ASTM F2005-21
(Terminology)Standard Terminology for Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys
Standard Terminology for Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys
SCOPE
1.1 This terminology is a compilation of definitions of terms used in ASTM documents relating to nickel-titanium shape memory alloys used for medical devices. This terminology includes only those terms for which ASTM either has standards or which are used in ASTM standards for nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. It is not intended to be an all-inclusive list of terms related to shape memory alloys.
1.2 Definitions that are similar to those published by another standards body are identified with abbreviations of the name of that organization; for example, ICTAC is the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F2005 − 21
Standard Terminology for
1
Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2005; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This terminology is a compilation of definitions of terms
active austenite finish temperature, n—term used to denote
used in ASTM documents relating to nickel-titanium shape
the austenite finish temperature of an aged, shape-set or
memory alloys used for medical devices. This terminology
tempered wire, tube, or component as determined by (1)a
includesonlythosetermsforwhichASTMeitherhasstandards
bend and free recovery (BFR) method pursuant to Test
orwhichareusedinASTMstandardsfornickel-titaniumshape
Method F2082,(2) by a uniform prestrain and free recovery
memory alloys. It is not intended to be an all-inclusive list of
(UPFR) method pursuant to Test Method E3098,or(3)
terms related to shape memory alloys.
another method as agreed upon between purchaser and
supplier rather than by calorimetry (DSC) pursuant to Test
1.2 Definitionsthataresimilartothosepublishedbyanother
standards body are identified with abbreviations of the name of Method F2004.
that organization; for example, ICTAC is the International
age, v—to heat treat at a low to intermediate temperature,
Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry.
typically in the range of 300 °C to 575 °C, usually for an
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
extended period of time, to form precipitates and/or adjust
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
transformation temperatures and thermoelastic properties.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- alloy phase, n—in a shape memory alloy, the crystal structure
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical stable at a particular temperature and stress.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
anneal, v—to heat treat at a temperature above the recrystal-
lization temperature, typically in the range of 700 °C to
2. Referenced Documents
950 °C, in order to essentially remove the effects of hot
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and/or cold working and dissolve precipitates.
E7 Terminology Relating to Metallography
E473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis and Rhe-
austenite,n—the high temperature parent phase in Ni-Ti shape
ology
memory alloys with a B2 crystal structure. This phase
E3098 Test Method for Mechanical Uniaxial Pre-strain and
transforms to R-phase or martensite on cooling.
Thermal Free Recovery of Shape Memory Alloys
austenite finish temperature (A ), n—the temperature at
f
F2004 Test Method for Transformation Temperature of
which the martensite to austenite transformation is com-
Nickel-Titanium Alloys by Thermal Analysis
pleted on heating in a single-stage transformation (Fig. 1)or
F2082 Test Method for Determination of Transformation
the temperature at which the R-phase to austenite transfor-
Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys
mation is completed on heating in a two-stage transforma-
by Bend and Free Recovery
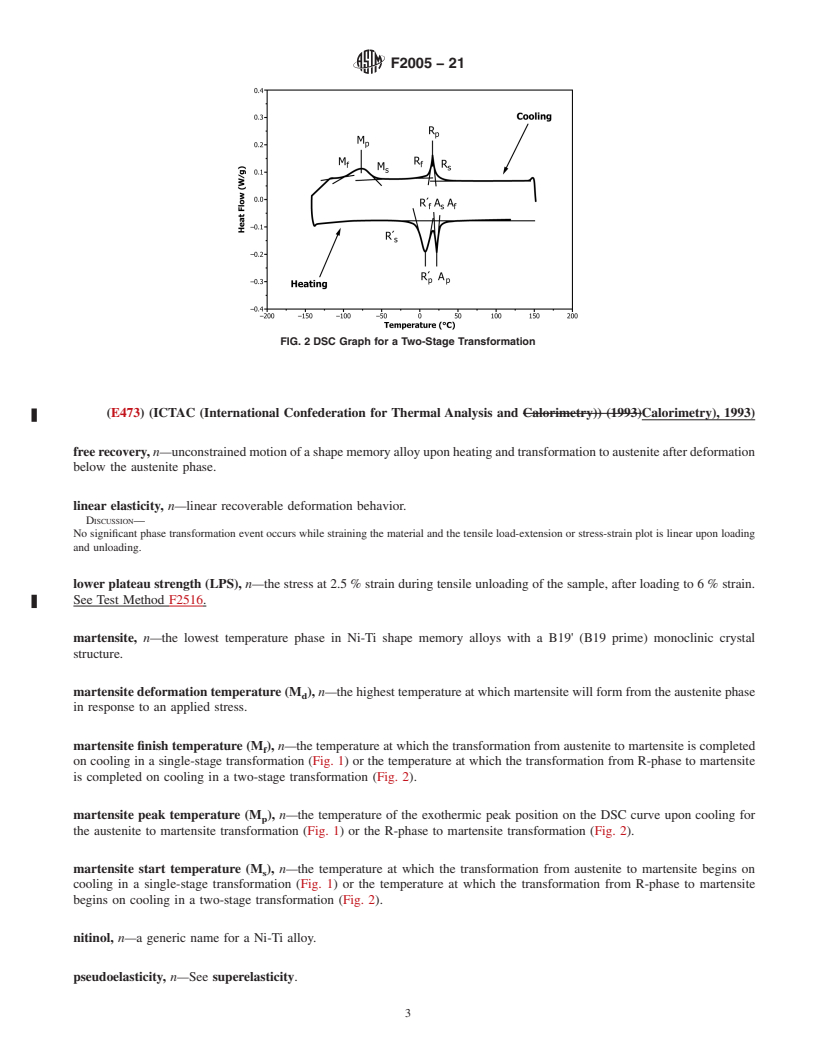
tion (Fig. 2).
F2516 Test Method for Tension Testing of Nickel-Titanium
Superelastic Materials
austenite peak temperature (A ), n—the temperature of the
p
endothermic peak position on the differential scanning
calorimeter (DSC) curve upon heating for the martensite to
1
ThisterminologyisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommittee F04onMedical
austenite transformation in a single-stage transformation
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
(Fig. 1) or the temperature of the endothermic peak position
F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved March 1, 2021. Published March 2021. Originally
on the DSC curve upon heating for the R-phase to austenite
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as F2005 – 05 (2015).
transformation in a two-stage transformation (Fig. 2).
DOI: 10.1520/F2005-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
austenite start temperature (A ),n—the temperature at which
s
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
the martensite to austenite transformation begins on heating
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. in a single-stage transformation (Fig. 1) or the temperature at
Copyright
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F2005 − 05 (Reapproved 2015) F2005 − 21
Standard Terminology for
1
Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2005; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This terminology is a compilation of definitions of terms used in ASTM documents relating to nickel-titanium shape memory
alloys used for medical devices. This terminology includes only those terms for which ASTM either has standards or which are
used in ASTM standards for nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. It is not intended to be an all-inclusive list of terms related to
shape memory alloys.
1.2 Definitions that are similar to those published by another standards body are identified with abbreviations of the name of that
organization; for example, ICTAC is the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E7 Terminology Relating to Metallography
E473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis and Rheology
E3098 Test Method for Mechanical Uniaxial Pre-strain and Thermal Free Recovery of Shape Memory Alloys
F2004 Test Method for Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Alloys by Thermal Analysis
F2082 Test Method for Determination of Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys by Bend and
Free Recovery
F2516 Test Method for Tension Testing of Nickel-Titanium Superelastic Materials
3. Terminology
active austenite finish temperature, n—term used to denote the austenite finish temperature of a finished an aged, shape-set
or tempered wire, tube, or component as determined by (1) a bend and free recovery method (BFR) method pursuant to Test
Method F2082, (2) by a uniform prestrain and free recovery (UPFR) method pursuant to Test Method E3098, or (3) another
method as agreed upon between purchaser and supplier rather than by DSC.calorimetry (DSC) pursuant to Test Method F2004.
age, v—to heat treat at a low to intermediate temperature, typically in the range of 300 °C to 575 °C, usually for an extended
period of time, to form precipitates and/or adjust transformation temperatures and thermoelastic properties.
1
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved March 1, 2015March 1, 2021. Published May 2015March 2021. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20102015 as
F2005 – 05 (2010).(2015). DOI: 10.1520/F2005-05R15.10.1520/F2005-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2005 − 21
alloy phase, n—in a shape memory alloy, the crystal structure stable at a particular temperature and stress.
anneal, v—to heat treat in order to remove the effect of cold-working.at a temperature above the recrystallization temperature,
typically in the range of 700 °C to 950 °C, in order to essentially remove the effects of hot and/or cold working and dissolve
precipitates.
austenite, n—the high temperature parent phase in Ni-Ti shape memory alloys with a B2 crystal structure. This phase transforms
to R-phase or martensite on cooling.
austenite finish temperature (A ), n—the temperature at which the martensite to austenite transformation is completed on
f
heating in a single-stage transformation (Fig. 1) or the temperature at which the R-phase to austenite transformation is completed
on heating in a two-stage transformation (Fig. 2).
austenite peak temperature (A ) , ), n—the temperature of the endothermic peak position on the differential scanning
p
ca
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.