ISO 1124:1988
(Main)Rubber compounding ingredients — Carbon black shipment sampling procedures
Rubber compounding ingredients — Carbon black shipment sampling procedures
Specifies procedures for the sampling of carbon black for use in the rubber industry, delivered in bulk, semi-bulk or packages.
Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc — Procédures d'échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir de carbone
La présente Norme internationale prescrit des procédures pour l'échantillonnage du noir de carbone utilisé dans l'industrie du caoutchouc, livré en vrac, semi-vrac ou en emballages individuels.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 09-Nov-1988
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 45/SC 3/WG 3 - Carbon black, silica and rubber chemicals
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 08-Sep-2023
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 1124:1988 (Third edition) specifies standardized procedures for sampling carbon black used as a rubber compounding ingredient. Intended for the rubber industry, the standard covers sampling from bulk, semi-bulk and package deliveries and defines apparatus, minimal sample sizes, handling and reporting to ensure representative, traceable samples for quality assessment.
Key Topics
Scope and definitions
- Bulk: containers holding not less than 2 000 kg.
- Semi-bulk: containers holding more than 50 kg and less than 2 000 kg.
- Packages: containers of 50 kg or less.
Required apparatus
- Sample Splitter: single-stage riffle-type splitter for reducing portions without bias.
- Sampling device for packages: open tube with a seal lip, diameter not less than 25 mm, to reach the package geometric centre.
- Scoop: designed to minimize pellet breakdown when removing sample material.
- Airtight containers: minimum capacity 3 dm3 for storage of retained samples.
Sampling quantities and procedure highlights
- For bulk compartments: discard at least 5 dm3 from each sampling port, then take at least 1 kg or 3 dm3 from each port and place in an airtight container.
- If no sampling ports are fitted, take 1 kg or 3 dm3 from loading ports approximately 30 mm below the surface to avoid contamination.
- For packages: insert the sampling tube to the geometric centre, discard about 0.5 dm3, then take at least 1 kg or 3 dm3; alternatively use the scoop after removing the top 30 mm of surface material.
- When preparing laboratory test samples, pass individual samples through the riffle-type splitter at least twice; composite samples should be passed at least three times to reduce stratification.
Handling and storage
- Handle sample portions carefully to prevent pellet breakdown.
- Store samples in airtight containers until testing; retain individual or composite portions as required.
Applications
- Establishing representative test samples for incoming carbon black shipments.
- Supporting quality control and material acceptance procedures in rubber compounding and manufacturing.
- Providing traceable, auditable sampling records for supplier verification and dispute resolution.
Related Standards
This document was prepared by ISO/TC 45 (Rubber and rubber products) and is the third edition, replacing the second edition (ISO 1124:1983).
When implementing ISO 1124:1988, consider cross-referencing other ISO standards on material sampling and laboratory testing procedures relevant to carbon black or rubber ingredient analysis.
Practical value: ISO 1124:1988 provides clear, repeatable sampling steps and reporting requirements so laboratories and quality teams can obtain representative samples, reduce variability from poor sampling, and maintain traceable records for shipment acceptance.
ISO 1124:1988 - Rubber compounding ingredients -- Carbon black shipment sampling procedures
ISO 1124:1988 - Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc -- Procédures d'échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir de carbone
ISO 1124:1988 - Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc -- Procédures d'échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir de carbone
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Smithers Quality Assessments
US management systems and product certification.

DIN CERTCO
DIN Group product certification.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 1124:1988 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Rubber compounding ingredients — Carbon black shipment sampling procedures". This standard covers: Specifies procedures for the sampling of carbon black for use in the rubber industry, delivered in bulk, semi-bulk or packages.
Specifies procedures for the sampling of carbon black for use in the rubber industry, delivered in bulk, semi-bulk or packages.
ISO 1124:1988 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 83.040.20 - Rubber compounding ingredients. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 1124:1988 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 1124:1983, ISO 1310:1974. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 1124:1988 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
ISO
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Third edition
1988-11-15
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEmYHAPOflHAfl OPI-AHM3AuMfl l-l0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM
Rubber compounding ingredients - Carbon black
shipment sampling procedures
lngrt!dients de melange du caoutchouc - Proc6dures d ’khan tiflonnage SW des livraisons de
noir de carbone
Reference number
ISO 1124: 1988 (E)
ISOll24:1988 (El
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national Standards bodies (ISO member bedies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Esch member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all
matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the ISO Council. They are approved in accordance with ISO procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard ISO 1124 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 45,
Rubber and rubber products.
This third edition cancels and replaces the second edition (ISO 1124 : 19831, of which
it constitutes a technical revision.
0 International Organkation for Standardkation, 1988 l
Printed in Switzerland
ISO 1124: 1988 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Rubber compounding ingredients - Carbon black
shipment sampling procedures
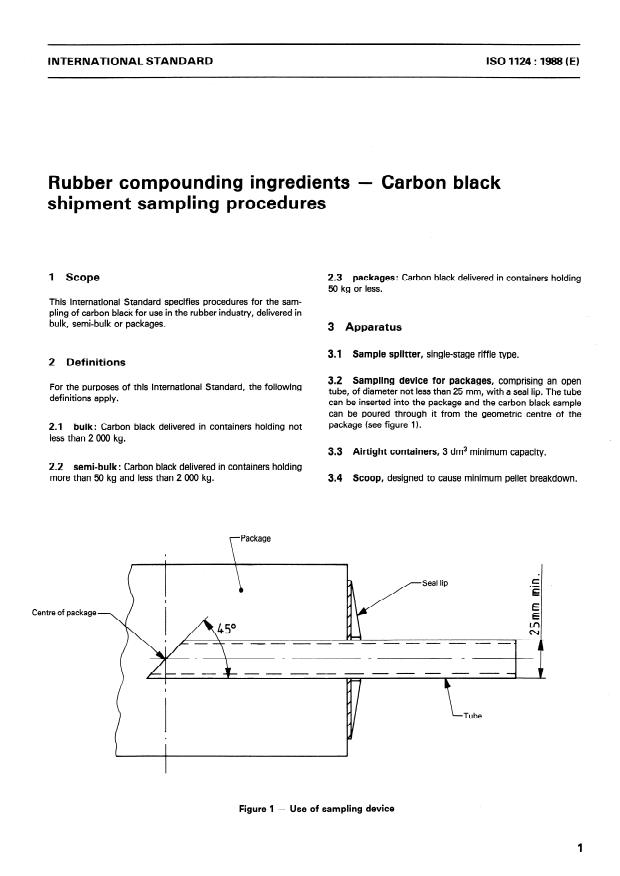
1 Scope 2.3 packages: Carbon black delivered in Containers holding
50 kg or less.
This International Standard specifies procedures for the sam-
pling of carbon black for use in the rubber industry, delivered in
bulk, semi-bulk or packages.
3 Apparatus
3.1 Sample Splitter, Single-Stage riffle type.
2 Definitions
3.2 Sampling device for packages, comprising an open
For the purposes of this International Standard, the following
tube, of diameter not less than 25 mm, with a seal lip. The tube
definitions apply.
tan be inserted into the package and the carbon black Sample
tan be poured through it from the geometric centre of the
package (sec figure 1).
2.1 bulk: Carbon black delivered in Containers holding not
less than 2 000 kg.
3.3 Airtight Containers, 3 dm3 minimum capacity.
2.2 semi-bulk: Carbon black delivered in Containers holding
more than 50 kg and less than 2 000 kg. 3.4 Scoop, designed to Cause minimum pellet breakdown.
Centre of package
Figure 1 - Use of sampling device
ISO 1124 : 1988(E)
Treatment and storage of samples
4 Sampling procedures for bulk and
semi-bulk Containers
6.1 If individual samples are taken for testing independently,
4.1 General
pass each Sample through the Single-Stage riffle-type Sample
Splitter at least twice, in Order to prevent stratification. This is
The method is for use in obtaining representative samples of
particularly important if pellet quality tests are to be carried out
the carbon black in each Container, compartment or entire ve-
on the samples. lt is highly recommended that the mean quality
hicle. The samples may be used to deter,mine the average quali-
of the shipment be calculated from the individual samples. This
ty or to ascertain the variability i
...
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Troisième édition
198%il-13
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOflHAR OPi-AHM3A~Wl f-l0 CTAHfiAPTM3A~MM
Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc - Procédures
d’échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir
de carbone
Rubber compounding ingredien ts - Carbon black shipmen t sampling procedures
Numéro de référence
ISO 1124: 1988 (F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1124 a été élaborée par le comité technique !SO/T@ 45,
Élastomères et produits à base d’élastomères.
Cette troisième édition annule et remplace la deuxième édition (ISO 1124 : 1983), dont
elle constitue une révision technique.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 a
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 1124: 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc - Procédures
d’échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir
de carbone
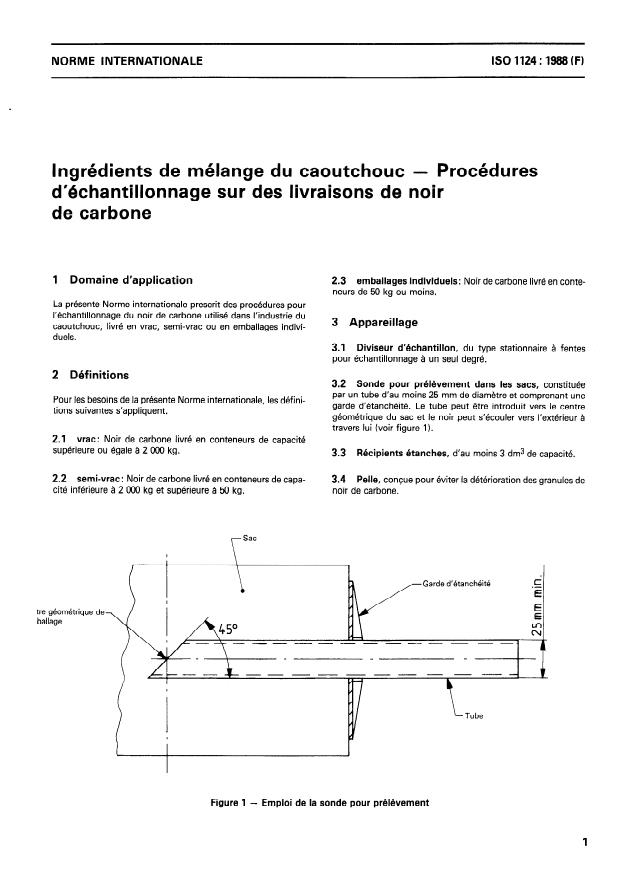
1 Domaine d’application 2.3 emballages individuels: Noir de carbone livré en conte-
neurs de 50 kg ou moins.
La présente Norme internationale prescrit des procédures pour
l’échantillonnage du noir de carbone utilisé dans l’industrie du
3 Appareillage
caoutchouc, livré en vrac, semi-vrac ou en emballages indivi-
duels.
3.1 Diviseur d’échantillon, du type stationnaire à fentes
pour échantillonnage à un seul degré.
2 Définitions
3.2 Sonde pour prélèvement dans les sacs, constituée
par un tube d’au moins 25 mm de diamètre et comprenant une
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale, les défini-
garde d’étanchéité. Le tube peut être introduit vers le centre
tions suivantes s’appliquent.
géométrique du sac et le noir peut s’écouler vers l’extérieur à
travers lui (voir figure 1).
21 vrac: Noir de carbone livré en conteneurs de capacité
supérieure ou égale à 2 000 kg.
3.3 Récipients étanches, d’au moins 3 dm3 de capacité.
2.2 semi-vrac: Noir de carbone livré en conteneurs de capa- 3.4 Pelle, concue pour éviter la détérioration des granules de
cité inférieure à 2 000 kg et supérieure à 50 kg.
noir de carbone.
Garde d’étanchéité
tre géométrique de
Figure 1 - Emploi de la sonde pour prélèvement
4 Procédures d’échantillonnage pour les 6 Préparation et conservation des
conteneurs vrac et semi-vrac échantillons
4.1 Généralités
6.1 Si des échantillons individuels sont prélevés pour être
évalues séparément, passer au moins deux fois chaque échan-
La méthode est destinée à obtenir des échantillons de noir de
tillon dans le diviseur d’échantillon (3.1) afin d’éviter toute sédi-
carbone représentatifs de chaque conteneur, compartiment ou
mentation. Ceci est particulièrement important si des essais
du véhicule tout entier. Les échantillons peuvent être utilisés
concernant la qualité de la granulation doivent être effectués
pour déterminer la qualité moyenne du lot ou pour constater les
sur ces échantillons. II est fortement recommandé que la qualité
variations de qualité.
moyenne du lot soit d
...
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Troisième édition
198%il-13
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOflHAR OPi-AHM3A~Wl f-l0 CTAHfiAPTM3A~MM
Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc - Procédures
d’échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir
de carbone
Rubber compounding ingredien ts - Carbon black shipmen t sampling procedures
Numéro de référence
ISO 1124: 1988 (F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1124 a été élaborée par le comité technique !SO/T@ 45,
Élastomères et produits à base d’élastomères.
Cette troisième édition annule et remplace la deuxième édition (ISO 1124 : 1983), dont
elle constitue une révision technique.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 a
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 1124: 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Ingrédients de mélange du caoutchouc - Procédures
d’échantillonnage sur des livraisons de noir
de carbone
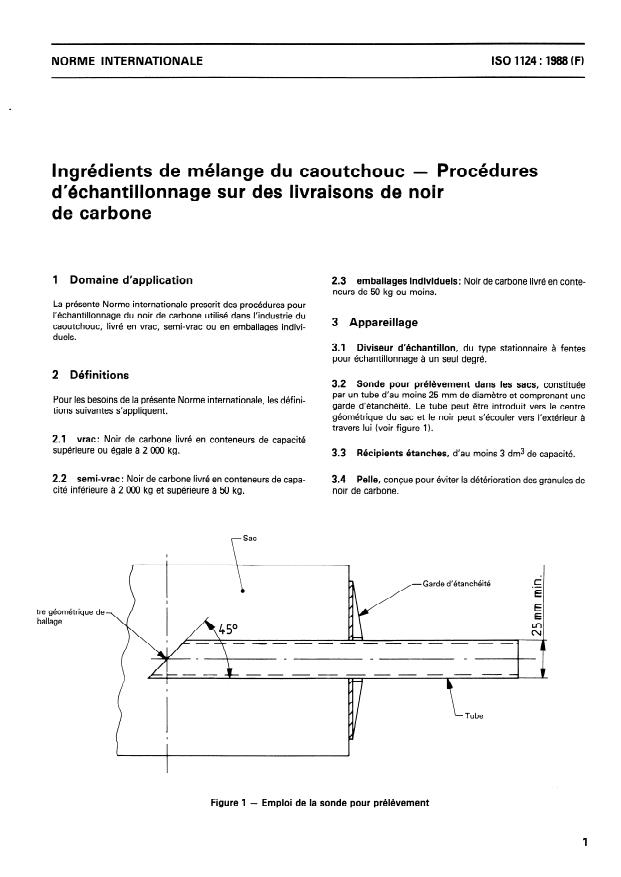
1 Domaine d’application 2.3 emballages individuels: Noir de carbone livré en conte-
neurs de 50 kg ou moins.
La présente Norme internationale prescrit des procédures pour
l’échantillonnage du noir de carbone utilisé dans l’industrie du
3 Appareillage
caoutchouc, livré en vrac, semi-vrac ou en emballages indivi-
duels.
3.1 Diviseur d’échantillon, du type stationnaire à fentes
pour échantillonnage à un seul degré.
2 Définitions
3.2 Sonde pour prélèvement dans les sacs, constituée
par un tube d’au moins 25 mm de diamètre et comprenant une
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale, les défini-
garde d’étanchéité. Le tube peut être introduit vers le centre
tions suivantes s’appliquent.
géométrique du sac et le noir peut s’écouler vers l’extérieur à
travers lui (voir figure 1).
21 vrac: Noir de carbone livré en conteneurs de capacité
supérieure ou égale à 2 000 kg.
3.3 Récipients étanches, d’au moins 3 dm3 de capacité.
2.2 semi-vrac: Noir de carbone livré en conteneurs de capa- 3.4 Pelle, concue pour éviter la détérioration des granules de
cité inférieure à 2 000 kg et supérieure à 50 kg.
noir de carbone.
Garde d’étanchéité
tre géométrique de
Figure 1 - Emploi de la sonde pour prélèvement
4 Procédures d’échantillonnage pour les 6 Préparation et conservation des
conteneurs vrac et semi-vrac échantillons
4.1 Généralités
6.1 Si des échantillons individuels sont prélevés pour être
évalues séparément, passer au moins deux fois chaque échan-
La méthode est destinée à obtenir des échantillons de noir de
tillon dans le diviseur d’échantillon (3.1) afin d’éviter toute sédi-
carbone représentatifs de chaque conteneur, compartiment ou
mentation. Ceci est particulièrement important si des essais
du véhicule tout entier. Les échantillons peuvent être utilisés
concernant la qualité de la granulation doivent être effectués
pour déterminer la qualité moyenne du lot ou pour constater les
sur ces échantillons. II est fortement recommandé que la qualité
variations de qualité.
moyenne du lot soit d
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...