ASTM D5762-12(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Nitrogen in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Boat-Inlet Chemiluminescence
Standard Test Method for Nitrogen in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Boat-Inlet Chemiluminescence
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Many nitrogen compounds can contaminate refinery catalysts. They tend to be the most difficult class of compounds to hydrogenate, so the nitrogen content remaining in the product of a hydrotreator is a measure of the effectiveness of the hydrotreating process. In lubricating oils the concentration of nitrogen is a measure of the presence of nitrogen containing additives. This test method is intended for use in plant control and in research.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of nitrogen in liquid hydrocarbons, including petroleum process streams and lubricating oils in the concentration range from 40 μg/g to 10 000 μg/g nitrogen. For light hydrocarbons containing less than 100 μg/g nitrogen, Test Method D4629 can be more appropriate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in Section 6, 7.1, 8.2, and 8.2.2.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5762 − 12 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Nitrogen in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Boat-Inlet
Chemiluminescence
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5762; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D6299Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofnitrogenin
Measurement System Performance
liquid hydrocarbons, including petroleum process streams and
lubricating oils in the concentration range from 40µg⁄g to
3. Summary of Test Method
10000µg⁄g nitrogen. For light hydrocarbons containing less
than 100µg⁄g nitrogen, Test Method D4629 can be more
3.1 A hydrocarbon sample is placed on a sample boat at
appropriate.
room temperature. The sample and boat are advanced into a
high-temperature combustion tube where the nitrogen is oxi-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
dized to nitric oxide (NO) in an oxygen atmosphere. The NO
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
contacts ozone and is converted to excited nitrogen dioxide
standard.
(NO ).ThelightemittedastheexcitedNO decaysisdetected
2 2
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
byaphotomultipliertube,andtheresultingsignalisameasure
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of the nitrogen contained in the sample.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning
4.1 Many nitrogen compounds can contaminate refinery
statements are given in Section 6, 7.1, 8.2, and 8.2.2.
catalysts.Theytendtobethemostdifficultclassofcompounds
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
to hydrogenate, so the nitrogen content remaining in the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
product of a hydrotreator is a measure of the effectiveness of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the hydrotreating process. In lubricating oils the concentration
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical of nitrogen is a measure of the presence of nitrogen containing
additives. This test method is intended for use in plant control
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
and in research.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Apparatus
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
5.1 Boat Inlet System,capableofbeingsealedtotheinletof
Petroleum Products
the combustion tube and swept with inert gas. The boats are
D4177Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
fabricated from platinum or quartz. To aid quantitative liquid
Petroleum Products
injection, it is recommended to add a small piece of quartz
D4629Test Method for Trace Nitrogen in Liquid Petroleum
woolorsuitableequivalent(see6.8)totheboat.Theboatdrive
HydrocarbonsbySyringe/InletOxidativeCombustionand
mechanism should be able to fully insert the boat into the
Chemiluminescence Detection
furnace tube inlet section. A drive mechanism that advances
and withdraws the sample boat into and out of the furnace at a
controlled and repeatable rate is required.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
5.2 Chemiluminescence Detector, capable of measuring
Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
lightemittedfromthereactionbetweennitricoxideandozone,
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2017.PublishedJuly2017.Originallyapproved
and containing a variable attenuation amplifier, integrator, and
in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D5762–12. DOI: 10.1520/
D5762-12R17. readout.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
NOTE 1—Detectors designed to maintain the chemiluminescence reac-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on tion cell at reduced pressure are acceptable for use and were included in
the ASTM website. the instruments used to determine the precision of this test method.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5762 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 1 Quartz Combustion Tube (Single-Zone Furnace)
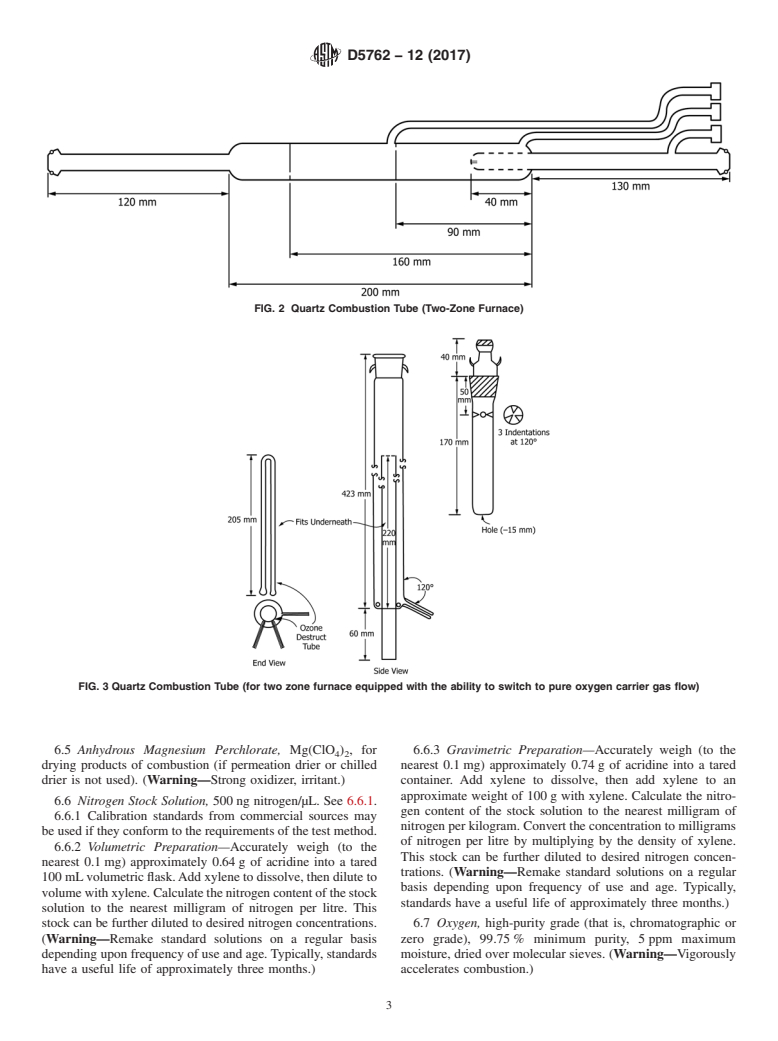
5.3 Combustion Tube, fabricated from quartz. The inlet end 5.5.2 Two-zone tube furnace with temperature controllers
ofthetubeshallbelargeenoughtoacceptthesampleboatand capable of maintaining the temperature of each furnace zone
tohavesidearmsforintroductionofoxygenandinertgas.The independently from 950°C to 1050°C (see 5.5). Or two-zone
construction is such that the carrier gases sweep the inlet zone tube furnace equipped with the ability to change to a pure
transporting all of the volatilized sample into a high- oxygencarriergasflowaftertheboatisfullyextendedintothe
temperature oxidation zone. The oxidation section should be furnaceandtemperaturecontrollerscapableofmaintainingthe
large enough to ensure complete oxidation of the sample. temperature of each furnace zone independently to 950°C.
Combustion tubes recommended for the two furnaces in 5.5.1
5.6 Microlitre Syringe,of5µLor10µLcapacity,capableof
and5.5.2aredescribedin5.3.1and5.3.2.Otherconfigurations
accurately delivering microlitre quantities.
are acceptable if precision and bias are not degraded.
5.7 Ozone Generator, to supply ozone to the detector
5.3.1 Quartz combustion tube for use with the single-zone
furnace is illustrated in Fig. 1.Awater-jacket around the inlet reaction cell.
section can be used to cool the boat prior to sample injection.
5.8 Recorder (Optional), for display of chemiluminescence
5.3.2 Quartz combustion tube for use with the two-zone
detector signal.
furnace is illustrated in Fig. 2. Fig. 3 illustrates a combustion
tube for a two-zone furnace that is equipped with the ability to
6. Reagents and Materials
switchtoapureoxygencarriergasflowaftertheboathasbeen
fully extended into the furnace (consult the instrument manual 6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
todetermineiftheinstrumentchangestoapureoxygencarrier
gas flow after the boat is inserted). The outlet end of the all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society
pyrolysis tube is constructed to hold a removable quartz insert
tube. The removable quartz insert tube is packed with an where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
oxidation catalyst as recommended by the instrument manu-
facturer. sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
accuracy of the determination.
5.4 Drier Tube,fortheremovalofwatervapor.Thereaction
products include water vapor that shall be eliminated prior to
6.2 Acridine, C H N, molecular weight 179.21, 7.82% by
13 9
measurement by the detector.This can be accomplished with a
mass nitrogen. (Warning—Irritant.)
magnesium perchlorate, Mg(ClO ) , scrubber, a membrane
4 2
6.3 Oxidation Catalyst: Cupric Oxide Wire, CuO, or Plati-
drying tube permeation drier, or a chilled dehumidifier assem-
num Catalyst, PtAl O , as recommended by the instrument
2 3
bly.
manufacturer.
5.5 Furnace, Electric, held at a temperature sufficient to
6.4 Inert Gas—Argon or Helium only, high-purity grade
pyrolyzeallofthesampleandoxidizethenitrogentoNO.The
(that is, chromatographic or zero grade), 99.998% minimum
followingfurnacedesignsmaybeused.Allfurnaceassemblies
purity, 5ppm maximum moisture.
include a method for gas flow control, such as needle valves,
flow restrictors or mass flow controllers. Furnaces that are
operated at temperatures below 1050°C shall be capable of
switching to 100% oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For Suggestions on the testing of reagents not
been fully extended into the furnace.
listed by the American Chemical Society, see Annual Standards for Laboratory
5.5.1 Single-zone tube furnace with temperature controller
Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
capableofmaintainingastablefurnacetemperatureof1100°C
and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
6 25°C. MD.
D5762 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 2 Quartz Combustion Tube (Two-Zone Furnace)
FIG. 3 Quartz Combustion Tube (for two zone furnace equipped with the ability to switch to pure oxygen carrier gas flow)
6.5 Anhydrous Magnesium Perchlorate, Mg(ClO ) , for 6.6.3 Gravimetric Preparation—Accurately weigh (to the
4 2
drying products of combustion (if permeation drier or chilled nearest 0.1mg) approximately 0.74g of acridine into a tared
drier is not used). (Warning—Strong oxidizer, irritant.) container. Add xylene to dissolve, then add xylene to an
approximate weight of 100g with xylene. Calculate the nitro-
6.6 Nitrogen Stock Solution, 500ng nitrogen/µL. See 6.6.1.
gen content of the stock solution to the nearest milligram of
6.6.1 Calibration standards from commercial sources may
nitrogenperkilogram.Converttheconcentrationtomilligrams
beusediftheyconformtotherequirementsofthetestmethod.
of nitrogen per litre by multiplying by the density of xylene.
6.6.2 Volumetric Preparation—Accurately weigh (to the
This stock can be further diluted to desired nitrogen concen-
nearest 0.1mg) approximately 0.64g of acridine into a tared
trations. (Warning—Remake standard solutions on a regular
100mLvolumetricflask.Addxylenetodissolve,thendiluteto
basis depending upon frequency of use and age. Typically,
volumewithxylene.Calculatethenitrogencontentofthestock
standards have a useful life of approximately three months.)
solution to the nearest milligram of nitrogen per litre. This
stock can be further diluted to desired nitrogen concentrations. 6.7 Oxygen, high-purity grade (that is, chromatographic or
(Warning—Remake standard solutions on a regular basis zero grade), 99.75% minimum purity, 5ppm maximum
dependinguponfrequencyofuseandage.Typically,standards moisture, dried over molecular sieves. (Warning—Vigorously
have a useful life of approximately three months.) accelerates combustion.)
D5762 − 12 (2017)
6.8 Quartz Wool (optional), or other suitable absorbent may be used if it can be shown that precision and bias are not
materialthatisstableandcapableofwithstandingtemperatures degraded. Set the furnace temperature to 1100°C 6 25°C.
inside the furnace (see Note 2). Adjust the boat drive mechanism to obtain a drive rate of
150mm⁄min 6 10mm⁄min. Refer to the manufacturer’s
NOTE 2—Materials meeting the requirements in 6.8 are recommended
instructions for descriptions of these settings.
to be used in sample boats to provide a more uniform injection of the
8.2.2 Forthetwo-zonefurnacewithouttheabilitytochange
sample into the boat by wicking any remainig drops of the sample from
the tip of the syringe needle prior to introduction of the sample into the
to a pure oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has been fully
furnace. Consult instrument manufacturer recommendations for further
extendedintothefurnace,adjustthecombustiontubegasflows
guidance.
to the following values: combustion oxygen, 165mL⁄min
6.9 Silver Wool, as recommended by the instrument manu-
616mL⁄min; inlet inert carrier, 85mL⁄min 6 9mL⁄min; and
facturer.
boat inert carrier, 50mL⁄min 6 5mL⁄min. Other gas flows
may be used if it can be shown that precision and bias are not
6.10 Xylene. (Warning—Flammable, health hazard.)
degraded. Set the inlet furnace temperature to 1050°C 6
6.11 Calibration Check Sample(s)—portionsofoneormore
25°C, and the outlet furnace temperature to 925°C 6 25°C.
liquid petroleum or product standards of known nitrogen
Adjust the boat drive mechanism to obtain a drive rate of
content and not used in the generation of the calibration curve.
150mm⁄min 6 10mm⁄min (boat speed number 4). Refer to
A calibration check sample or samples shall be used to verify
the manufacturer’s instructions for the description of these
the validity of the calibration curve as described in Section 10.
settings.(Warning—Hightemperatureisemployedinthistest
6.12 Quality Control (QC) Sample(s)—preferably portions
method. Use flammable materials with care near the pyrolysis
of one or more liquid petroleum materials that are stable and
furnace.)
representative of the samples of interest. These QC samples
8.2.3 For the two-zone furnace with the ability to change to
can be used to verify that the testing process is in statistical
a pure oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has been fully
control as described in Section 10.
extended in to the furnace, adjust the combustion tube gas
flows to the following values: main oxygen, 400mL⁄min 6
7. Sampling
40mL⁄min; inlet argon carrier, 0.4L⁄min 6 0.04L⁄min, and
7.1 Obtain a test sample in accordance with Practice D4057 inlet oxygen carrier, 0.4L⁄min 6 0.04L⁄min. Other gas flows
or D4177.(Warning—Samples that are collected at tempera- may be used if it can be shown that precision and bias are not
tures below room temperature can undergo expansion at degraded.Settheinletfurnacetemperatureto600°C 625°C,
laboratory temperatures and rupture the container. For such andtheoutlet(catalyst)temperatureto950°C 625°C.Setthe
samples,donotfillthecontainertothetop.Leavesufficientair automatic boat control as follows: 1 Fuc FWD 125 speed 10
space above the sample to allow room for expansion.) time30,2Fuc285speed05time30,5Fuctime30,6Fuctime
(Warning—To minimize loss of volatile components, which 90, A Fuc time 60. Refer to manufacturer’s instructions for a
canbepresentinsometestsamples,donotuncoveranylonger description of these settings.
than necessary. Test samples should be analyzed as soon as
8.3 Insert boat into furnace for a minimum of 2min to
possible after taking from bulk supplies to prevent loss of
remove any residual nitrogen species.
nitrogen or contamination due to exposure or contact with
sample container.)
9. Calibration and Standardization
7.2 If the test sample is not used immediately, then
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5762 − 12 D5762 − 12 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Nitrogen in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Boat-Inlet
Chemiluminescence
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5762; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of nitrogen in liquid hydrocarbons, including petroleum process streams and
lubricating oils in the concentration range from 4040 μg ⁄g to 10 000 μg10 000 μg ⁄g nitrogen. For light hydrocarbons containing
less than 100100 μg μg/g ⁄g nitrogen, Test Method D4629 can be more appropriate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in Section 6, 7.1, 8.2, and 8.2.2.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4629 Test Method for Trace Nitrogen in Liquid Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Syringe/Inlet Oxidative Combustion and
Chemiluminescence Detection
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A hydrocarbon sample is placed on a sample boat at room temperature. The sample and boat are advanced into a
high-temperature combustion tube where the nitrogen is oxidized to nitric oxide (NO) in an oxygen atmosphere. The NO contacts
ozone and is converted to excited nitrogen dioxide (NO ). The light emitted as the excited NO decays is detected by a
2 2
photomultiplier tube, and the resulting signal is a measure of the nitrogen contained in the sample.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Many nitrogen compounds can contaminate refinery catalysts. They tend to be the most difficult class of compounds to
hydrogenate, so the nitrogen content remaining in the product of a hydrotreator is a measure of the effectiveness of the
hydrotreating process. In lubricating oils the concentration of nitrogen is a measure of the presence of nitrogen containing
additives. This test method is intended for use in plant control and in research.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Boat Inlet System, capable of being sealed to the inlet of the combustion tube and swept with inert gas. The boats are
fabricated from platinum or quartz. To aid quantitative liquid injection, it is recommended to add a small piece of quartz wool or
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved April 15, 2012July 1, 2017. Published June 2012July 2017. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20112012 as
D5762D5762 – 12.–11. DOI: 10.1520/D5762-12.10.1520/D5762-12R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5762 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 1 Quartz Combustion Tube (Single-Zone Furnace)
suitable equivalent (see 6.8) to the boat. The boat drive mechanism should be able to fully insert the boat into the furnace tube
inlet section. A drive mechanism that advances and withdraws the sample boat into and out of the furnace at a controlled and
repeatable rate is required.
5.2 Chemiluminescence Detector, capable of measuring light emitted from the reaction between nitric oxide and ozone, and
containing a variable attenuation amplifier, integrator, and readout.
NOTE 1—Detectors designed to maintain the chemiluminescence reaction cell at reduced pressure are acceptable for use and were included in the
instruments used to determine the precision of this test method.
5.3 Combustion Tube, fabricated from quartz. The inlet end of the tube shall be large enough to accept the sample boat and to
have side arms for introduction of oxygen and inert gas. The construction is such that the carrier gases sweep the inlet zone
transporting all of the volatilized sample into a high-temperature oxidation zone. The oxidation section should be large enough to
ensure complete oxidation of the sample. Combustion tubes recommended for the two furnaces in 5.5.1 and 5.5.2 are described
in 5.3.1 and 5.3.2. Other configurations are acceptable if precision and bias are not degraded.
5.3.1 Quartz combustion tube for use with the single-zone furnace is illustrated in Fig. 1. A water-jacket around the inlet section
can be used to cool the boat prior to sample injection.
5.3.2 Quartz combustion tube for use with the two-zone furnace is illustrated in Fig. 2. Fig. 3 illustrates a combustion tube for
a two-zone furnace that is equipped with the ability to switch to a pure oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has been fully
extended into the furnace (consult the instrument manual to determine if the instrument changes to a pure oxygen carrier gas flow
after the boat is inserted). The outlet end of the pyrolysis tube is constructed to hold a removable quartz insert tube. The removable
quartz insert tube is packed with an oxidation catalyst as recommended by the instrument manufacturer.
5.4 Drier Tube, for the removal of water vapor. The reaction products include water vapor that shall be eliminated prior to
measurement by the detector. This can be accomplished with a magnesium perchlorate, Mg(ClO ) , scrubber, a membrane drying
4 2
tube permeation drier, or a chilled dehumidifier assembly.
5.5 Furnace, Electric, held at a temperature sufficient to pyrolyze all of the sample and oxidize the nitrogen to NO. The
following furnace designs may be used. All furnace assemblies include a method for gas flow control, such as needle valves, flow
restrictors or mass flow controllers. Furnaces that are operated at temperatures below 1050°C1050 °C shall be capable of switching
to 100%100 % oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has been fully extended into the furnace.
5.5.1 Single-zone tube furnace with temperature controller capable of maintaining a stable furnace temperature of 11001100 °C
6 25°C.25 °C.
5.5.2 Two-zone tube furnace with temperature controllers capable of maintaining the temperature of each furnace zone
independently from 950950 °C to 1050°C1050 °C (see 5.5). Or two-zone tube furnace equipped with the ability to change to a pure
oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat is fully extended in to the furnace and temperature controllers capable of maintaining the
temperature of each furnace zone independently to 950°C.950 °C.
5.6 Microlitre Syringe, of 55 μL or 10-μL10 μL capacity, capable of accurately delivering microlitre quantities.
5.7 Ozone Generator, to supply ozone to the detector reaction cell.
5.8 Recorder (Optional), for display of chemiluminescence detector signal.
6. Reagents and Materials
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society where
D5762 − 12 (2017)
FIG. 2 Quartz Combustion Tube (Two-Zone Furnace)
FIG. 3 Quartz Combustion Tube (for two zone furnace equipped with the ability to switch to pure oxygen carrier gas flow)
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
6.2 Acridine, C H N, molecular weight 179.21, 7.82 7.82 % by mass % nitrogen. (Warning—WarningIrritant.)—Irritant.)
13 9
6.3 Oxidation Catalyst: Cupric Oxide Wire, CuO, or Platinum Catalyst, PtAl O , as recommended by the instrument
2 3
manufacturer.
6.4 Inert Gas—Argon or Helium only, high-purity grade (that is, chromatographic or zero grade), 99.998 % minimum purity,
5 ppm 5 ppm maximum moisture.
6.5 Anhydrous Magnesium Perchlorate, Mg(ClO ) , for drying products of combustion (if permeation drier or chilled drier is
4 2
not used). (Warning—WarningStrong—Strong oxidizer, irritant.)
6.6 Nitrogen Stock Solution, 500 ng 500 ng nitrogen/μL. See 6.6.1.
6.6.1 Calibration standards from commercial sources may be used if they conform to the requirements of the test method.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For Suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by
the American Chemical Society, see Annual Standards for Laboratory Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia and National
Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville, MD.
D5762 − 12 (2017)
6.6.2 Volumetric Preparation—Accurately weigh (to the nearest 0.1 mg) approximately 0.64 g 0.1 mg) approximately 0.64 g of
acridine into a tared 100-mL100 mL volumetric flask. Add xylene to dissolve, then dilute to volume with xylene. Calculate the
nitrogen content of the stock solution to the nearest milligram of nitrogen per litre. This stock can be further diluted to desired
nitrogen concentrations. (Warning—Remake standard solutions on a regular basis depending upon frequency of use and age.
Typically, standards have a useful life of approximately three months.)
6.6.3 Gravimetric Preparation—Accurately weigh (to the nearest 0.1 mg) approximately 0.74 g 0.1 mg) approximately 0.74 g
of acridine into a tared container. Add xylene to dissolve, then add xylene to an approximate weight of 100 g 100 g with xylene.
Calculate the nitrogen content of the stock solution to the nearest milligram of nitrogen per kilogram. Convert the concentration
to milligrams of nitrogen per litre by multiplying by the density of xylene. This stock can be further diluted to desired nitrogen
concentrations. (Warning—Remake standard solutions on a regular basis depending upon frequency of use and age. Typically,
standards have a useful life of approximately three months.)
6.7 Oxygen, high-purity grade (that is, chromatographic or zero grade), 99.75 % minimum purity, 5 ppm 5 ppm maximum
moisture, dried over molecular sieves. (Warning—WarningVigorously—Vigorously accelerates combustion.)
6.8 Quartz Wool (optional), or other suitable absorbent material that is stable and capable of withstanding temperatures inside
the furnace (see Note 2).
NOTE 2—Materials meeting the requirements in 6.8 are recommended to be used in sample boats to provide a more uniform injection of the sample
into the boat by wicking any remainig drops of the sample from the tip of the syringe needle prior to introduction of the sample into the furnace. Consult
instrument manufacturer recommendations for further guidance.
6.9 Silver Wool, as recommended by the instrument manufacturer.
6.10 Xylene. (Warning—WarningFlammable,—Flammable, health hazard.)
6.11 Calibration Check Sample(s)—portions of one or more liquid petroleum or product standards of known nitrogen content
and not used in the generation of the calibration curve. A calibration check sample or samples shall be used to verify the validity
of the calibration curve as described in Section 10.
6.12 Quality Control (QC) Sample(s)—preferably portions of one or more liquid petroleum materials that are stable and
representative of the samples of interest. These QC samples can be used to verify that the testing process is in statistical control
as described in Section 10.
7. Sampling
7.1 Obtain a test sample in accordance with Practice D4057 or D4177. (Warning—WarningSamples—Samples that are
collected at temperatures below room temperature can undergo expansion at laboratory temperatures and rupture the container. For
such samples, do not fill the container to the top. Leave sufficient air space above the sample to allow room for expansion.)
(Warning—WarningTo—To minimize loss of volatile components, which can be present in some test samples, do not uncover any
longer than necessary. Test samples should be analyzed as soon as possible after taking from bulk supplies to prevent loss of
nitrogen or contamination due to exposure or contact with sample container.)
7.2 If the test sample is not used immediately, then thoroughly mix it in its container prior to taking a test specimen. Some test
samples require heating in order to thoroughly homogenize.
8. Preparation of Apparatus
8.1 Assemble apparatus in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
8.2 Adjust the oxygen flow for the ozone generator in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Adjust the combustion
tube gas flows and the pyrolysis temperature to the recommended operating conditions using the following guidelines for each
furnace type. (Warning—WarningOzone—Ozone is extremely toxic. Make sure that appropriate steps are taken to prevent
discharge of ozone within the laboratory work area.)
8.2.1 For the single-zone furnace without the ability to change to a pure oxygen carrier gas flow after the boat has been fully
extended into the furnace, adjust the combustion tube gas flows to the following values: pyrolysis oxygen, 360360 mL ⁄min 6
3636 mL mL/min; ⁄min; inlet oxygen, 6060 mL ⁄min 6 66 mL mL/min; ⁄min; and inert carrier inlet, 155155 mL ⁄min 6 1515 mL
mL/min. ⁄min. Other
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.