ASTM D2272-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Steam Turbine Oils by Rotating Pressure Vessel
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Steam Turbine Oils by Rotating Pressure Vessel
SCOPE
1.1 This test method utilizes an oxygen-pressured vessel to evaluate the oxidation stability of new and in service turbine oils having the same composition (base stock and additives) in the presence of water and a copper catalyst coil at 150°C.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable S1 units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning, see 6.2, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 6.10, 6.11.
General Information
Relations
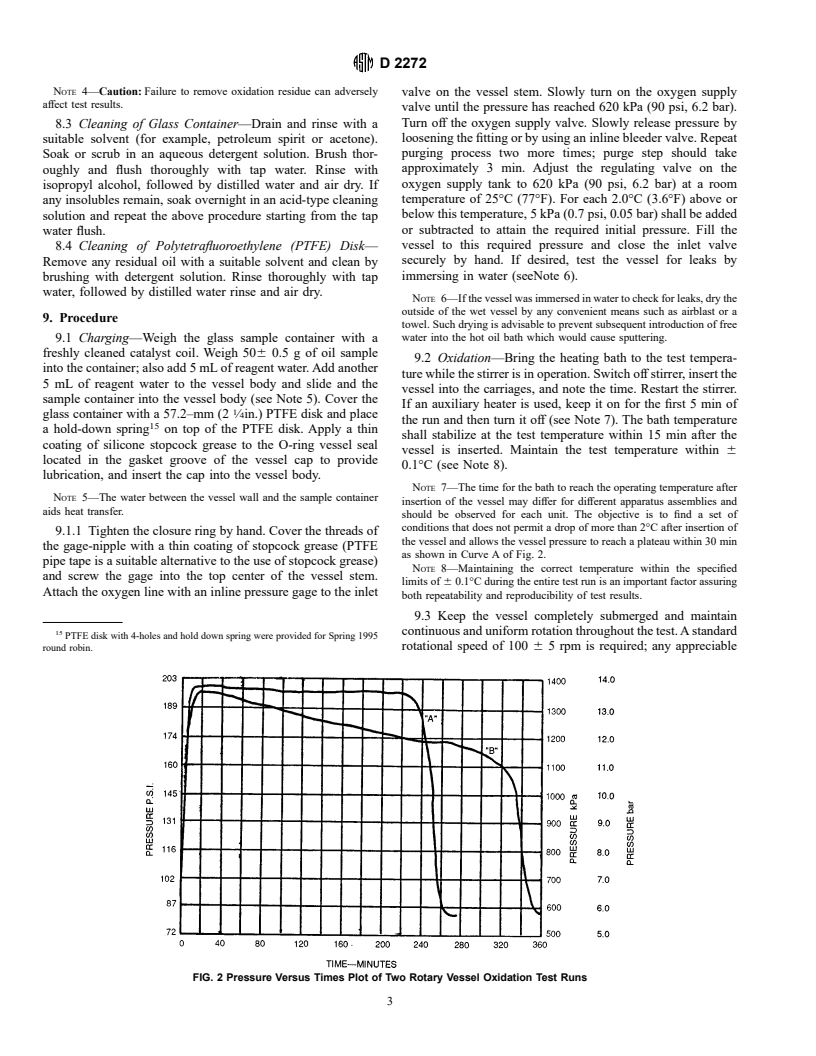
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: D 2272 – 98
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Oxidation Stability of Steam Turbine Oils by Rotating
1
Pressure Vessel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2272; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake
9
2
(TFOUT)
1.1 This test method utilizes an oxygen-pressured vessel to
10
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
evaluate the oxidation stability of new and in-service turbine
11
2.2 British Standard:
oils having the same composition (base stock and additives) in
B2 2000 Part 0: Section 0.1,
the presence of water and a copper catalyst coil at 150°C.
IP 37C Thermometer
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be
12
2.3 Institute of Petroleum Standard:
regarded as the standard.
IP 229
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of the this standard to establish
3.1 The test oil, water, and copper catalyst coil, contained in
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
a covered glass container, are placed in a vessel equipped with
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
a pressure gage. The vessel is charged with oxygen to a gage
warning, see 6.2, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 6.10, 6.11.
pressure of 620 kPa (90 psi, 6.2 bar) (see Note 1), placed in a
2. Referenced Documents constant-temperature oil bath set at 150°C, and rotated axially
at 100 rpm at an angel of 30° from the horizontal. The number
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3 of minutes required to reach a specific drop in gage pressure is
B 1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
the oxidation stability of the test sample.
D 235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits)
4
(Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
NOTE 1—100 kPa 5 1.00 bar 5 14.5 psi.
4
D 329 Specification for Acetone
4
4. Significance and Use
D 770 Specification for Isopropyl Alcohol
D 943 Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of Inhib-
4.1 The estimate of oxidation stability is useful in control-
5
ited Mineral Oils
ling the continuity of this property for batch acceptance of
6
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
production lots having the same operation. It is not intended
D 2112 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Inhibited
that this test method be a substitute for Test Method D 943 or
7
Mineral Insulating Oil by Rotating Bomb
be used to compare the service lives of new oils of different
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
compositions.
8
Petroleum Products
4.2 This test method is also used to assess the remaining
D 4742 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline
oxidation test life of in-service oils.
NOTE 2—A modification of the rotating vessel method has been
published as Test Method D 2112, which uses a similar procedure and
apparatus but a lower (140°C) bath temperature. Test Method D 2112
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
requires duplicate testing and Test Method D 2272 conducted duplicate
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
testing in the past.
D02.09 on Oxidation.
Current edition approved June 10, 1998. Published November 1998. Originally
5. Apparatus
published as D 2272-64 T. Last previous edition D 2272-91.
2
von Fuchs, G. H., Claridge, E. L., and Zuidema, H. H., “The Rotary Bomb
5.1 Oxidation Vessel, Glass Sample Container with Four-
Oxidation Test for Inhibited Turbine Oils,” Materials Research and Standards,
Hole PTFE Disk, Hold-Down Spring, Catalyst-Coil, Pressure
MTRSA (formerly ASTM Bullein), No. 186, December 1952, pp. 43-46; von Fuchs,
G. H., “Rotary Bomb Oxidation Test”, Lubrication Engineering, Vol 16, No. 1,
January 1960, pp. 22-31.
3
9
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.03. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.03.
4 10
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
5 11
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01. Available from British Standards Institute, 2 Park St., London, England
6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. W1A2B5.
7 12
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.03. Available from Institute of Petroleum, 61 New Cavendish St., London, W. I.,
8
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02. England.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 2272
Gage, Thermometer, and Test Bath, as described in Annex A1. 6.10 Petroleum Spirit , (Warning—Combustible. Health
The assembled apparatus is shown schematically in Fig. 1 and hazard.) Conforming to Specifica
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.