ASTM D524-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products
Standard Test Method for Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The carbon residue value of burner fuel serves as a rough approximation of the tendency of the fuel to form deposits in vaporizing pot-type and sleeve-type burners. Similarly, provided alkyl nitrates are absent (or if present, provided the test is performed on the base fuel without additive) the carbon residue of diesel fuel correlates approximately with combustion chamber deposits.
The carbon residue value of motor oil, while at one time regarded as indicative of the amount of carbonaceous deposits a motor oil would form in the combustion chamber of an engine, is now considered to be of doubtful significance due to the presence of additives in many oils. For example, an ash-forming detergent additive can increase the carbon residue value of an oil yet will generally reduce its tendency to form deposits.
The carbon residue value of gas oil is useful as a guide in the manufacture of gas from gas oil, while carbon residue values of crude oil residuum, cylinder and bright stocks, are useful in the manufacture of lubricants.
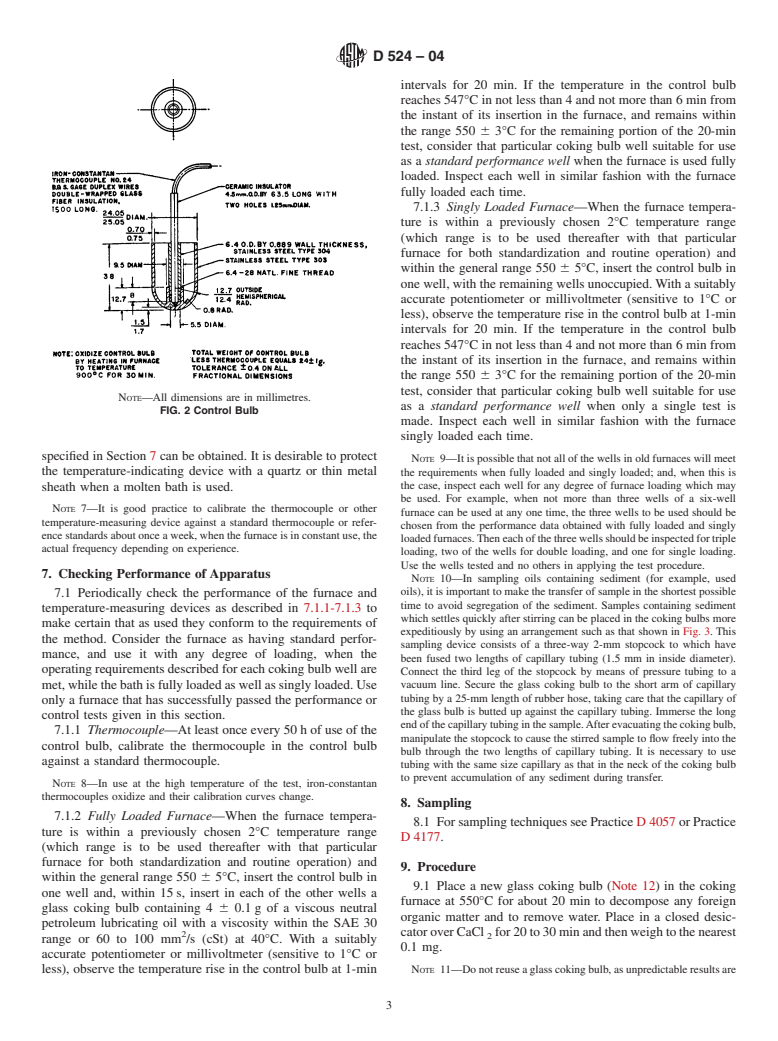
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the amount of carbon residue (Note 1) left after evaporation and pyrolysis of an oil, and it is intended to provide some indication of relative coke-forming propensity. This test method is generally applicable to relatively nonvolatile petroleum products which partially decompose on distillation at atmospheric pressure. This test method also covers the determination of carbon residue on 10% (V/V) distillation residues (see Section 10). Petroleum products containing ash-forming constituents as determined by Test Method D 482, will have an erroneously high carbon residue, depending upon the amount of ash formed (Note 2 Note 3).
Note 1—The term carbon residue is used throughout this test method to designate the carbonaceous residue formed during evaporation and pyrolysis of a petroleum product. The residue is not composed entirely of carbon, but is a coke which can be further changed by pyrolysis. The term carbon residue is continued in this test method only in deference to its wide common usage.
Note2—Values obtained by this test method are not numerically the same as those obtained by Test Method D 189, or Test Method D 4530. Approximate correlations have been derived (see Fig. X2.1) but need not apply to all materials which can be tested because the carbon residue test is applicable to a wide variety of petroleum products. The Ramsbottom Carbon Residue test method is limited to those samples that are mobile below 90°C.
Note3—In diesel fuel, the presence of alkyl nitrates such as amyl nitrate, hexyl nitrate, or octyl nitrate, causes a higher carbon residue value than observed in untreated fuel, which can lead to erroneous conclusions as to the coke-forming propensity of the fuel. The presence of alkyl nitrate in the fuel can be detected by Test Method D 4046.
Note 4—The test procedure in Section 10 is being modified to allow the use of a 100-mL volume automated distillation apparatus. No precision data is available for the procedure at this time, but a round robin is being planned to develop precision data. The 250-mL volume bulb distillation method described in Section 10 for determining carbon residue on a 10 % distillation residue is considered the referee test.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D524–04
Designation: 14/94
Standard Test Method for
1
Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 524; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
distillationmethoddescribedinSection10fordeterminingcarbonresidue
1. Scope*
on a 10 % distillation residue is considered the referee test.
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationoftheamount
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
of carbon residue (Note 1) left after evaporation and pyrolysis
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of an oil, and it is intended to provide some indication of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
relative coke-forming propensity.This test method is generally
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
applicable to relatively nonvolatile petroleum products which
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
partially decompose on distillation at atmospheric pressure.
This test method also covers the determination of carbon
2. Referenced Documents
residue on 10% (V/V) distillation residues (see Section 10).
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Petroleum products containing ash-forming constituents as
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at
determined by Test Method D 482, will have an erroneously
Atmospheric Pressure
highcarbonresidue,dependingupontheamountofashformed
D 189 Test Method for Conradson Carbon Residue of
(Notes 2 and 3).
Petroleum Products
NOTE 1—The term carbon residue is used throughout this test method
D 482 Test Method for Ash from Petroleum Products
to designate the carbonaceous residue formed during evaporation and
D 4046 Test Method for Alkyl Nitrate in Diesel Fuels by
pyrolysis of a petroleum product. The residue is not composed entirely of
Spectrophotometry
carbon, but is a coke which can be further changed by pyrolysis.The term
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
carbon residue is continued in this test method only in deference to its
wide common usage. Petroleum Products
NOTE 2—Values obtained by this test method are not numerically the
D 4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
same as those obtained by Test Method D 189, or Test Method D 4530.
Products, and Lubricants
Approximate correlations have been derived (see Fig. X2.1) but need not
D 4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
apply to all materials which can be tested because the carbon residue test
Petroleum Products
is applicable to a wide variety of petroleum products. The Ramsbottom
D 4530 Test Method for Determination of Carbon Residue
Carbon Residue test method is limited to those samples that are mobile
(Micro Method)
below 90°C.
NOTE 3—In diesel fuel, the presence of alkyl nitrates such as amyl E1 Specification forASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
nitrate, hexyl nitrate, or octyl nitrate, causes a higher carbon residue value
E 133 Specification for Distillation Equipment
than observed in untreated fuel, which can lead to erroneous conclusions
2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
astothecoke-formingpropensityofthefuel.Thepresenceofalkylnitrate
3
Appendix AP-A Specifications—IP Thermometers
in the fuel can be detected by Test Method D 4046.
NOTE 4—The test procedure in Section 10 is being modified to allow
3. Terminology
the use of a 100–mL volume automated distillation apparatus. No
3.1 Definitions:
precision data is available for the procedure at this time, but a round robin
is being planned to develop precision data. The 250–mL volume bulb 3.1.1 carbon residue, n—the residue formed by evaporation
and thermal degradation of a carbon containing material.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
D02.06 on Analysis of Lubricants. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2004. Published November 2004. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1939. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 524–03. IP Standard Methods for Analysis and Testing of Petroleum and Related
In the IP, this test method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization Products, 1998. Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., Lond
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.