ISO 6896:1984
(Main)Cinematography — Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors — Dimensions
Cinematography — Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors — Dimensions
This International Standard specifies the dimensions of two types of 16-tooth intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motionpicture projectors. This International Standard is applicable to sprockets used in conjunction with film perforated in accordance with IS0 491.
Cinématographie — Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur cinématographique 35 mm — Dimensions
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les dimensions de deux types de débiteurs dentés à avance intermittente, utilisés dans les projecteurs cinématographiques 35 mm. La présente Norme internationale est applicable aux débiteurs utilisés avec du film perforé conformément à I'ISO 491.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 30-Nov-1984
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 10-Jul-2023
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 6896:1984 is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that specifies the precise dimensions of intermittent sprockets used in 35 mm motion-picture projectors. This standard covers two types of 16-tooth intermittent sprockets designed to work with film perforated according to ISO 491. The sprockets are essential components responsible for advancing film intermittently, frame by frame, ensuring smooth projection in cinematography equipment.
Developed by the ISO Technical Committee ISO/TC 36 (Cinematography), ISO 6896:1984 provides detailed dimensional requirements, ensuring compatibility and minimizing damage to the film during projection. By standardizing sprocket dimensions, the standard facilitates uniformity and interchangeability across equipment from different manufacturers worldwide.
Key Topics
Intermittent Sprocket Function
Sprockets described in this standard advance 35 mm motion-picture film intermittently, typically moving one frame at a time. The sprockets engage with the film perforations to ensure precise frame positioning.Types of Sprocket Teeth
The standard defines two tooth profiles for sprockets:- Type S (Square Tooth): The traditional square-shaped tooth often referred to as the AC type tooth per ISO 491.
- Type R (Rounded Tooth): Features rounded edges to reduce sharp contact points, minimizing wear on the film perforations and potential damage.
Dimensional Specifications
Critical sprocket dimensions are carefully specified, including:- Pitch circle diameter and tooth spacing
- Width and profile of the tooth (square or rounded)
- Radius of curvature on tooth faces and edges
- Diameter of the root of the tooth where the film bears pressure
- Tooth height and clearance diameters
Interaction with Film Perforations
The sprockets are designed to engage with films perforated according to ISO 491, which standardizes film and perforation dimensions. Proper design and dimensioning reduce deformation and abrasion on the film.Usage Notes
The standard highlights typical dimensional variations in sprockets used as feed (upper) and take-up (lower) sprockets in projectors and the stresses acting on the sprockets during film advancement and tension.
Applications
ISO 6896:1984 is crucial for manufacturers and engineers involved in the design, maintenance, and production of 35 mm motion-picture projectors and film handling equipment. Its applications include:
Projector Manufacturing: Ensuring sprockets meet dimensions that allow compatibility with standardized film perforations reduces film damage and improves reliability.
Film Handling Equipment: Devices that advance or transport 35 mm motion-picture film benefit from sprockets designed per this standard for precise intermittent film movement.
Quality Control and Compliance: Maintenance personnel and quality assurance teams use ISO 6896 to verify sprockets meet specifications to maintain projector performance and protect film integrity.
Film Preservation: By minimizing film abrasion through appropriately designed sprockets, archives and cinemas can prolong the lifespan of valuable motion-picture films.
Related Standards
ISO 491: Cinematography - 35 mm motion-picture film perforations
Defines the dimensions and placement of perforations in 35 mm film, which is essential for the correct engagement with intermittent sprockets specified in ISO 6896.ISO 2301: Cinematography - Film motion and transport mechanisms
Relevant for overall standards of film transport movement in projectors, where intermittent sprockets are a key component.Other ISO Cinematography Standards
Various ISO standards govern film formats, projection speeds, and magnetic sound tracks that complement the mechanical specifications of sprockets under ISO 6896.
Keywords: ISO 6896, intermittent sprockets, 35 mm motion-picture projectors, sprocket dimensions, film perforations, ISO 491, cinematography standards, film handling, projector components, film advancement, sprocket tooth profiles, square tooth, rounded tooth, film preservation, motion-picture film transport.
Buy Documents
ISO 6896:1984 - Cinematography -- Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors -- Dimensions
ISO 6896:1984 - Cinématographie -- Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur cinématographique 35 mm -- Dimensions
ISO 6896:1984 - Cinématographie -- Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur cinématographique 35 mm -- Dimensions
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 6896:1984 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Cinematography — Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors — Dimensions". This standard covers: This International Standard specifies the dimensions of two types of 16-tooth intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motionpicture projectors. This International Standard is applicable to sprockets used in conjunction with film perforated in accordance with IS0 491.
This International Standard specifies the dimensions of two types of 16-tooth intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motionpicture projectors. This International Standard is applicable to sprockets used in conjunction with film perforated in accordance with IS0 491.
ISO 6896:1984 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 37.060.10 - Motion picture equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 6896:1984 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDiZATlON.MEIKAYHAPOflHAR OPI-AHM3ALWlR f-IO CTAHAAPTM3AL4MM.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cinematography - Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm
motion-picture projectors - Dimensions
Cirkmatographie - Dkbiteur intermittent pour projecteur cinkma tographique 35 mm - Dimensions
First edition - 1984-12-15
UDC 778.553.1 Ref. No. IS0 6896-1984 E)
Descriptors : cinematography, motion-picture film 35 mm, motion-picture projector, intermittent sprockets, dimensions, definitions.
Price based on 4 pages
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council. They are approved in accordance with IS0 procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard IS0 6996 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 36,
Cinema tograph y.
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1984
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IS0 6896-1984 (E)
Cinematography - Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm
motion-picture projectors - Dimensions
1 Scope and field of application motion since it has to accelerate the film from zero velocity and achieve
an average rate of film advance. The root diameter is usually larger
than that of a feed sprocket because of greater perforation distortion.
This International Standard specifies the dimensions of two
types of 16-tooth intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-
picture projectors. This International Standard is applicable to
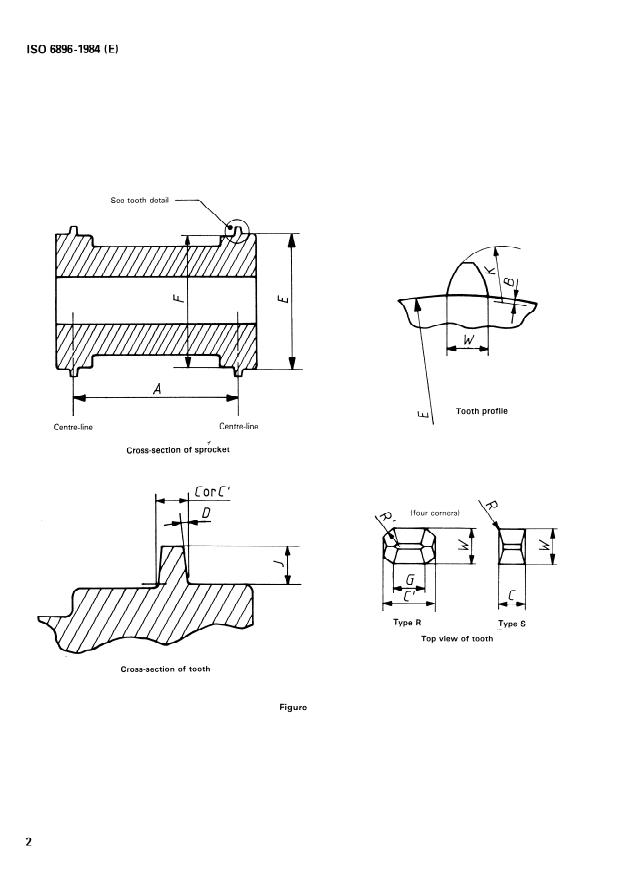
4 Sprocket tooth types
sprockets used in conjunction with film perforated in ac-
cordance with IS0 491.
4.1 Type S is the standard square tooth that is used inter-
nationally and known as Type AC sprocket tooth, specified in
IS0 491.
2 Reference
IS0 491, Cinematography - 35 mm motion-picture film and
4.2 Type R is the round tooth that eliminates sharp corners
magnetic film - Cutting and perforating dimensions.
on film contacting surfaces.
5 Dimensions
3 Definition
5.1 The dimensions shall be as shown in the figure and given
For the purpose of this International Standard the following
in the table.
definition applies.
5.2 The sprocket tooth pitch is measured at the midpoint of
intermittent sprocket: A feed sprocket used to advance the
0,15 mm film thickness :
film periodically (frame-by-frame),
(diameter E + 0,15 mm) 71
NOTE - The sprocket is usually completely at rest during the intervals
number of teeth
between advances. It is normally heavily loaded during a portion of its
IS0 6896-1984 (El
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDlZATION.MEIK~YHAPOAHAR OPrAHM3AUMR l-l0 CTAHAAPTM3ALWl~ORGANISATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cinématographie - Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur
cinématographique 35 mm - Dimensions
Cinema tograph y - Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors - Dimensions
Première édition - 1984-12-15
CDU 778.553.1 Réf. no : ISO 68964984 (FI
Descripteurs : cinématographie, film cinématographique 35 mm, projecteur cinématographique, débiteur intermittent, dimension, définition.
Prix basé sur 4 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 6896 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 6896-1984 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur
Cinématographie -
cinématographique 35 mm - Dimensions
1 Objet et domaine d’application du film. Son diamètre de fond de dent est, d’habitude, supérieur à celui
d’un débiteur d’alimentation à cause d’une déformation plus grande
des perforations.
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les dimensions de
deux types de débiteurs dentés à avance intermittente, utilisés
dans les projecteurs cinématographiques 35 mm. La présente
Norme internationale est applicable aux débiteurs utilisés avec
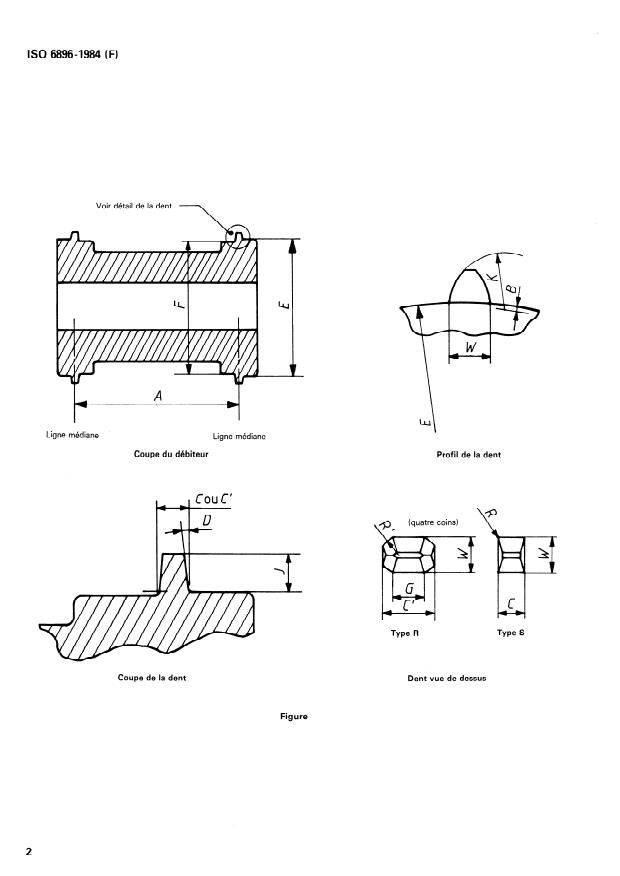
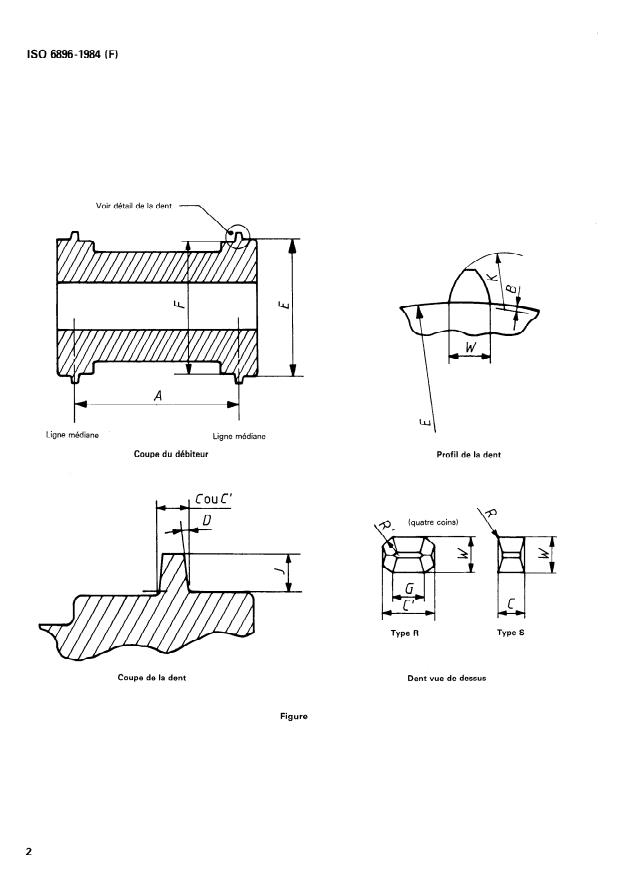
4 Types de dents des débiteurs
du film perforé conformément à I’ISO 491.
4.1 Le type S est la. dent carrée normale, employée interna-
tionalement, et connue comme dent de débiteur type AC, spé-
2 Référence
cifiée dans I’ISO 491.
ISO 491, Cinématographie - Film cinématographique et
Dimensions de coupe et de perfora-
magnétique de 35 mm -
4.2 Le type R est une dent arrondie, éliminant les angles vifs
tion.
des surfaces en contact avec le film.
3 Définition
5 Dimensions
Dans le cadre de la présente Norme internationale, la définition
suivante est applicable.
5.1 Les dimensions doivent être celles indiquées sur la figure
et données dans le tableau.
débiteur intermittent: Débiteur d’alimentation utilisé pour
faire avancer le film périodiquement (vue par vue).
5.2 Le pas des dents du débiteur est mesuré au milieu de
l’épaisseur d’un film de 0,15 mm :
NOTE - Le débiteur est, normalement, complètement arrêté dans
l’intervalle entre les avances. II subit, normalement, une forte con-
(diamètre E + 0,15 mm) n:
trainte pendant une partie de son mouvement puisqu’il doit accélérer le
nombre de dents
film à partir de la vitesse zéro pour atteindre un taux moyen d’avance
ISO 6896-1984 (F)
Voir détail de la dent
I
-
Ligne médiane
Ligne médiane
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDlZATION.MEIK~YHAPOAHAR OPrAHM3AUMR l-l0 CTAHAAPTM3ALWl~ORGANISATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cinématographie - Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur
cinématographique 35 mm - Dimensions
Cinema tograph y - Intermittent sprockets for 35 mm motion-picture projectors - Dimensions
Première édition - 1984-12-15
CDU 778.553.1 Réf. no : ISO 68964984 (FI
Descripteurs : cinématographie, film cinématographique 35 mm, projecteur cinématographique, débiteur intermittent, dimension, définition.
Prix basé sur 4 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 6896 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 6896-1984 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Débiteur intermittent pour projecteur
Cinématographie -
cinématographique 35 mm - Dimensions
1 Objet et domaine d’application du film. Son diamètre de fond de dent est, d’habitude, supérieur à celui
d’un débiteur d’alimentation à cause d’une déformation plus grande
des perforations.
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les dimensions de
deux types de débiteurs dentés à avance intermittente, utilisés
dans les projecteurs cinématographiques 35 mm. La présente
Norme internationale est applicable aux débiteurs utilisés avec
4 Types de dents des débiteurs
du film perforé conformément à I’ISO 491.
4.1 Le type S est la. dent carrée normale, employée interna-
tionalement, et connue comme dent de débiteur type AC, spé-
2 Référence
cifiée dans I’ISO 491.
ISO 491, Cinématographie - Film cinématographique et
Dimensions de coupe et de perfora-
magnétique de 35 mm -
4.2 Le type R est une dent arrondie, éliminant les angles vifs
tion.
des surfaces en contact avec le film.
3 Définition
5 Dimensions
Dans le cadre de la présente Norme internationale, la définition
suivante est applicable.
5.1 Les dimensions doivent être celles indiquées sur la figure
et données dans le tableau.
débiteur intermittent: Débiteur d’alimentation utilisé pour
faire avancer le film périodiquement (vue par vue).
5.2 Le pas des dents du débiteur est mesuré au milieu de
l’épaisseur d’un film de 0,15 mm :
NOTE - Le débiteur est, normalement, complètement arrêté dans
l’intervalle entre les avances. II subit, normalement, une forte con-
(diamètre E + 0,15 mm) n:
trainte pendant une partie de son mouvement puisqu’il doit accélérer le
nombre de dents
film à partir de la vitesse zéro pour atteindre un taux moyen d’avance
ISO 6896-1984 (F)
Voir détail de la dent
I
-
Ligne médiane
Ligne médiane
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...