ASTM E2618-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Particulate Emissions and Heating Efficiency of Outdoor Solid Fuel-Fired Hydronic Heating Appliances
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Particulate Emissions and Heating Efficiency of Outdoor Solid Fuel-Fired Hydronic Heating Appliances
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The measurement of particulate matter emission rates is an important test method widely used in the practice of air pollution control.
These measurements, when approved by federal or state agencies, are often required for the purpose of determining compliance with regulations and statutes.
The measurements made before and after design modifications are necessary to demonstrate the effectiveness of design changes in reducing emissions and make this standard an important tool in manufacturer’s research and development programs.
Measurement of heating efficiency provides a uniform basis for comparison of product performance that is useful to the consumer. It is also required to relate emissions produced to the useful heat production.
This is a laboratory method and is not intended to be fully representative of all actual field use. It is recognized that users of hand-fired wood burning equipment have a great deal of influence over the performance of any wood-burning appliance. Some compromises in realism have been made in the interest of providing a reliable and repeatable test method.
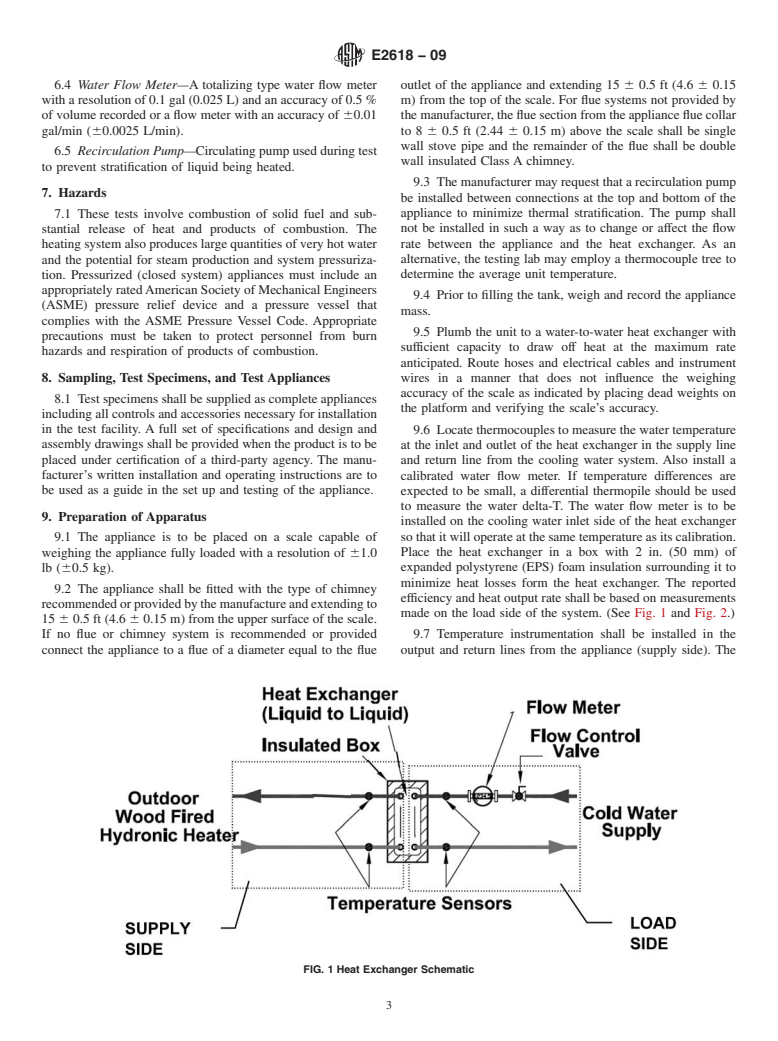
SCOPE
1.1 This test method applies to wood-fired or automatically fed biomass burning hydronic heating appliances, which the manufacturer specifies for outdoor installation or in structures not normally occupied by humans. These appliances transfer heat to the indoor environment through circulation of a liquid heat exchange media such as water or a water-antifreeze mixture.
1.2 The test method simulates hand loading of seasoned cordwood or fueling with a specified biomass fuel and measures particulate emissions and delivered heating efficiency at specified heat output rates based on the appliance’s rated heating capacity.
1.3 Particulate emissions are measured by the dilution tunnel method as specified in Test Method E 2515. Delivered efficiency is measured by determining the heat output through measurement of the flow rate and temperature change of water circulated through a heat exchanger external to the appliance and determining the input from the mass of dry fuel and its higher heating value. Delivered efficiency does not attempt to account for pipeline loss.
1.4 Products covered by this test method include both pressurized and non-pressurized heating appliances intended to be fired with wood or automatically fed biomass fuels. These products are hydronic heating appliances which the manufacturer specifies for outdoor installation or in structures not normally occupied by humans. They are often connected to an indoor heat exchanger by insulated pipes buried in the ground and normally include a pump to circulate heated liquid. They are used to heat structures such as homes, barns, and greenhouses and can heat domestic hot water, spas, or swimming pools.
1.5 Distinguishing features of products covered by this standard include:
1.5.1 Manufacturers specify outdoor installation or installation in structures not normally occupied by humans.
1.5.2 A firebox with an access door for hand loading of fuel or a hopper and automated feed system for delivery of particulate fuel such as wood pellets or solid biomass fuel to a burn pot or combustion chamber.
1.5.3 Typically a thermostatic control device that controls combustion air supply or fuel delivery, or both, to maintain the liquid in the appliance within a predetermined temperature range provided sufficient fuel is available in the firebox or hopper.
1.5.4 A chimney or vent that exhausts combustion products from the appliance.
1.6 The values stated are to be regarded as the standard whether in inch-pound or SI units. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2618 − 09
StandardTest Method for
Measurement of Particulate Emissions and Heating
Efficiency of Outdoor Solid Fuel-Fired Hydronic Heating
1
Appliances
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2618; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5.1 Manufacturers specify outdoor installation or installa-
tion in structures not normally occupied by humans.
1.1 This test method applies to wood-fired or automatically
1.5.2 Afirebox with an access door for hand loading of fuel
fed biomass burning hydronic heating appliances, which the
or a hopper and automated feed system for delivery of
manufacturer specifies for outdoor installation or in structures
particulate fuel such as wood pellets or solid biomass fuel to a
not normally occupied by humans. These appliances transfer
burn pot or combustion chamber.
heat to the indoor environment through circulation of a liquid
heat exchange media such as water or a water-antifreeze 1.5.3 Typically a thermostatic control device that controls
mixture.
combustion air supply or fuel delivery, or both, to maintain the
liquid in the appliance within a predetermined temperature
1.2 The test method simulates hand loading of seasoned
range provided sufficient fuel is available in the firebox or
cordwood or fueling with a specified biomass fuel and mea-
hopper.
sures particulate emissions and delivered heating efficiency at
1.5.4 Achimney or vent that exhausts combustion products
specified heat output rates based on the appliance’s rated
heating capacity. from the appliance.
1.3 Particulate emissions are measured by the dilution
1.6 The values stated are to be regarded as the standard
tunnel method as specified in Test Method E2515. Delivered
whether in inch-pound or SI units. The values given in
efficiency is measured by determining the heat output through
parentheses are for information only.
measurement of the flow rate and temperature change of water
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
circulated through a heat exchanger external to the appliance
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and determining the input from the mass of dry fuel and its
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
higher heating value. Delivered efficiency does not attempt to
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
account for pipeline loss.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 Products covered by this test method include both
pressurized and non-pressurized heating appliances intended to
2. Referenced Documents
be fired with wood or automatically fed biomass fuels. These
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
products are hydronic heating appliances which the manufac-
D4442 Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measure-
turer specifies for outdoor installation or in structures not
normally occupied by humans. They are often connected to an ment of Wood and Wood-Base Materials
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
indoor heat exchanger by insulated pipes buried in the ground
and normally include a pump to circulate heated liquid. They E711 Test Method for Gross Calorific Value of Refuse-
Derived Fuel by the Bomb Calorimeter (Withdrawn
are used to heat structures such as homes, barns, and green-
3
2011)
houses and can heat domestic hot water, spas, or swimming
E2515 Test Method for Determination of Particulate Matter
pools.
Emissions Collected by a Dilution Tunnel
1.5 Distinguishing features of products covered by this
standard include:
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.54 contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
on Solid Fuel Burning Appliances. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2008. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E2618 – 08. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E2618-09. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2618 − 09
3. Terminology appliance weight and temperature at the beginning and end of
a test cycle are used to correct for heat stored in the appliance.
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Te
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E2618–08 Designation:E2618–09
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Particulate Emissions and Heating
Efficiency of Outdoor Solid Fuel-Fired Hydronic Heating
1
Appliances
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2618; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method applies to wood-fired or automatically fed biomass burning hydronic heating appliances, which the
manufacturer specifies for outdoor installation or in structures not normally occupied by humans. These appliances transfer heat
to the indoor environment through circulation of a liquid heat exchange media such as water or a water-antifreeze mixture.
1.2 The test method simulates hand loading of seasoned cordwood or fueling with a specified biomass fuel and measures
particulate emissions and delivered heating efficiency at specified heat output rates based on the appliance’s rated heating capacity.
1.3 Particulate emissions are measured by the dilution tunnel method as specified in Test Method E 2515. Delivered Efficiency
is measured by determining the heat output through measurement of the flow rate and temperature change of water circulated
throughaheatexchangerexternaltotheapplianceanddeterminingtheinputfromthemassofdryfuelanditshigherheatingvalue.
Delivered efficiency does not attempt to account for pipeline loss.
1.4 Products covered by this test method include both pressurized and non-pressurized heating appliances intended to be fired
with wood or automatically fed biomass fuels. These products are hydronic heating appliances which the manufacturer specifies
for outdoor installation or in structures not normally occupied by humans. They are often connected to an indoor heat exchanger
by insulated pipes buried in the ground and normally include a pump to circulate heated liquid. They are used to heat structures
such as homes, barns, and greenhouses and can heat domestic hot water, spas, or swimming pools.
1.5 Distinguishing features of products covered by this standard include:
1.5.1 Manufacturers specify outdoor installation or installation in structures not normally occupied by humans.
1.5.2 Afirebox with an access door for hand loading of fuel or a hopper and automated feed system for delivery of particulate
fuel such as wood pellets or solid biomass fuel to a burn pot or combustion chamber.
1.5.3 Typically a thermostatic control device that controls combustion air supply or fuel delivery, or both, to maintain the liquid
in the appliance within a predetermined temperature range provided sufficient fuel is available in the firebox or hopper.
1.5.4 A chimney or vent that exhausts combustion products from the appliance.
1.6 The values stated are to be regarded as the standard whether in inch-pound or SI units. The values given in parentheses are
for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 4442 Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measurement of Wood and Wood-Base Materials
E 631 Terminology of Building Constructions
E711 Test Method for Gross Calorific Value of Refuse-Derived Fuel by the Bomb Calorimeter
E 2515 Test Method for Determination of Particulate Matter Emissions Collected by a Dilution Tunnel
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology E 631, unless otherwise indicated.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E06 on Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.54 on Solid Fuel
Burning Appliances.
Current edition approved July 1, 2008. Published August 2008.
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 2009. Published March 2009. Originally approved in 2008. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E 2618 – 08.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.