ASTM D7964/D7964M-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Activity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts in a Fluidized Bed
Standard Test Method for Determining Activity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts in a Fluidized Bed
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The fluidized bed test provides data to assess the relative performances of FCC catalysts. Because results are affected by catalyst pretreatment, feedstock characteristics, and operating parameters, this test method is written specifically to address the accuracy and precision when a common catalyst and oil are tested under the same conditions but at different sites, using Kayser Technologies Advanced Catalytic Evaluation (ACE) unit.4,5 Analytical procedures may vary among the sites. However, significant variations are not expected.
Note 1: ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
5.2 The standard reaction temperature for purposes of the accuracy and precision statement is 532 °C [990 °F]. Other reaction temperatures can be used in practice; however, yield data developed at temperatures other than 532 °C [990 °F] will not be the same. Also, test precision may be different at other reaction temperatures.
SCOPE
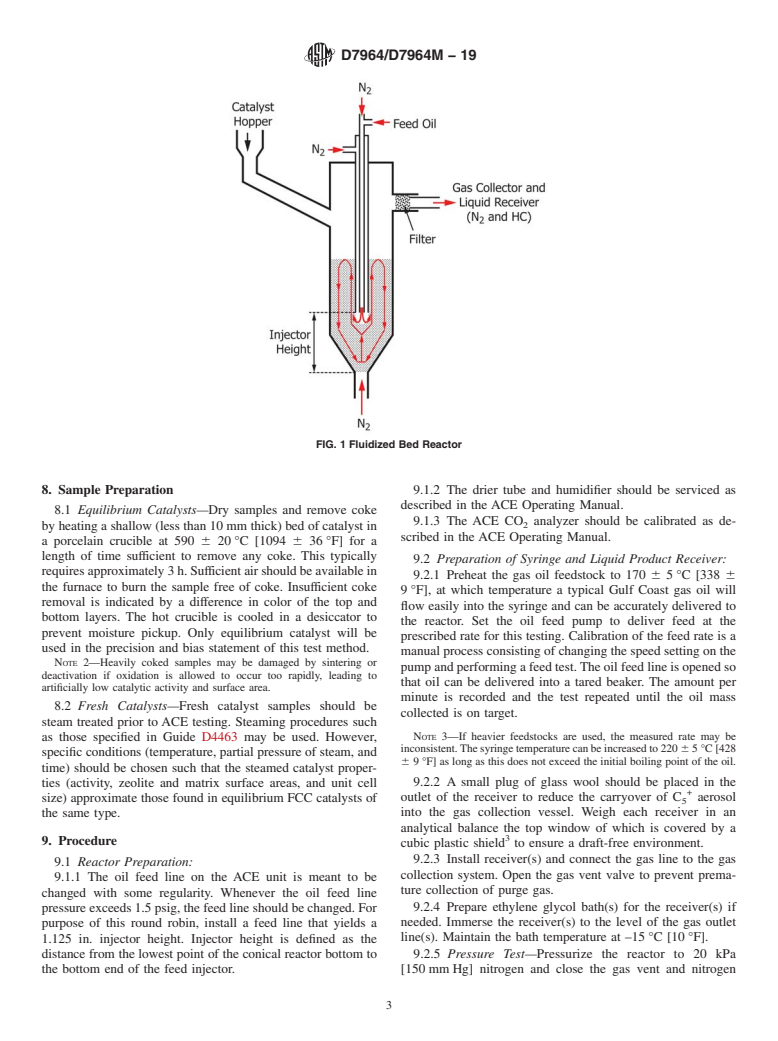
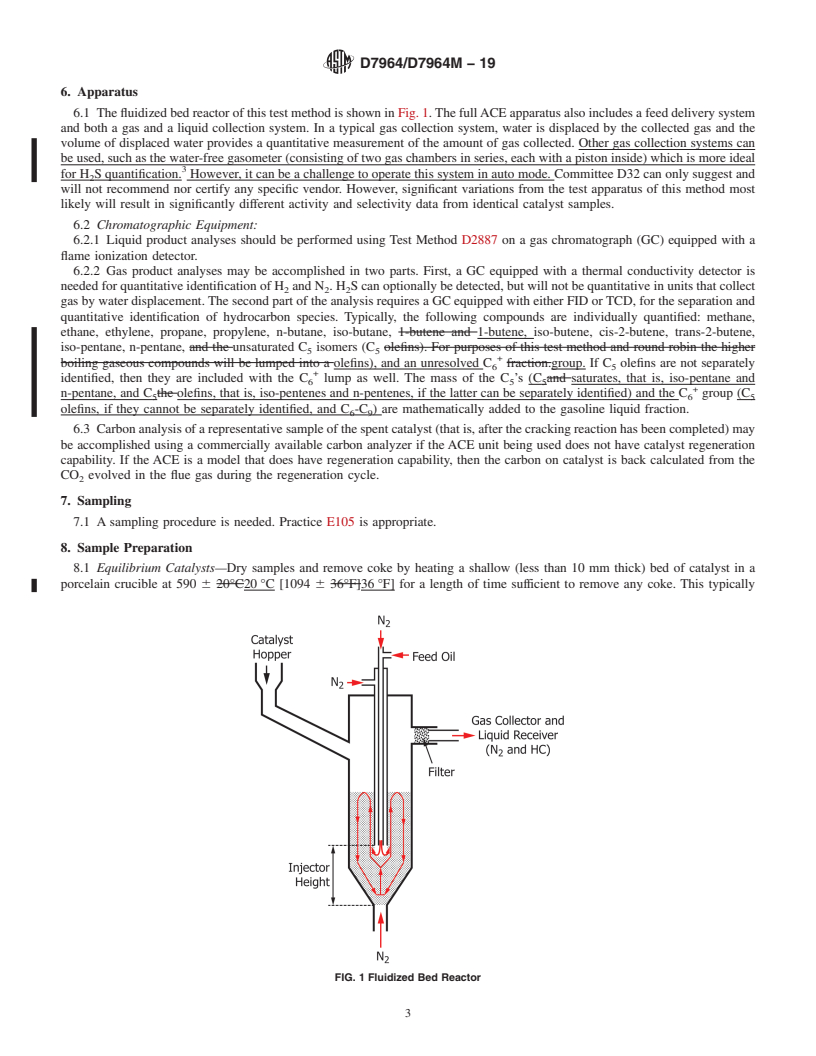
1.1 This test method covers determining the activity and coke selectivity of either equilibrium or laboratory deactivated fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evaluated on the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil feed in a fluidized bed reactor. The coke yield is defined as the mass of carbon laid down on the catalyst, also expressed as a percent of the gas oil feed. The scope of the round robin will be limited to the determination of activity and coke. All other analyses are thus beyond this scope and should be noted as “optional.”
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7964/D7964M − 19
Standard Test Method for
Determining Activity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)
1
Catalysts in a Fluidized Bed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7964/D7964M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D4463 Guide for Metals Free Steam Deactivation of Fresh
Fluid Cracking Catalysts
1.1 This test method covers determining the activity and
D5154/D5154M Test Method for Determining Activity and
coke selectivity of either equilibrium or laboratory deactivated
SelectivityofFluidCatalyticCracking(FCC)Catalystsby
fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evalu-
Microactivity Test
ated on the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil feed in
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
a fluidized bed reactor.The coke yield is defined as the mass of
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
carbon laid down on the catalyst, also expressed as a percent of
ASTM Test Methods
the gas oil feed. The scope of the round robin will be limited
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
tothedeterminationofactivityandcoke.Allotheranalysesare
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
thus beyond this scope and should be noted as “optional.”
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3. Terminology
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to
3.1.1 activity, n—a measure of the rate of a specific catalytic
ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
reaction, calculated in the present case by dividing conversion
used independently of the other, and values from the two
by the difference of 100 minus conversion.
systems shall not be combined.
3.1.2 catalyst/oil (C/O) ratio, n—the mass of catalyst used
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in the test divided by the mass of feed fed to the reactor.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.3 coke, n—mass of carbon laid down on the catalyst
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
during the FCC reaction times 1.083.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.4 conversion, n—the starting mass of reactant feed
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
minus the mass of the liquid product that boils above 221 °C
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
[430 °F]; this delta is then reported as a percentage of the
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
starting mass of feed.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.5 delivery time, n—this is the time, in seconds, during
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
which feed is introduced to the reactor.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.6 FCC, n—fluid catalytic cracking.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.7 gasoline, n—C compounds through compounds boil-
5
2
ing at 221 °C [430 °F].
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe- 3.1.8 HCO, n—theheavycycleoilproduct,whichisdefined
troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography to have a minimum boiling point of 343 °C [650 °F].
3.1.9 LCO, n—the light cycle oil product, which is defined
to have a boiling point range of 221 to 343 °C [430 to 650 °F].
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.04 on Catalytic 3.1.10 liquid product, n—all products formed in the cata-
Properties.
lytic reaction that can be condensed in the chiller bath
Current edition approved April 1, 2019. Published May 2019. Originally
afterward, usually a combination of gasoline, LCO, and HCO,
approved in 2014. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D7964/D7964M – 14.
but can contain a trace of C and C minus compounds.
DOI: 10.1520/D7964-19.
4 4
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1.11 normalized product yield, n—the result obtained
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
when each product yield has been corrected for non-perfect
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. mass balances.
Copyright © ASTM International
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7964/D7964M − 14 D7964/D7964M − 19
Standard Test Method for
Determining Activity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)
1
Catalysts in a Fluidized Bed
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7964/D7964M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers determining the activity and coke selectivity of either equilibrium or laboratory deactivated fluid
catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The activity is evaluated on the basis of mass percent conversion of gas oil feed in a fluidized
bed reactor. The coke yield is defined as the mass of carbon laid down on the catalyst, also expressed as a percent of the gas oil
feed. The scope of the round robin will be limited to the determination of activity and coke. All other analyses are thus beyond
this scope and should be noted as “optional.”
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system mayare not benecessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combiningother, and values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
standard.shall not be combined.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Petroleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
D4463 Guide for Metals Free Steam Deactivation of Fresh Fluid Cracking Catalysts
D5154/D5154M Test Method for Determining Activity and Selectivity of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Catalysts by
Microactivity Test
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 activity—activity, n—a measure of the rate of a specific catalytic reaction, calculated in the present case by dividing
conversion by the difference of 100 minus conversion.
3.1.2 catalyst/oil (C/O) ratio—ratio, n—the mass of catalyst used in the test divided by the mass of feed fed to the reactor.
3.1.3 coke—coke, n—mass of carbon laid down on the catalyst during the FCC reaction times 1.083.
3.1.4 conversion—conversion, n—the starting mass of reactant feed minus the mass of the liquid product that boils above 221°C
[430°F];221 °C [430 °F]; this delta is then reported as a percentage of the starting mass of feed.
3.1.5 delivery time—time, n—this is the time, in seconds, during which feed is introduced to the reactor.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.04 on Catalytic Properties.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014April 1, 2019. Published January 2015May 2019. Originally approved in 2014. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as
D7964/D7964M – 14. DOI: 10.1520/D7964-14.10.1520/D7964-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7964/D7964M − 19
3.1.6 FCC—FCC, n—fluid catalytic cracking.
3.1.7 gasoline—gasoline, n—C compounds through compounds boiling at 221°C [430°F].221 °C [430 °F].
5
3.1.8 HCO—HCO, n—the heavy cycle oil product, which is defined to have a minimum
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.