yaw axis (of a spacecraft) so določene s konvencijo o vesoljskih plovilih
− axe de lacet (d’un engin spatial) in uporabljene kot referenca za postavljanje
− Gierachse (eines elementov vesoljskega plovila, opisovanje
Weltraumfahrzeugs) vrtenja vesoljskega plovila in za ugotavljanje
položaja vesoljskega plovila glede na sistem
zunanjih koordinat.
OPOMBA: Za geostacionarni satelit je sučna os
ponavadi usmerjena proti središču Zemlje.
725-11-49 − sukanje (vesoljskega plovila) Gibanje vesoljskega plovila okrog njegove
− yaw (of a spacecraft) sučne osi.
− lacet (d’un engin spatial)
− Gierbewegung (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-50 − sučni kot; kot sukanja Kotni premik vesoljskega plovila okrog sučne
(vesoljskega plovila) osi glede na sistem zunanjih koordinat, merjen
− yaw (angle) (of a spacecraft) v odvisnosti od neke začetne usmerjenosti
− angle de lacet (d’un engin spatial) vesoljskega plovila.
− Gierwinkel (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-51 − sučna hitrost; hitrost sukanja Kotna hitrost kroženja okrog sučne osi glede
(vesoljskega plovila) na sistem zunanjih koordinat.
− yaw rate (of a spacecraft)
− vitesse de lacet (d’un engin spatial)
− Giergeschwindigkeit (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
725-11-52 − senzor položaja (vesoljskega Naprava na vesoljskem plovilu, ki daje
plovila) informacije o položaju vesoljskega plovila
− attitude sensor (of a spacecraft) glede na zunanjo referenco, kot je npr. Sonce,
− capteur d’orientation (d’un engin druga zvezda ali Zemlja.
spatial); capteur d’attitude (d’un
engin spatial)
− Lagesensor (eines
Weltraumfahrzeugs)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-53 − precesija (vrtečega se telesa) Konično gibanje osi vrtenja vrtečega se telesa
− precession (of a rotating body) okrog smeri, ki je stalna glede na zvezde,
− précession (d’un corps en rotation) zaradi delovanja zunanje sile.
− Präzession (eines rotierenden
Körpers)
725-11-54 − nutacija Majhno periodično gibanje vrtečega se telesa,
− nutation ki je dodano precesiji in povzroča, da os
− nutation vrtenja telesa oscilira okrog stožca precesije.
− Nutation
OPOMBA: Nutacija ima na splošno periodo, ki je
krajša od periode precesije.
725-11-55 − blažilnik nutacije Naprava na krovu vrtečega se vesoljskega
− nutation damper plovila, ki zmanjša amplitudo gibanja,
− amortisseur de nutation nastalega zaradi motilnih vrtilnih momentov.
− Nutationsdämpfer
OPOMBA: Ne glede na uporabljeni izraz blažilnik
nutacije zmanjša precesijo in nutacijo.
725-11-56 − položajno stabilizirani satelit Satelit, katerega vsaj ena os vzdržuje
− attitude stabilized satellite določeno smer proti zemeljskemu središču,
− satellite à commande d’orientation Soncu ali določeni točki v vesolju.
− lagestabilisierter Satellit
725-11-57 − rotacijsko (s spinom) stabilizirani Položajno stabilizirani satelit, katerega ena os
satelit ohranja določeno smer z vrtenjem telesa
− spin-stabilized satellite satelita ali njegovega večjega dela okrog te
− satellite stabilisé par rotation osi.
− spinstabilisierter Satellit
725-11-58 − triosno stabilizirani satelit Položajno stabilizirani satelit, pri katerem se tri
− three-axis-stabilized satellite osi vzdržujejo v določenih smereh s
− satellite stabilisé (selon) trois axes kombinacijo naprav, ki merijo, nadzirajo in
− dreiachsenstabilisierter Satellit stabilizirajo položaj vseh treh pravokotnih osi.
725-11-59 − perioda kroženja zvezd Perioda vrtenja okrog masnega središča
− sidereal period of rotation telesa v vesolju v okviru referenc, ki so stalne
− période de rotation sidérale glede na zvezde.
− siderische Rotationsdauer
Satelit, katerega položaj masnega središča
725-11-60 − satelit na stalnem mestu
− station-keeping satellite sledi določenemu zakonu, tako v odnosu do
− satellite maintenu en position ostalih satelitov, ki pripadajo istemu
− geführtes Satellit vesoljskemu sistemu, kot do točke na Zemlji,
ki je stalna ali pa se giblje na določen način.
Satelit, ki je krmiljen tako, da ima
725-11-61 − sinhronizirani satelit
− synchronised satellite anomalistično periodo ali periodo sečišča
− satellite synchronisé enako periodi drugega satelita ali planeta ali
− synchronisierter Satellit danega fenomena, in prečka karakteristično
točko v svoji orbiti v določenem trenutku.
725-11-62 − sinhroni satelit Satelit, katerega srednja zvezdna perioda
− synchronous satellite kroženja je enaka ali približno enaka periodi
− satellite synchrone kroženja osnovnega telesa.
− Synchronsatellit
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-63 − subsinhroni satelit Satelit, katerega srednja zvezdna perioda
− sub-synchronous satellite kroženja osnovnega telesa je večkratnik
− satellite sous-synchrone periode kroženja osnovnega telesa.
− subsynchroner Satellit
725-11-64 − supersinhroni satelit Satelit, katerega srednja zvezdna perioda
− super-synchronous satellite kroženja osnovnega telesa je manjkratnik
− satellite supersynchrone periode kroženja osnovnega telesa.
− supersynchroner Satellit
Zemeljski sinhroni satelit.
725-11-65 − geosinhroni satelit
− geosynchronous satellite
OPOMBA: Perioda kroženja Zemlje je okrog 23 ur in
− satellite géosynchrone
56 minut.
− geosynchroner Satellit
725-11-66 − stacionarni satelit Satelit, ki je fiksiran ali približno fiksiran glede
− stationary satellite na koordinatni sistem osnovnega telesa in ki je
− satellite stationnaire videti nepremičen za opazovalca na površini
− stationärer Satellit osnovnega telesa.
725-11-67 − geostacionarni satelit Stacionarni satelit, ki ima Zemljo za osnovno
− geostationary satellite telo.
− satellite géostationnaire
OPOMBA: Nagib orbitne ravnine geostacionarnega
− geostationärer Satellit
satelita da dvig očitnega premika satelita,
kot je vidno z Zemlje, kar je ponavadi proti
severu ali jugu. Eliptičnost in nenatančnost
orbite pri vzdrževanju kroženja satelita pa
dasta dvig očitnega premika, kot se vidi z
Zemlje, kar je ponavadi proti vzhodu ali
zahodu.
725-11-68 − orbita geostacionarnega satelita Unikatna orbita vseh geostacionarnih satelitov,
(GSO); geostacionarna orbita katerih višina je približno 35.800 km.
− geostationary satellite orbit; GSO
(abbreviation); geostationary orbit
− orbite des satellites
géostationnaires; orbite
géostationnaire
− geostationäre Satellitenumlaufbahn
725-11-69 − heliosinhroni satelit Zemeljski satelit v orbiti, pri kateri se vesoljska
− sun-synchronous satellite dolžina rastočega sečišča zavrti za 360 stopinj
− satellite héliosynchrone na leto.
− heliosynchroner Satellit
725-11-70 − konjunkcija s Soncem Poravnanost umetnega zemeljskega satelita s
− solar conjunction Soncem, kot se vidi z zemeljske postaje.
− conjonction solaire
− Sonnenlinie
725-11-71 − konjunkcija z Luno Poravnanost umetnega zemeljskega satelita z
− lunar conjunction Luno, kot se vidi z zemeljske postaje.
− conjonction lunaire
− Mondlinie
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-11-72 − geocentrični kot Kot, ki ga tvorita navidezni ravni črti, ki
− geocentric angle povezujeta dani točki s središčem Zemlje.
− angle géocentrique
− geozentrischer Winkel
725-11-73 − topocentrični kot Kot, ki ga tvorita navidezni ravni črti, ki
− topocentric angle povezujeta dve dani točki v vesolju z določeno
− angle topocentrique točko na površini Zemlje.
− topozentrischer Winkel
Kot, ki ga tvorita navidezni ravni črti, ki
725-11-74 − eksocentrični kot
− exocentric angle povezujeta dve dani točki z določeno točko v
− angle exocentrique vesolju.
− exozentrischer Winkel
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Podpoglavje 725-12: Vesoljski radiokomunikacijski sistemi
OPOMBA: Izrazi so definirani za zemeljske postaje, ki imajo specifične funkcije, in se nanašajo na tiste, ki se uporabljajo v
zemeljskih radiokomunikacijskih sistemih. Za radiokomunikacije z mobilnimi postajami veljajo izrazi za postaje, ki
so mobilne, in tiste, ki niso namenjene za uporabo v gibanju (glej tabelo 725-I). Za vse izraze v tabeli veljajo
definicije v tem poglavju ali v poglavju 713.
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
Eden ali več radijskih oddajnikov ali
725-12-01 − (radijska) postaja
− (radio) station sprejemnikov ali kombinacija oddajnikov in
− station (radioélectrique) sprejemnikov, vključno s pripadajočo opremo, na
− Funkstelle eni lokaciji ali izvajalec radiokomunikacijskih
dejavnosti ali radioastronomskih dejavnosti.
725-12-02 − vesoljska postaja (v Radijska postaja, nameščena na objektu, ki je
radiokomunikacijah) zunaj glavnega dela zemeljske atmosfere.
− space station (in
radiocommunication)
− station spatiale (en
radiocommunication)
− Weltraumfunkstelle
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Razpredelnica 725-I: Radiokomunikacije z mobilnimi postajami
Izrazi za radijske postaje, ki se Izrazi za radijske postaje, ki se
Tip mobilne
uporabljajo pri vesoljskih uporabljajo pri zemeljskih
postaje
radiokomunikacijah radiokomunikacijah
Mobilna Nemobilna Mobilna Nemobilna
vsi tipi mobilna kopenska mobilna postaja kopenska
zemeljska zemeljska postaja
postaja postaja
(725) (725) (725) (725)
ladje ladijska obalna ladijska postaja obalna postaja
zemeljska zemeljska
postaja postaja
(725) (725) (725) (725)
zrakoplovi zrakoplovna aeronavtična zrakoplovna aeronavtična
zemeljska zemeljska postaja postaja
postaja postaja
(725) (725) (713) (713)
na kopnem kopenska zemeljska kopenska bazna postaja
mobilna bazna postaja mobilna postaja
zemeljska
postaja
(725) (725) (713) (713)
Razpredelnica 725-I: Radiocommunication with mobiles
Terms for radio stations used in Terms for radio stations used in
Type of mobile
space radiocommunication terrestrial radiocommunication
mobile non-mobile mobile non-mobile
all types mobile earth land earth mobile station land station
station station
(725) (725) (725) (725)
ships ship earth coast earth ship station coast station
station station
(725) (725) (713) (713)
aircraft aircraft earth aeronautical aircraft station aeronautical
station earth station station
(725) (725) (713) (713)
on land land mobile base earth land mobile base station
earth station station station
(725) (725) (713) (713)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Razpredelnica 725-I: Radiocommunications avec mobiles
Termes pour les stations Termes pour les stations
Type de mobile
radioélectriques utilisées dans utilisées dans les
les radiocommunications radiocommunications de Terre
spatiales
mobile non mobile mobile non mobile
tous types station terrienne station terrienne station mobile station terrestre
mobile terrestre
(725) (725) (725) (725)
navires station terrienne station terrienne station de navire station côtiere
de navire côtiere
(725) (725) (713) (713)
aéronef station terrienne station terrienne station d'aéronef station
d'aéronef aéronautique aéronautique
(725) (725) (713) (713)
terrestre station tierrenne station terrienne station mobile station de base
mobile terrestre de base terrestre
(725) (725) (713) (713)
Razpredelnica 725-I: Mobilier Funk
Weltraumfunk terrestrischer Funk
Fahrzeugtyp
mobil ortsfest mobil ortsfest
alle Typen mobile ortsfeste mobile ortsfeste
Erdfunkstelle Erdfunkstelle Funkstelle Funkstelle
(725) (725)
(725) (725)
Schiff Schiffs- Küsten Seefunkstelle Küstenfunkstelle
Erdfunkstelle Erdfunkstelle
(725) (725) (713) (713)
Luftfahrzeug Luftfahrzeug- Flugfunk- Luftfunkstelle Bodenfunkstelle
Erdfunkstelle Erdfunkstelle
(725) (725) (713) (713)
Land mobile Boden- Erdfunkstellen- mobile ortsfeste
Erdfunkstelle Basisstation Landfunkstelle Landfunkstelle
(725) (725) (713) (713)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-12-03 − zemeljska postaja Radijska postaja na zemeljski površini ali
− earth station drugje v zemeljski atmosferi, ki je namenjena
− station terrienne; station terrestre komunikacijam:
(terme à proscrire dans ce sens)
− z eno ali več vesoljskimi postajami ali
− Erdfunkstelle
− z eno ali več drugimi postajami iste vrste,
kar pomeni enega ali več odbojnih satelitov
ali drugih objektov v vesolju.
OPOMBI: 1. Kjer izraz “zemeljska postaja” ni posebej
obrazložen, ga je mogoče razumeti kot
zemeljska postaja na stalni lokaciji, ki se
ne uporablja primarno za komunikacijo z
zemeljskimi mobilnimi postajami.
2. V francoščini se izrazi “station terrienne”,
“station terrestre” in “station de Terre”
nanašajo na različne koncepte, in sicer na
“zemeljska (na planetu Zemlja) postaja”,
“kopenska (na kopnem) postaja” in
“prizemna (ang. terrestrial) postaja”.
725-12-04 − prizemna postaja Radijska postaja, ki vpliva na zemeljske
− terrestrial station radiokomunikacije.
− station de Terre
OPOMBA: V francoščini se izrazi “station de Terre”,
− terrestrische Funkstelle
“station terrienne” in “station terrestre”
nanašajo na različne koncepte, in sicer na
“prizemna (ang. terrestrial) postaja”,
“zemeljska (na planetu Zemlja) postaja”,
“kopenska (na kopnem) postaja”.
725-12-05 − kopenska zemeljska postaja Zemeljska postaja, ki skrbi za povezavo prek
− land earth station satelita, ki služi mobilnim zemeljskim
− station terrienne terrestre postajam.
− ortsfeste Erdfunkstelle
−
725-12-06 − mobilna zemeljska postaja Zemeljska postaja na ladji, zrakoplovu,
− mobile earth station kopenskem vozilu ali ročni prenosni zemeljski
− station terrienne mobile postaji, namenjena uporabi med gibanjem, ali
− mobile Erdfunkstelle prenosna zemeljska postaja, namenjena
uporabi na točkah, ki niso določene posebej.
725-12-07 − kopenska postaja Radijska postaja za mobilne storitve, ki ni
− land station namenjena uporabi med gibanjem.
− station terrestre
OPOMBI: 1. Kopenske postaje omogočajo zemeljske
− ortsfeste Funkstelle
radiokomunikacije.
2. V francoščini se izrazi “station terrestre”,
“station de Terre” in “station terrienne”
nanašajo na različne koncepte, in sicer na
“kopenska (na kopnem) postaja”,
“prizemna (ang. terrestrial) postaja“ in
“zemeljska (na planetu Zemlja) postaja”.
725-12-08 − mobilna (prizemna) postaja Radijska postaja za mobilne storitve,
− mobile (terrestrial) station namenjena uporabi med gibanjem ali premori
− station mobile (de Terre) na točkah, ki niso določene posebej.
− mobile (terrestrische) Funkstelle
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-12-09 − obalna zemeljska postaja Kopenska zemeljska postaja, ki služi ladijskim
− coast earth station zemeljskim postajam.
− station terrienne côtière
− Küsten-Erdfunkstelle
725-12-10 − ladijska zemeljska postaja Mobilna zemeljska postaja, nameščena na
− ship earth station ladji.
− station terrienne de navire
− Schiffs-Erdfunkstelle
Kopenska zemeljska postaja, ki služi
725-12-11 − aeronavtična zemeljska postaja
− aeronautical earth station zrakoplovnim zemeljskim postajam.
− station terrienne aéronautique
− Flugfunk-Erdfunkstelle
725-12-12 − zrakoplovna zemeljska postaja Mobilna zemeljska postaja, nameščena na
− aircraft earth station zrakoplovu.
− station terrienne d’aéronef
− Luftfahrzeug-Erdfunkstelle
725-12-13 − bazna zemeljska postaja Kopenska zemeljska postaja, ki služi
− base earth station kopenskim mobilnim zemeljskim postajam.
− station terrienne de base
− Erdfunkstellen-Basisstation
725-12-14 − kopenska mobilna zemeljska Mobilna zemeljska postaja na kopenskem
postaja vozilu ali ročno prenosna ali drugače
− land mobile earth station prestavljiva, ki se uporablja na ne točno
− station terrienne mobile terrestre določenih točkah.
− mobile Boden-Erdfunkstelle
725-12-15 − vesoljska radiokomunikacija Vsaka radiokomunikacija, ki vključuje uporabo
− space radiocommunication ene ali več vesoljskih postaj ali uporabo enega
− radiocommunication spatiale ali več odbojnih satelitov ali drugih objektov v
− Weltraumfunk prostoru.
OPOMBA: Komunikacija med dvema točkama na
Zemlji prek sredstev vesoljske
radiokomunikacije se na splošno imenuje
“satelitska komunikacija”.
725-12-16 − prizemne radiokomunikacije Vsaka radiokomunikacija razen vesoljske
− terrestrial radiocommunication radiokomunikacije ali radioastronomije.
− radiocommunication de Terre
− terrestrischer Funk
Uporaba radiokomunikacij za povezavo
725-12-17 − fiksna satelitska storitev
− fixed-satellite service zemeljskih postaj na danih lokacijah prek
− service fixe par satellite enega ali več satelitov.
− fester Funkdienst über Satelliten
OPOMBA: Dana lokacija je lahko na določeni stalni
točki ali na katerikoli stalni točki znotraj
določenega področja.
725-12-18 − aktivni satelit Satelit, ki nosi vsaj eno vesoljsko postajo z
− active satellite oddajnikom.
− satellite actif
− aktiver Satellit
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-12-19 − odbojni (pasivni) satelit Satelit za odbijanje elektromagnetnih valov.
− reflecting satellite
− satellite réflecteur; satellite passif
(terme à proscrire)
− reflektierender Satellit
725-12-20 − vesoljski sistem Vsaka kombinacija zemeljskih postaj, vesoljskih
− space system postaj in izjemoma odbojnih satelitov, ki
− système spatial zagotavljajo vesoljske radiokomunikacije za
− Weltraumfunksystem posebne namene.
725-12-21 − satelitski sistem Vesoljski sistem, ki uporablja enega ali več
− satellite system umetnih satelitov.
− système à satellite
OPOMBA: Če osnovno telo ni Zemlja, ga je treba
− Satellitenfunksystem
določiti.
725-12-22 − satelitsko omrežje Kombinacija enega satelita in vseh pridruženih
− satellite network zemeljskih postaj.
− réseau à satellite
− Satellitenfunknetz
725-12-23 − povezava navzgor; navzgorna Radijska povezava med oddajno zemeljsko
povezava postajo in sprejemno vesoljsko postajo.
− up-link
− liaison montante
− Aufwärtsstrecke
725-12-24 − povezava navzdol; navzdolna Radijska povezava med oddajno vesoljsko
povezava postajo in sprejemno zemeljsko postajo.
− down-link
− liaison descendante
− Abwärtsstrecke
725-12-25 − medsatelitska povezava Radijska povezava med oddajno vesoljsko
− inter-satellite link postajo in sprejemno vesoljsko postajo brez
− liaison intersatellite vmesne zemeljske postaje.
− Intersatellitenfunkverbindung
725-12-26 − povezava prek satelita Radijske povezave med oddajno in sprejemno
− connection by satellite postajo prek enega ali več satelitov in v nekaterih
− liaison par satellite primerih ene ali več vmesnih zemeljskih postaj.
− Verbindung über Satellit
OPOMBI: 1. Končni postaji v povezavi prek satelita sta
lahko dve zemeljski postaji, dve vesoljski
postaji ali ena zemeljska in ena vesoljska
postaja.
2. V francoščini radijska pravila ITU omejujejo
pomen izraza “liasion par satellite” na izraz
satelitska povezava.
725-12-27 − satelitska povezava Povezava prek satelita med oddajno postajo in
− satellite link sprejemno postajo, in sicer prek enega
− liaison unisatellite satelita.
− Satellitenfunkverbindung
OPOMBA: Satelitska povezava med dvema
zemeljskima postajama, kjer gre za eno
povezavo navzgor in eno povezavo navzdol.
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-12-28 − večsatelitska povezava Povezava prek satelita med oddajno postajo in
− multi-satellite link sprejemno postajo, in sicer prek dveh ali več
− liaison multisatellite satelitov, brez vmesnih zemeljskih postaj.
− Mehrsatellitenfunkverbindung
OPOMBA: Večsatelitska povezava med zemeljskimi
postajami vključuje: eno povezavo
navzgor, eno ali več medsatelitskih
povezav in eno povezavo navzdol.
725-12-29 − satelitska povezava z več skoki Povezava prek satelita, sestavljena iz dveh ali
− multi-hop satellite link več satelitskih povezav, povezanih na
− liaison multibond par satellite zemeljske postaje.
− Satellitenfunkverbindung mit
mehreren Funkfeldern
725-12-30 − naprejšnja povezava (do vesoljske Povezava prek satelita od oddajne zemeljske
postaje) postaje do vesoljske postaje, na npr. daljinsko
− forward link (to a space station) dosegljivem satelitu, prek druge vesoljske
− liaison aller (vers une station postaje, na npr. podatkovnem relejnem
spatiale) satelitu.
− Vorwärtsstrecke (zu einer
Weltraumfunkstelle)
725-12-31 − povratna povezava (od vesoljske Povezava prek satelita od oddajne vesoljske
postaje) postaje, na npr. daljinsko dosegljivem satelitu,
− return link (from a space station) do sprejemne zemeljske postaje prek druge
− liaison retour (depuis une station vesoljske postaje, na npr. podatkovnem
spatiale) relejnem satelitu.
− Rückwärtsstrecke (von einer
Weltraumfunkstelle)
725-12-32 − naprejšnja povezava (v mobilnih Povezava prek satelita od oddajne kopenske
satelitskih komunikacijah) zemeljske postaje prek satelita do sprejemne
− forward link (in mobile satellite mobilne zemeljske postaje.
communication)
− liaison aller (en radiocommunication
par satellite avec des mobiles)
− Vorwärtsstrecke (im mobilen
Funkdienst über Satelliten)
725-12-33 − povratna povezava (v mobilnih Povezava prek satelita od oddajne mobilne
satelitskih komunikacijah) zemeljske postaje prek satelita do sprejemne
− return link (in mobile satellite kopenske zemeljske postaje.
communication)
− liaison retour (en
radiocommunication par satellite
avec des mobiles)
− Rückwärtsstrecke (im mobilen
Funkdienst über Satelliten)
SIST IEC 60050(725) : 2005
Izraz v slovenščini
Izraz v angleščini
Zap. št. Definicija
Izraz v francoščini
Izraz v nemščini
725-12-34 − napajalna povezava Radijska povezava od zemeljske postaje na
− feeder link dani lokaciji do vesoljske postaje (ali obratno),
− liaison de connexion ki prinaša informacijo za vesoljsko
− Speiseverbindung radiokomunikacijsko storitev, drugačno od
fiksne satelitske storitve.
OPOMBI: 1. Dana lokacija je lahko na določeni stalni
točki ali na katerikoli stalni točki znotraj
določenih področij.
2. Primeri napajalnih povezav:
- povezava navzgor za oddajni
(broadcast) satelit;
- del naprejšnje povezave do vesoljske
postaje ali povratne povezave od
vesoljske postaje, ki je med zemeljsko
postajo in podatkovnim relejnim satelitom;
- povezava navzgor in povezava navzdol
med obalno zemeljsko postajo in
satelitom v pomorskih mobilno
satelitskih storitvah.
725-12-35 − vidnostni lok (satelitskega Lok orbite geostacionarnega satelita, na
omrežja) katerem je vesoljska postaja vidna prek
− visible arc (of a satellite network) lokalnega radijskega horizonta iz vseh
− arc de visibilité (d’un réseau à zemeljskih postaj v tem satelitskem omrežju.
satellite)
− sichtbarer Bogen (eines
Satellitenfunknetzes)
725-12-36 − storitveni lok (vesoljske postaje) Lok orbite geostacionarnega satelita, na
− service arc (of a space station) katerem določena vesoljska postaja lahko
− arc de service (d’une station zagotovi zahtevano kakovost storitve vsem
spatiale) zemeljskim postajam v tem satelitskem
− nutzbarer Bogen (einer omrežju.
Weltraumfunkstelle)
725-12-37 − nazivni orbitni položaj Vesoljska dolžina položaja na orbiti
− nominal orbital position geostacionarnega satelita, ki je združena s
− position nominale sur orbite frekvenco, dodeljeno vesoljski postaji na
− nominelle Orbitposition danem geostacionarnem satelitu.
725-12-38 − sateliti na isti lokaciji Geostacionarni sateliti, ki zasedajo isti nazivni
− co-located satellites orbitni položaj.
− satellites copositionnés
OPOMBA: Sateliti na isti lokaciji uporabljajo dodeljene
− Satelliten gleicher Orbitposition
frekvence, ki se prekrivajo, toda njihove
emisije se lahko razlikujejo druga od druge
v sevalnih lastnostih njihovih anten (v npr.
smeri žarka in polarizaciji).
725-12-39 − razdalja za koordinacijo Razdalja od radijske postaje v določeni smeri,
− co-ordination distance za katero je interferenca do drugih radijskih
− distance de coordination postaj, ki souporabljajo isti frekvenčni pas, ali
− Koordinierungsentfernung od njih zanemarljiva za planske namene.
OPOMBA: V praksi je lahko razdalja z
...











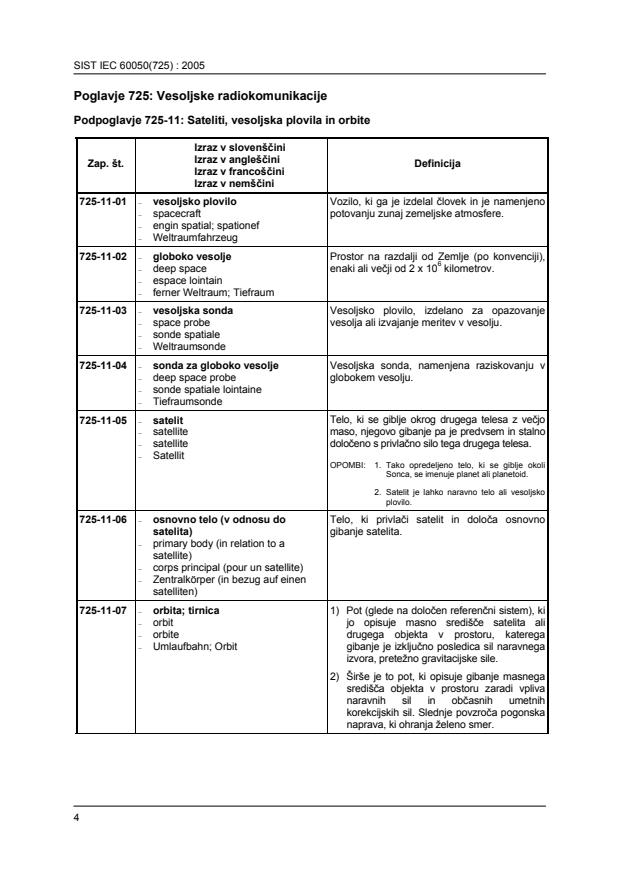
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...