ASTM F2136-01e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
Standard Test Method for Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used to determine the susceptibility of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resins or corrugated pipe to slow-crack-growth under a constant ligament-stress in an accelerating environment. This test method is intended to apply only to HDPE of a limited melt index and density range as defined in AASHTO Standard Specification M 294. This test method may be applicable for other materials, but data are not available for other materials at this time.
1.2 This test method measures the failure time associated with a given test specimen at a constant, specified, ligament-stress level.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. Values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D 1600, unless otherwise specified.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
e1
Designation:F2136–01
Standard Test Method for
Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to
Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins
1
or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2136; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—ReplacedreferencetowithdrawnstandardPracticeD1928withcurrentstandardPracticeD4703inNovember2003.
1. Scope stant Tensile Load Test
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Materials
1.1 This test method is used to determine the susceptibility
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resins or corrugated pipe
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
to slow-crack-growth under a constant ligament-stress in an
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
acceleratingenvironment.Thistestmethodisintendedtoapply
F 1473 Test Method for Notch Tensile Test to Measure the
only to HDPE of a limited melt index and density range as
Resistance to Slow Crack Growth of Polyethylene Pipes
defined in AASHTO Standard Specification M 294. This test
and Resins
method may be applicable for other materials, but data are not
2.2 Other Document:
available for other materials at this time.
3
AASHTO Standard Specification M 294
1.2 This test method measures the failure time associated
with a given test specimen at a constant, specified, ligament-
3. Summary of Test Method
stress level.
3.1 This test method subjects a dumbbell-shaped, notched
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
test-specimen (Fig. 1) to a constant ligament-stress in the
asthestandard.Valuesgiveninparenthesesareforinformation
presence of a surface-active agent at an elevated temperature.
only.
It differs from Test Method D 5397 in that a constant ligament
1.4 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412,
stress is used instead of a constant tensile load.
and abbreviations are in accordance withTerminology D 1600,
unless otherwise specified.
4. Significance and Use
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This test method does not purport to interpret the data
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
generated.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.2 This test method is intended to compare slow-crack-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
growth (SCG) resistance for a limited set of HDPE resins.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.3 This test method may be used on virgin HDPE resin
compression-molded into a plaque or on extruded HDPE
2. Referenced Documents
2 corrugated pipe that is chopped and compression-molded into
2.1 ASTM Standards:
a plaque (see 7.1.1 for details).
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
Plastics
5. Apparatus
D 4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
5.1 Blanking Die—Adie suitable for cutting test specimens
Materials in Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
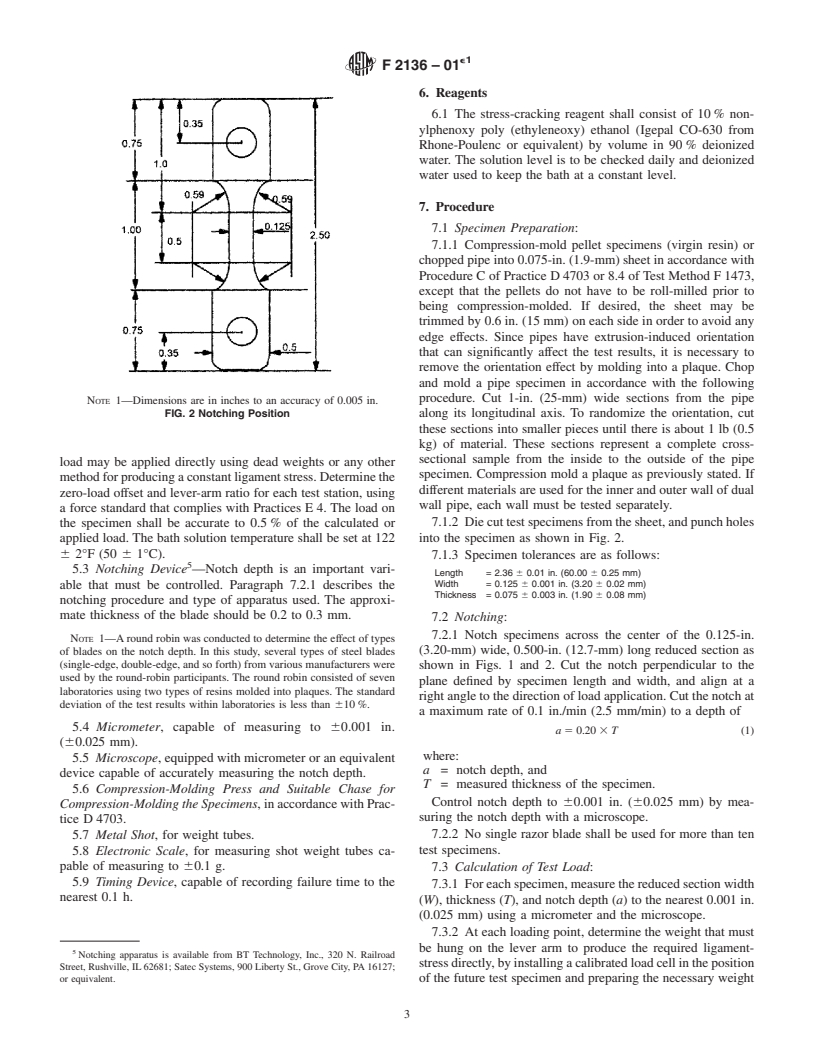
with holes to the dimensions and tolerances specified in Fig. 2.
D 5397 Test Method for Evaluation of Stress Crack Resis-
4
5.2 Stress-Crack Testing Apparatus —A lever loading ma-
tance of Polyolefin Geomembranes Using Notched Con-
chine, with a lever arm ratio of 2:1 to 5:1 similar to that
described in Test Method D 5397. Alternatively, the tensile
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test
3
Methods. Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2001. Published October 2001. Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Testing apparatus is available from BT Technology, Inc., 320 N. Railroad St.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Rushville, IL 62681; Materials Performance, Inc., 2151 Harvey Mitchell Pkwy, S.,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Suite 208, College Station, TX 77840; Satec Systems, 900 Liberty St., Grove City,
the ASTM website. PA 16127; or equivalent.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
e1
F2136–01
T = thickness.
W = specimen width.
NOTE 1—ThetestspecimenisintendedtohavethesamegeometryusedforTestMethodD 5397specimens.Thelengthofthespecimenca
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.