ISO 1781:1983
(Main)Cinematography — Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection
Cinematography — Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection
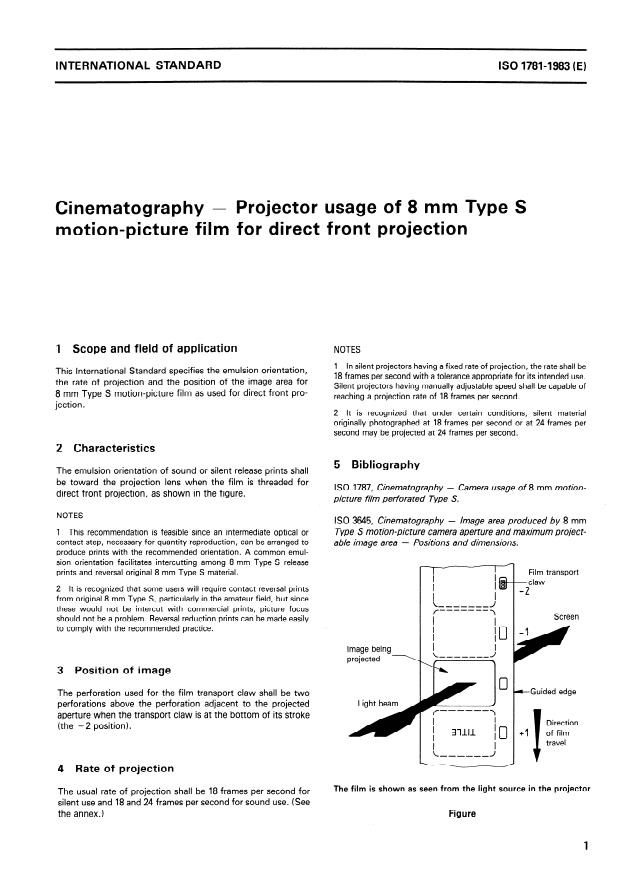
This International Standard specifies the emulsion orientation, the rate of projection and the Position of the image area for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film as used for direct front projection.
Cinématographie — Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
La présente Norme internationale spécifie l'orientation de l'émulsion, la vitesse de défilement et la position de l'image du film cinématographique 8 mm type S, utilisé en projection frontale directe.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 30-Nov-1983
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 03-Jun-2028
Overview
The ISO 1781:1983 standard, titled "Cinematography - Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection," provides essential specifications for the proper use of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film in direct front projection. Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), this document addresses critical parameters such as emulsion orientation, image positioning, and projection speed, focusing primarily on silent and sound film projectors operating with this film type.
This standard ensures consistency and compatibility in the technical handling of 8 mm Type S film, facilitating improved image quality and projector performance in both amateur and professional cinematography.
Key Topics
Emulsion Orientation:
The standard specifies that the emulsion side of the 8 mm Type S film must be directed toward the projector lens during direct front projection. This alignment is critical for achieving optimal image clarity and focus.Projection Speed:
- For silent projectors with fixed speed, the standard mandates a projection rate of 18 frames per second (fps), allowing for a tolerance suitable to their operation.
- Sound film projectors can operate at either 18 fps or 24 fps, accommodating variations in professional sound film playback.
Image Positioning and Perforation:
The exact position of the image area relative to the film perforations is standardized to ensure stable image projection. The sprocket hole used by the drive claw must be the second one above the one adjacent to the projection window when the claw is at its lowest point, minimizing image jitter due to perforation pitch variation.Compatibility and Copy Orientation:
The standard acknowledges variations in film copying processes, noting that reversible copies used especially in amateur filming may have different emulsion orientations. However, it emphasizes the importance of maintaining standard orientation in commercial copies to facilitate consistent editing and projection.
Applications
The ISO 1781:1983 standard is highly relevant for:
- Projector Manufacturers: Ensuring their 8 mm Type S projectors meet international specifications for emulsion orientation, image placement, and frame rates.
- Cinematographers and Film Processors: Maintaining consistent film handling during duplication and editing processes, which enhances the reproducibility and compatibility of films.
- Archivists and Restoration Specialists: Applying correct projection methods for archival 8 mm Type S films to preserve image integrity during playback.
- Educational and Amateur Film Use: Enabling hobbyists to understand and apply standard projection techniques, particularly when working with silent films or sound films with magnetic tracks.
Related Standards
ISO 1787: Cinematography - Position of 8 mm perforated Type S film in the camera gate
Defines the film position and perforations within the camera, complementing ISO 1781 for projector-side specifications.ISO 3645: Cinematography - Image fields recorded by camera and maximum projectable image field for 8 mm Type S
Provides detailed measurements of image dimensions and projection tolerances, essential for framing and projection alignment.
Summary
ISO 1781:1983 establishes practical guidelines for the correct use of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film in front projection systems, focusing on emulsion direction, frame rates, and image positioning relative to film perforations. By adhering to these specifications, projection systems can optimize image quality, minimize technical inconsistencies, and ensure compatibility across various 8 mm Type S film applications. This standard is instrumental for professionals and amateurs alike, aiming to preserve the cinematic quality and technical reliability of 8 mm film projection.
Keywords: ISO 1781, 8 mm Type S film, motion-picture film, projector standards, front projection, emulsion orientation, projection speed, cinematography standards, film perforations, silent film projection, sound film projection.
ISO 1781:1983 - Cinematography -- Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection
ISO 1781:1983 - Cinématographie -- Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
ISO 1781:1983 - Cinématographie -- Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 1781:1983 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Cinematography — Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection". This standard covers: This International Standard specifies the emulsion orientation, the rate of projection and the Position of the image area for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film as used for direct front projection.
This International Standard specifies the emulsion orientation, the rate of projection and the Position of the image area for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film as used for direct front projection.
ISO 1781:1983 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 37.060.10 - Motion picture equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 1781:1983 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEIKKLZYHAPO~HAR OPrAHM3AL&lR l-l0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Projector usage of 8 mm Type S
Cinematography -
motion-picture film for direct front projection
Utilisa tion du film 8 mm type S, dans Ie projecteur pour Ia projection frontale directe
Cinkma tographie -
Second edition - 1983-12-15
UDC 778.55 Ref. No. ISO 1781-1983 (E)
z
Descriptors: cinematography, motion picture projectors, motion picture film, photographic images, Position (location), orientation, Camera
Speed.
Price based on 2 pages
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of developing International
Standards is carried out through ISO technical committees. Every member body
interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been authorized has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the ISO Council.
International Standard ISO 1781 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 36,
Cinematography.
This second edition was submitted directly to the ISO Council, in accordance with
clause 6.11.2 of part 1 of the Directives for the technical work of ISO. lt cancels and
replaces the first edition (i.e. ISO 1781-1973), which had been approved by the
member bodies of the following countries:
Austria India Switzerland
Belgium Italy Thailand
Canada Netherlands Turkey
Czechoslova kia Romania United Kingdom
Egypt, Arab Rep. of South Africa, Rep. of USA
France Spain USSR
Germany, F. R. Sweden
The member body of the following country had expressed disapp roval of the docu-
ment on technical grounds:
Japan
0 ‘International Organkation for Standardkation, 1983
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1781-1983 (E)
Cinematography - Projector usage of 8 mm Type S
motion-picture film for direct front projection
1 Scope and field of application NOTES
1 In silent projectors having a fixed rate of projection, the rate shall be
This International Standard specifies the emulsion orientation,
18 frames per second with a tolerante appropriate for its intended use.
the rate of projection and the Position of the image area for
Silent projectors having manually adjustable Speed shall be capable of
8 mm Type S motion-picture film as used for direct front pro-
reaching a projection rate of 18 frames per second.
jection.
2 lt is recognized that under certain conditions, silent material
originally photographed at 18 frames per second or at 24 frames per
second may be projected at 24 frames per second.
2 Characteristics
5 Bibliography
The emulsio
...
Norme internationale 1781
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWlE~YHAPO~HAR OPTAHM3ALWlR t-l0 CTAH~APTM3ALWlM*ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cinématographie - Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans
le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
Cinematography - Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection
Deuxième édition - 1983-12-15
CDU 778.55
Réf. no : ISO 1781-1983 (F)
Descripteurs : cinématographie, projecteur cinématographique, pellicule cinématographique,
image photographique, position, orientation,
vitesse de prise de vue.
Prix basé sur 2 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 1781 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
Cette deuxième édition fut soumise directement au Conseil de I’ISO, conformément au
paragraphe 6.11.2 de la partie 1 des Directives pour les travaux techniques de I’ISO.
Elle annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 1781-19731, qui avait été approuvée par
les comités membres des pays suivants:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’
France Suisse
Allemagne, R.F.
Inde Tchécoslovaquie
Autriche
Italie Thailande
Belgique
Pays- Bas Turquie
Canada
Roumanie URSS
Égypte, Rép. Arabe d’ Royaume-Uni USA
Espagne
Suède
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’avait désapprouvée pour des raisons techniques:
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1983 l
Imprimé en Suisse
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 1781-1983 (F)
Cinématographie - Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans
le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
NOTES
1 Objet et domaine d’application
1 Pour les projecteurs muets ayant une vitesse de défilement fixe,
La présente Norme internationale spécifie l’orientation de
cette vitesse doit être de 18 images par seconde, avec une tolérance
l’émulsion, la vitesse de défilement et la position de l’image du
appropriée à leur utilisation. Les projecteurs muets, munis d’un réglage
film cinématographique 8 mm type S, utilisé en projection
manuel de vitesse, doivent être capables d’atteindre la vitesse de
frontale directe.
18 images par seconde.
2 II est reconnu que sous certaines conditions, le matériel muet
exposé originalement à 18 images par seconde ou à 24 images par
2 Caractéristiques
seconde, peut être projeté à une cadence de 24 images par seconde.
L’émulsion des copies d’exploitation sonores ou muettes doit
être dirigée vers l’objectif du projecteur lorsque le film est placé
5 Bibliographie
pour la projection frontale directe, comme indiqué dans la
figure.
ISO 1787, Cinématographie - Position du fi
...
Norme internationale 1781
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWlE~YHAPO~HAR OPTAHM3ALWlR t-l0 CTAH~APTM3ALWlM*ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cinématographie - Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans
le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
Cinematography - Projector usage of 8 mm Type S motion-picture film for direct front projection
Deuxième édition - 1983-12-15
CDU 778.55
Réf. no : ISO 1781-1983 (F)
Descripteurs : cinématographie, projecteur cinématographique, pellicule cinématographique,
image photographique, position, orientation,
vitesse de prise de vue.
Prix basé sur 2 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 1781 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
Cette deuxième édition fut soumise directement au Conseil de I’ISO, conformément au
paragraphe 6.11.2 de la partie 1 des Directives pour les travaux techniques de I’ISO.
Elle annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 1781-19731, qui avait été approuvée par
les comités membres des pays suivants:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’
France Suisse
Allemagne, R.F.
Inde Tchécoslovaquie
Autriche
Italie Thailande
Belgique
Pays- Bas Turquie
Canada
Roumanie URSS
Égypte, Rép. Arabe d’ Royaume-Uni USA
Espagne
Suède
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’avait désapprouvée pour des raisons techniques:
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1983 l
Imprimé en Suisse
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 1781-1983 (F)
Cinématographie - Utilisation du film 8 mm type S, dans
le projecteur pour la projection frontale directe
NOTES
1 Objet et domaine d’application
1 Pour les projecteurs muets ayant une vitesse de défilement fixe,
La présente Norme internationale spécifie l’orientation de
cette vitesse doit être de 18 images par seconde, avec une tolérance
l’émulsion, la vitesse de défilement et la position de l’image du
appropriée à leur utilisation. Les projecteurs muets, munis d’un réglage
film cinématographique 8 mm type S, utilisé en projection
manuel de vitesse, doivent être capables d’atteindre la vitesse de
frontale directe.
18 images par seconde.
2 II est reconnu que sous certaines conditions, le matériel muet
exposé originalement à 18 images par seconde ou à 24 images par
2 Caractéristiques
seconde, peut être projeté à une cadence de 24 images par seconde.
L’émulsion des copies d’exploitation sonores ou muettes doit
être dirigée vers l’objectif du projecteur lorsque le film est placé
5 Bibliographie
pour la projection frontale directe, comme indiqué dans la
figure.
ISO 1787, Cinématographie - Position du fi
...











Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...