ISO 11380:1994
(Main)Optics and optical instruments — Ophthalmic optics — Formers
Optics and optical instruments — Ophthalmic optics — Formers
Specifies the characteristics of formers which are used in edging machines to edge lenses designed for insertion into spectacle frames. Not applicable to separate formers required for supplementary treatment of lenses, for example facetting.
Optique et instruments d'optique — Optique ophtalmique — Gabarits
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les caractéristiques des gabarits utilisés sur les machines à façonner les verres destinés à être adaptés dans les montures de lunettes. Elle ne traite pas des gabarits spéciaux destinés à des opérations complémentaires, par exemple le facettage des verres.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 28-Sep-1994
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 172/SC 7 - Ophthalmic optics and instruments
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 172/SC 7 - Ophthalmic optics and instruments
- Current Stage
- 9020 - International Standard under periodical review
- Start Date
- 15-Jan-2026
- Completion Date
- 15-Jan-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 11-Feb-2026
- Effective Date
- 09-Feb-2026
- Effective Date
- 09-Feb-2026
- Effective Date
- 09-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 11380:1994 is an international standard established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that specifies the essential characteristics and requirements for formers used in edging machines for ophthalmic lenses. These formers shape lenses to fit precisely into spectacle frames. The standard ensures consistency, reliability, and quality in the production of eyewear lenses by defining dimensions, tolerances, materials, and marking requirements for formers.
This standard is critical for manufacturers and suppliers in the ophthalmic optics industry, helping to standardize the tooling used during lens edging and enabling compatibility across different equipment and frames. It does not cover special formers used for secondary treatments such as faceting.
Key Topics
Scope and Application
ISO 11380:1994 applies specifically to formers utilized in lens edging machines intended to produce spectacle lenses that fit into frames. It excludes formers for additional lens treatments.Former Types
Formers are classified based on either:- The dimensions and shape of the lens to be cut (glass dimension system)
- The dimensions of the spectacle frame opening (frame opening system)
The standard recognizes two systems for identifying and designing formers and recommends stable material selection to maintain dimensional integrity.
Dimensional Requirements
The standard outlines precise dimensional tolerances - for example, no two formers of nominally identical size and shape should differ by more than 0.2 mm in any circumferential measurement. This ensures a perfect lens fit in the frame without gaps visible with normal corrected vision.Markings and Identification
Clear marking on formers is mandatory to include:- Manufacturer or supplier identification
- Model identification
- Nasal side indicator (letter N with a symbol)
- Horizontal dimension of the lens or the opening (depending on former type), in millimeters
- Optional axis indicators for horizontal and vertical alignment (with a tolerance of ±1 degree)
Markings must be placed as per the standard’s recommendations to ensure easy recognition and traceability.
Materials and Thickness
The standard specifies the use of materials and thicknesses that guarantee dimensional stability, contributing to consistent lens edging quality.
Applications
ISO 11380:1994 formers play an essential role in the eyewear manufacturing industry, particularly in:
- Lens edging processes - providing standardized shapes and dimensions to cut lenses accurately and fit spectacle frames securely.
- Quality assurance - enabling manufacturers to maintain consistent optical and mechanical performance through tightly controlled tooling specifications.
- Compatibility across equipment - ensuring formers from different suppliers can be used interchangeably on edging machines, supporting workflow efficiency.
- Customization and variety - accommodating different lens sizes and frame types through classification by lens or frame dimensions.
Adopting this standard helps optical labs, lens manufacturers, and frame producers optimize production, reduce waste from ill-fitting lenses, and meet international quality standards in ophthalmic optics.
Related Standards
For comprehensive ophthalmic optics manufacturing and quality control, ISO 11380:1994 relates closely to other ISO standards, such as:
- ISO 8980 series - Optical lenses specifications for spectacle lenses
- ISO 12870 - Ophthalmic optics - Spectacle frames - Requirements and test methods
- ISO 21987 - Ophthalmic optics - Mounted spectacle lenses - Vocabulary and measurable parameters
These complementary standards collaboratively ensure holistic quality in the design, production, and testing of optical instruments and eyewear components.
By adhering to ISO 11380:1994, optical manufacturers ensure precision and quality in lens edging operations, facilitating superior spectacle fitting and enhancing wearer comfort. This standard is fundamental for anyone involved in the design or production of ophthalmic lenses and spectacle frames.
Buy Documents
ISO 11380:1994 - Optics and optical instruments -- Ophthalmic optics -- Formers
ISO 11380:1994 - Optique et instruments d'optique -- Optique ophtalmique -- Gabarits
ISO 11380:1994 - Optique et instruments d'optique -- Optique ophtalmique -- Gabarits
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

BSI Group
BSI (British Standards Institution) is the business standards company that helps organizations make excellence a habit.

TÜV Rheinland
TÜV Rheinland is a leading international provider of technical services.

TÜV SÜD
TÜV SÜD is a trusted partner of choice for safety, security and sustainability solutions.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 11380:1994 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Optics and optical instruments — Ophthalmic optics — Formers". This standard covers: Specifies the characteristics of formers which are used in edging machines to edge lenses designed for insertion into spectacle frames. Not applicable to separate formers required for supplementary treatment of lenses, for example facetting.
Specifies the characteristics of formers which are used in edging machines to edge lenses designed for insertion into spectacle frames. Not applicable to separate formers required for supplementary treatment of lenses, for example facetting.
ISO 11380:1994 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 11.040.70 - Ophthalmic equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 11380:1994 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to EN ISO 12870:2018, EN ISO 12870:2012, EN ISO 12870:2025, EN ISO 12870:2014. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 11380:1994 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL
ISO
STANDARD
First edition
1994-10-01
Optics and Optical instruments -
Ophthalmic optics - Formers
Op tique et instrumen ts d ’optique - Optique oph talmique - Gabarits
Refet-ence numbes
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work
of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Esch member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be
represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 11380 was prepared by Technical Committee
lSO/TC 172, Optics and optica! instruments, Subcommittee SC 8,
Oph thalmic op tics.
0 ISO 1994
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no patt of this publication may be reproduced
or utilized in any form or by any means, electronie or mechanical, including photocopying and
microfilm, without Permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD 0 ISO ISO 11380:1994(E)
Optics and Optical instruments - Ophthalmic
optics - Formers
be capable of being fitted firmly, by hand, into the
1 Scope
aperture of the specified frame size without altering
the size or shape of the rim, as designed, and without
This International Standard specifies the character-
gaps between the rim and the former being
istics of formers which are used in edging machines
discernable with normally corrected Vision.
to edge lenses designed for insertion into spectacle
frames.
lt is not applicable to separate formers required for
3 Dimensional requirements
supplementary treatment of lenses, for example
facetting.
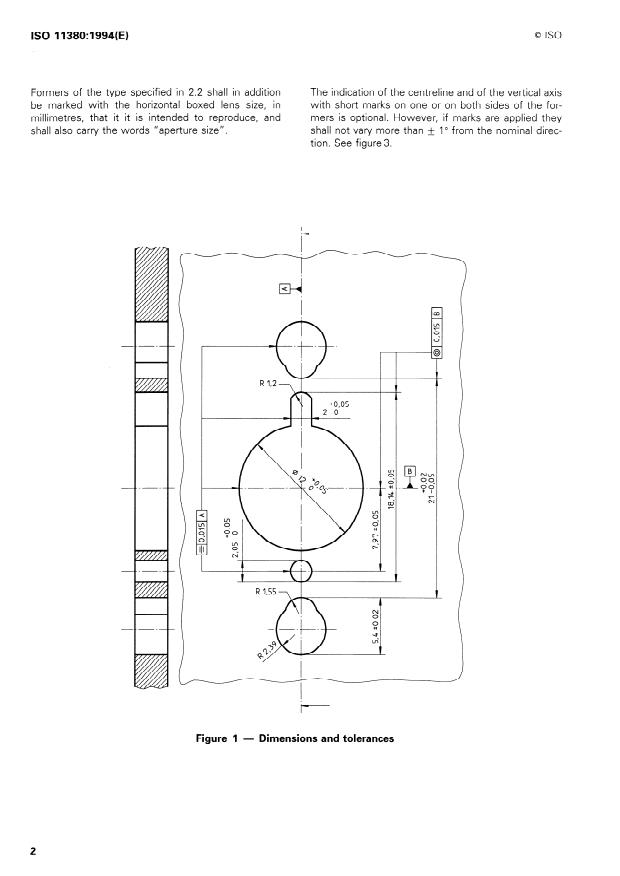
All dimensions and tolerantes given in figure 1 shall
aPPlY*
2 Types of former
The dimensional differente between two formers of
the same nominal size and shape shall not at any
Lens formers shall be classed by lens size (see 2.1)
corresponding Point, on the circumference, exceed
or aperture size (see 2.2).
0,2 mm.
Mater
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
Première édition
1994-l O-OI
Optique et instruments d’optique -
Optique ophtalmique - Gabarits
Optics and op tical instruments - Ophthalmic optics - Formers
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 11380 a été élaborée par le comité technique
lSO/TC 172, Optique et instruments d’optique, sous-comité SC 8, Opti-
que ophtalmique.
0 ISO 1994
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE 0 ISO ISO 11380:1994(F)
Optique et instruments d’optique - Optique
Gabarits
ophtalmique -
espace ne soit discernable, en vision normalement
1 Domaine d’application
corrigée, entre le cercle et le gabarit.
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les carac-
téristiques des gabarits utilisés sur les machines à
3 Prescriptions dimensionnelles
façonner les verres destinés à être adaptés dans les
montures de lunettes.
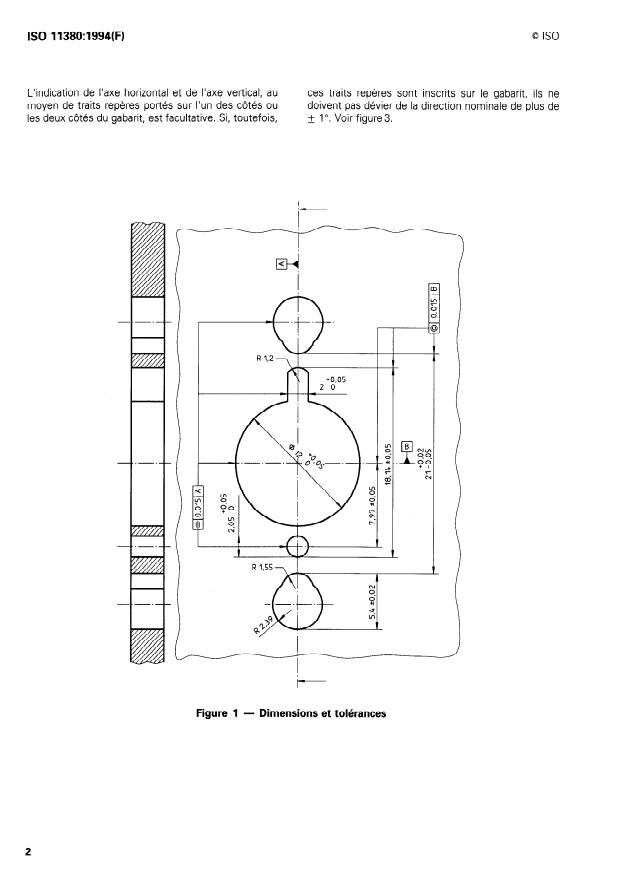
Toutes les dimensions et tolérances indiquées à la fi-
gure 1 doivent s’appliquer.
Elle ne traite pas des gabarits spéciaux destinés à des
exemple le
opérations complémentaires,
Par
II ne doit pas exister entre deux gabarits de mêmes
facettage des verres.
dimension et forme nominales de différence dimen-
sionnelle supérieure à 0,2 mm, quel que soit le point
de circonférence considéré.
2 Types de gabarits
NOTE 1 Le système de trous normalisé reprend les sys-
Les gabarits pour verres de lunettes doivent être
ternes utilisés à l’échelle internationale qui sont représentés
classés selon les dimensions du verre (voir 2.1) ou
à la figure2
selon les dimensions
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
Première édition
1994-l O-OI
Optique et instruments d’optique -
Optique ophtalmique - Gabarits
Optics and op tical instruments - Ophthalmic optics - Formers
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 11380 a été élaborée par le comité technique
lSO/TC 172, Optique et instruments d’optique, sous-comité SC 8, Opti-
que ophtalmique.
0 ISO 1994
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE 0 ISO ISO 11380:1994(F)
Optique et instruments d’optique - Optique
Gabarits
ophtalmique -
espace ne soit discernable, en vision normalement
1 Domaine d’application
corrigée, entre le cercle et le gabarit.
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les carac-
téristiques des gabarits utilisés sur les machines à
3 Prescriptions dimensionnelles
façonner les verres destinés à être adaptés dans les
montures de lunettes.
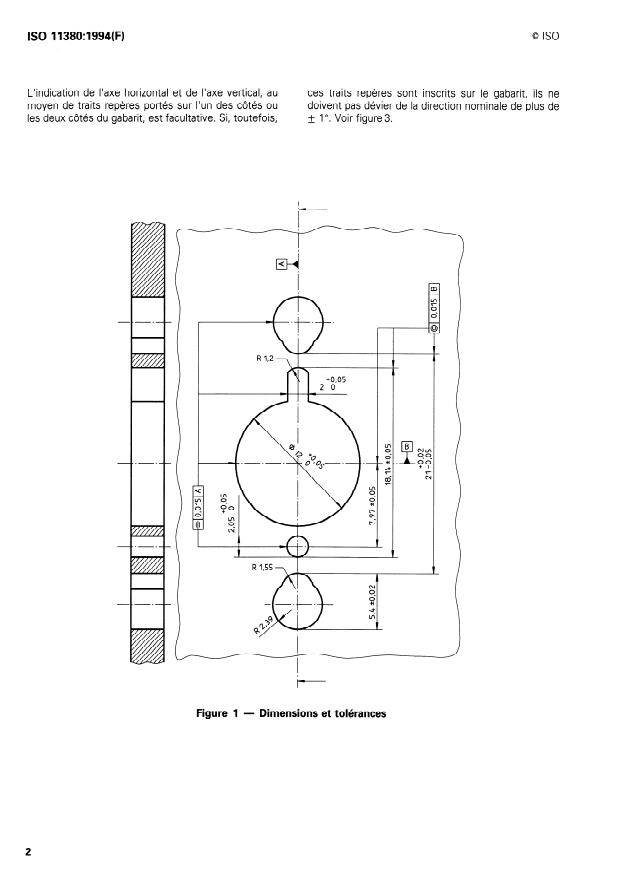
Toutes les dimensions et tolérances indiquées à la fi-
gure 1 doivent s’appliquer.
Elle ne traite pas des gabarits spéciaux destinés à des
exemple le
opérations complémentaires,
Par
II ne doit pas exister entre deux gabarits de mêmes
facettage des verres.
dimension et forme nominales de différence dimen-
sionnelle supérieure à 0,2 mm, quel que soit le point
de circonférence considéré.
2 Types de gabarits
NOTE 1 Le système de trous normalisé reprend les sys-
Les gabarits pour verres de lunettes doivent être
ternes utilisés à l’échelle internationale qui sont représentés
classés selon les dimensions du verre (voir 2.1) ou
à la figure2
selon les dimensions
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...