ASTM F3059-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Gratings Used in Marine Construction and Shipbuilding
Standard Specification for Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Gratings Used in Marine Construction and Shipbuilding
SCOPE
1.1 This specification provides the testing and performance requirements for fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) gratings used in marine construction and shipbuilding as an equivalency to the specification of steel gratings rated for a maximum load of 94 lbf/ft2 (4.5 kN/m2).
1.2 The purpose of this specification is to ensure that all FRP gratings are designed and tested appropriately to ensure personnel safety. It does not address the ability of the gratings to support either moving or stationary equipment during or after a fire exposure.
1.3 This specification addresses fire conditions based on Test Methods E119 fire exposure and does not address hydrocarbon pool or jet fire exposures.
1.4 This specification is intended for use by all persons designing, manufacturing, testing, inspecting, and maintaining FRP gratings.
1.5 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This specification does not constitute regulations or ship classification rules, which shall be consulted where applicable.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F3059 −14 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Specification for
Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Gratings Used in Marine
Construction and Shipbuilding
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3059; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2047 Test Method for Static Coefficient of Friction of
Polish-Coated Flooring Surfaces as Measured by the
1.1 This specification provides the testing and performance
James Machine
requirements for fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) gratings used
D4060 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic
in marine construction and shipbuilding as an equivalency to
Coatings by the Taber Abraser
the specification of steel gratings rated for a maximum load of
2 2 D4329 Practice for Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Ap-
94 lbf/ft (4.5 kN/m ).
paratus Exposure of Plastics
1.2 The purpose of this specification is to ensure that all
E84 Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of
FRP gratings are designed and tested appropriately to ensure
Building Materials
personnel safety. It does not address the ability of the gratings
E119 Test Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction
to support either moving or stationary equipment during or
and Materials
after a fire exposure.
E695 Test Method of Measuring Relative Resistance of
1.3 This specification addresses fire conditions based on Wall, Floor, and Roof Construction to Impact Loading
2.2 Other Standards:
Test Methods E119 fire exposure and does not address hydro-
carbon pool or jet fire exposures. 46 CFR 159 Shipping—Approval of Equipment and Mate-
rials
1.4 This specification is intended for use by all persons
NVIC 02-06 Follow-Up Programs for Fire-Safety Type-
designing, manufacturing, testing, inspecting, and maintaining
Approved Products
FRP gratings.
NVIC 9-97 Change 1—Guide to Structural Fire Protection
1.5 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
3. Terminology
regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
3.1 Definitions:
information only and are not considered standard.
3.1.1 compression molding, v—manufacturing process in-
volving match die molds that compress the fiber reinforced
1.6 This specification does not constitute regulations or ship
matrix, generally under pressure and heat, to produce the
classification rules, which shall be consulted where applicable.
finished product.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 fiber-reinforced polymer, FRP, n—composite material
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
made of a resin matrix reinforced with fibers.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.2.1 Discussion—The fibers are usually made of glass or
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
carbon fiber, while the polymer is usually an epoxy, vinyl ester,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
or polyester thermosetting plastic. The term “polymer” is
2. Referenced Documents
sometimes replaced by “plastic.”
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.3 fire integrity, n—ability of a structure to retain func-
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
tionality after a fire.
1 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.03 on 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
Outfitting and Deck Machinery. www.access.gpo.gov.
Current edition approved July 1, 2014. Published August 2014. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from United States Coast Guard (USCG), U.S. Coast Guard
F3059-14. Headquarters, 2100 2nd ST SW Stop 7000, Washington, DC, 20593-7000, http://
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or www.uscg.mil/hq/cg5/cg5214/docs/NVIC02-06.pdf.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from United States Coast Guard (USCG), U.S. Coast Guard
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Headquarters, 2100 2nd ST SW Stop 7000, Washington, DC, 20593-7000, http://
the ASTM website. www.uscg.mil/hq/cg5/nvic/pdf/1997/n9-97ch1.pdf.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F3059−14
3.1.3.1 Discussion—Fire integrity levels for FRP gratings 3.2.1 shall, v—in this specification, indicates a mandatory
are described as (from lowest to highest) Level 3, Level 2, and requirement.
Level 1. Level 0 gratings are not qualified for fire integrity.
3.2.2 should, n—in this specification, indicates a recom-
3.1.4 glass-reinforced polymer, GRP, n—fiber-reinforced mended requirement.
polymer made of a resin matrix reinforced by glass fibers.
3.3 Abbreviations:
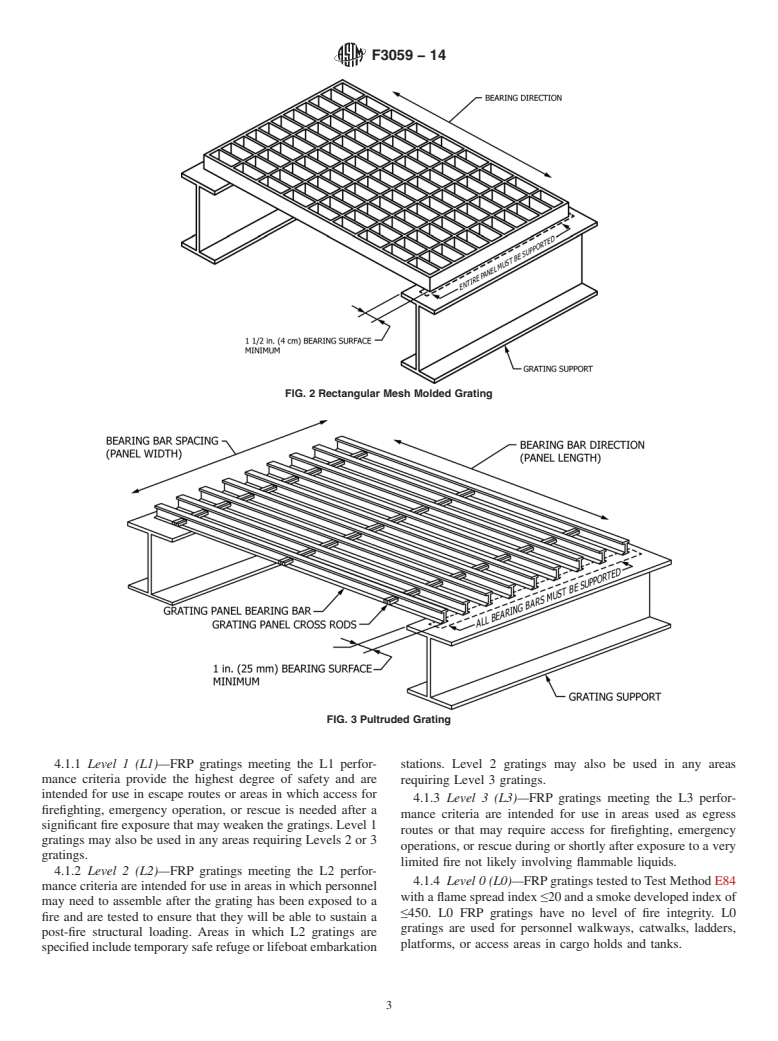
3.1.5 molded grating, n—FRPgrating produced by the open
3.3.1 AFFF—Aqueous film-forming foam
mold process in which dry glass fiber and thermoset resin is
3.3.2 AHJ—Authority having jurisdiction
placed in the mold in both directions.
3.3.3 ASTM—American Society for Testing and Materials
3.1.5.1 Discussion—After filling the mold with the desig-
nated amount of material, the resin is allowed to cure in the
3.3.4 L1—Level 1 fire integrity grating
open mold. Square mesh molded grating has nearly equal
3.3.5 L2—Level 2 fire integrity grating
strength and stiffness in longitudinal and transverse directions.
3.3.6 L3—Level 3 fire integrity grating
Molded grating is usually manufactured in square mesh or
rectangular mesh configurations. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. 3.3.7 L0—Flame spread only
3.1.6 open molding, v—manual process involving the com- 3.3.8 MODU—Mobile offshore drilling unit
bination of liquid resin and fiber reinforcements in an open
3.3.9 NVIC—Navigation and Vessel Inspection Circular
mold to produce a finished part resembling the inverse of the
3.3.10 USCG—U.S. Coast Guard
mold.
3.3.11 UV—Ultraviolet
3.1.6.1 Discussion—Liquid resin and continuous fibers are
systematically laid in a mold—layer upon layer manually to a
desired thickness and panel dimension. 4. Significance and Use
3.1.7 pultruded grating, n—grating produced from an as-
4.1 This specification is for FRPgratings used in machinery
sembly of pultruded structural shapes assembled into a grid
spaces, cargo areas, and on-deck areas but not within
pattern.
accommodation, service, control spaces, and areas where
3.1.7.1 Discussion—Pultruded FRP grating products are
smoke and toxicity is a concern. The test requirements and
assembledfrombearingbarsandcrossrodsmanufacturedfrom
criteria for FRP gratings have been developed based on the
thepultrusionprocessasshowninFig.3.Pultrudedgratinghas
expected environmental conditions, intended use, and fire
more strength and stiffness in the direction of the bearing bars.
hazard the gratings could be exposed to in conjunction with
requirements for means of escape and fire brigade access to the
3.1.8 pultrusion, n—manufacturingprocesstoformcontinu-
area where the FRPgratings will be located. The structural fire
ous lengths of reinforced polymer structural shapes.
integrity test requirements have been developed based on
3.1.9 qualified span, n—FRP grating span used during
comparativetestingwithsteelgratingsratedformaximumload
preload and post load fire tests [minimum 44 in. (112 cm)].
2 2
of 94 lbf/ft (4.5 kN/m ). The structural fire integrity require-
3.1.10 surface flame spread, n—propagation of a flame
ments for the specific locations are summarized inTable 1.The
away from the source of ignition across the surface of the
fire test requirements include surface flammability testing and
specimen.
structuralfireintegritytestingwiththreelevelsofstructuralfire
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: integrity that may be achieved as follows:
FIG. 1Square Mesh Molded Grating
F3059−14
FIG. 2Rectangular Mesh Molded Grating
FIG. 3Pultruded Grating
4.1.1 Level 1 (L1)—FRP gratings meeting the L1 perfor- stations. Level 2 gratings may also be used in any areas
mance criteria provide the highest degree of safety and are
requiring Level 3 gratings.
intended for use in escape routes or areas in which access for
4.1.3 Level 3 (L3)—FRP gratings meeting the L3 perfor-
firefighting, emergency operation, or rescue is needed after a
mance criteria are intended for use in areas used as egress
significant fire exposure that may weaken the gratings. Level 1
routes or that may require access for firefighting, emergency
gratings may also be used in any areas requiring Levels 2 or 3
operations, or rescue during or shortly after exposure to a very
gratings.
limited fire not likely involving flammable liquids.
4.1.2 Level 2 (L2)—FRP gratings meeting the L2 perfor-
4.1.4 Level 0 (L0)—FRPgratings tested to Test Method E84
mance criteria are intended for use in areas in which personnel
with a flame spread index≤20 and a smoke developed index of
may need to assemble after the grating has been exposed to a
≤450. L0 FRP gratings have no level of fire integrity. L0
fire and are tested to ensure that they will be able to sustain a
gratings are used for personnel walkways, catwalks, ladders,
post-fire structural loading. Areas in which L2 gratings are
platforms, or access areas in cargo holds and tanks.
specifiedincludetemporarysaferefugeorlifeboatembarkation
F3059−14
TABLE 1 Structural Fire Integrity Requirements
4.2.1 Full information as to the performance of the FRP
Structural grating with materials, construction, dimensions, coatings, and
Location Service Fire
so forth, other than tested.
Integrity
4.3 Inthesetestmethods,thetestspecimensaresubjectedto
Machinery Walkways or areas which may be used
A
spaces for escape, or access for firefighting, L1
one or more specific tests under laboratory conditions. When
emergency operation, or rescue
different test conditions are substituted or the end-use condi-
tions are changed, it is not always possible by, or from, these
Personnel walkways, catwalks, ladders,
platforms, or access areas other than L3
testmethodstopredictchangestothecharacteristicsmeasured.
those described above
Therefore,theresultsoftheselaboratorytestsarevalidonlyfor
Cargo pump All personnel walkways, catwalks, the test conditions described in these test methods.
L1
rooms ladders, platforms, or access areas
4.4 The fire-resistance test methods specified herein require
Cargo holds Walkways or areas which may be used
testspecimenstobeexposedtoastandardfirethatiscontrolled
for escape, or access for firefighting, L1
to achieve specified temperatures throughout a specified time
emergency operation, or rescue
period or heat exposure. These are followed by the application
Personnel walkways, catwalks, ladders,
of specified loads. These test methods provide a relative
platforms, or access areas other than L0
measure of performance under the specified test conditions.
those described above
The fire exposure is not representative of all fire conditions.
Cargo tanks All personnel walkways, catwalks,
Variation from the test conditions or test specimen
L0
ladders, platforms, or access areas
construction, such as size, materials, method of assembly, and
so forth, may affect the fire-test response. For these reasons,
Fuel oil tanks All personnel walkways, catwalks,
L0
ladders, platforms, or access areas
evaluationofsuchvariationsmayberequiredforapplicationto
construction in the field. However, variations in the required
Ballast water All personnel walkways, catwalks,
L0
test exposure conditions are considered outside the scope of
tanks ladders, platforms, or access areas
this specification.
Cofferdams, void All personnel walkways, catwalks,
spaces, double ladders, platforms, or access areas
5. Sampling
bottoms, pipe L0
tunnels, and so
5.1 Sampling methods shall be as required to provide
forth
reasonable assurance that the test samples are truly represen-
Accommodation, All personnel walkways, catwalks,
tative of the standard manufactured product. When required,
service, and ladders, platforms, or access areas Not permitted
test specimens of products shall be sampled at the manufac-
control spaces
turing facility by personnel representing an accredited testing
Lifeboat All personnel walkways, catwalks,
laboratory, accredited inspection agency, or accredited certifi-
embarkation or ladders, platforms, or access areas
cation agency. Sampling at a warehouse or distribution center
temporary safe
L2
in lieu of sampling at the manufacturing facility is permitted
refuge stations
in open deck
provided the testing laboratory, inspection agency, or certifi-
areas
cation agency samples the materials and correlates the sampled
materials with the finished product specification. The test
Open decks or Operational areas and access routes for
semi-enclosed deck foam firefighting systems on tank L2
specimens shall be representative of the FRP gratings to be
areas vessels
qualifiedincludingmaterials,construction,profile,dimensions,
Walkways or areas that may be used for coatings, and so forth.
escape, or access for firefighting systems
and AFFF hose reels, emergency
6. Number of Tests and Retests
L2
operation, or rescue on MODUs and
production platforms including safe
6.1 General—The number of tests are as described in the
access to tanker bows
test requirements portion of this specification. If significant
Walkways or areas that may be used for changes occur to the manufacturing process or material speci-
escape or access for firefighting systems,
fications that may affect the physical properties or system
L3
emergency operation, or rescue other
qualification requirements, qualification tests related to the
than those described above
significant change shall be required.
Personnel walkways, catwalks, ladders,
platforms, or access areas other than L3
TEST REQUIREMENTS
those described above
A
If the machinery space does not contain any internal combustion machinery,
7. Summary
other oil burning, oil heating, or oil pumping units, fuel oil filling stations, or other
2 2
potential hydrocarbon fire sources and has not more than 5.5 lb/ft (2.5 kg/m )of 7.1 The following test requirements shall be met: deflection
combustible storage, gratings of L3 structural fire integrity may be used in lieu of
limits, assembled grating ultimate failure, wheel loading,
L1.
assembled panel impact resistance, skid resistance, durability,
ultraviolet (UV) resistance, salt spray, surface flammability,
4.2
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.