ASTM C578-11a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rigid, Cellular Polystyrene Thermal Insulation
Standard Specification for Rigid, Cellular Polystyrene Thermal Insulation
ABSTRACT
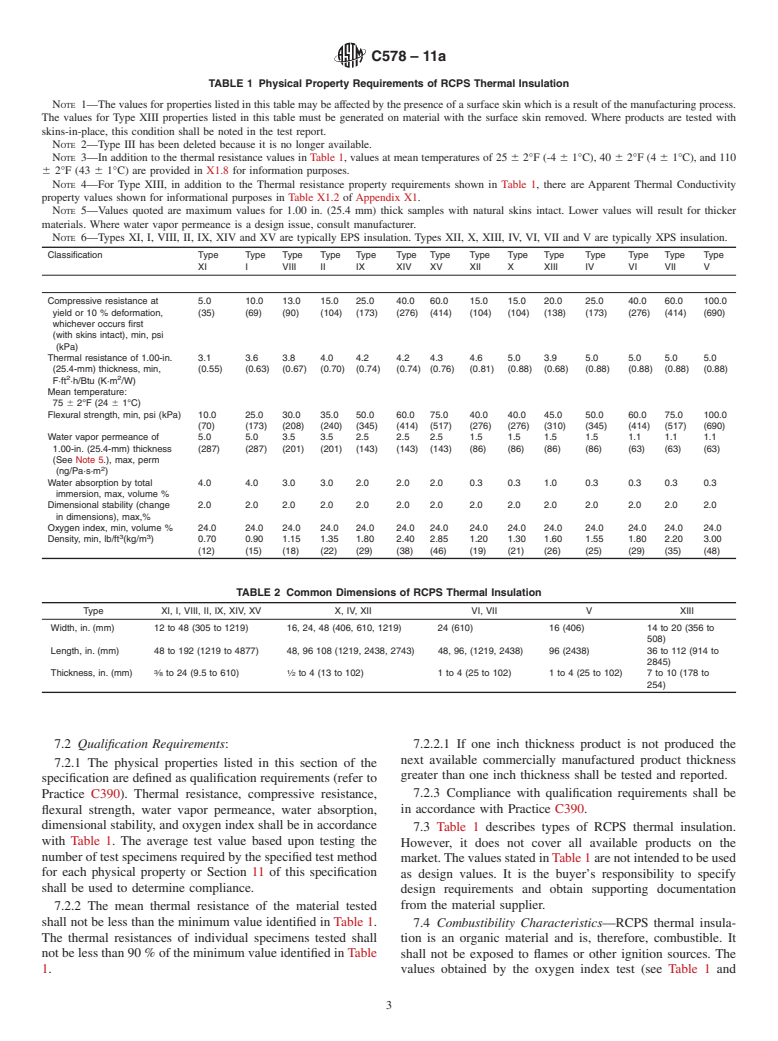
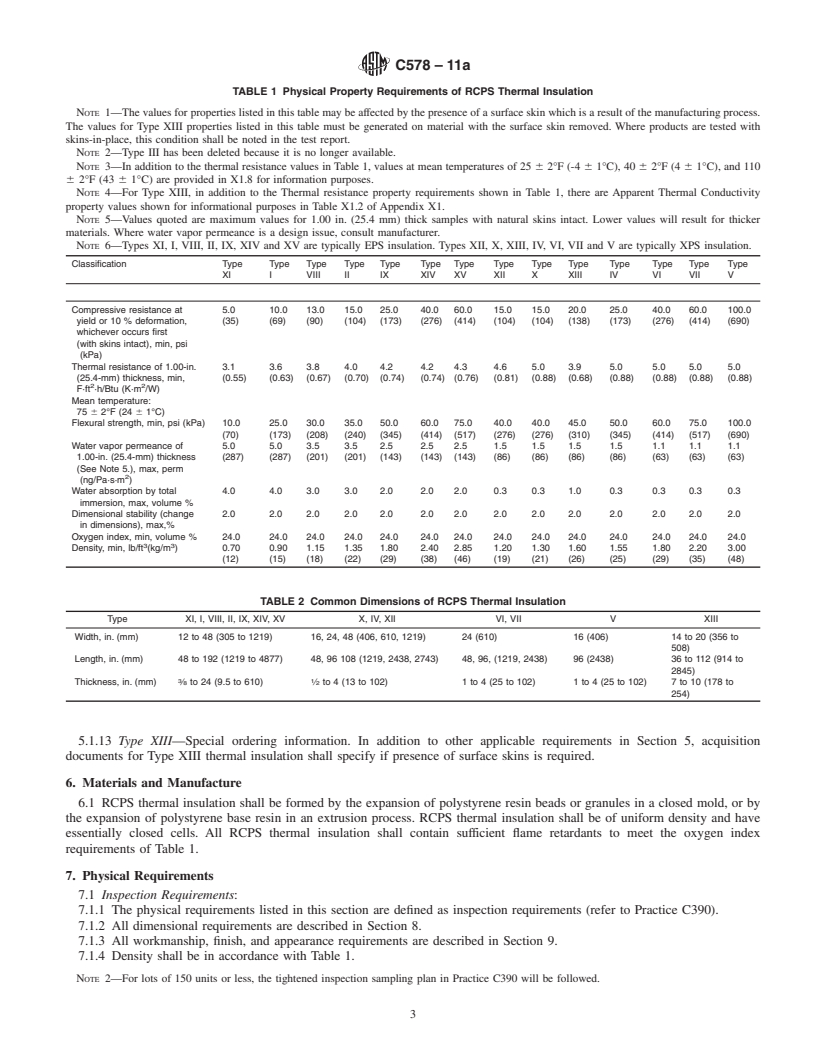
This specification covers the standards for the types, physical properties and dimensions of cellular polystyrene boards with or without facings or coatings made by molding (EPS) or extrusion (XPS) of expandable polystyrene proposed for use as thermal insulation. This specification, however, does not cover laminated products manufactured with any type of rigid board facer including fiberboard, perlite board, gypsum board, or oriented strand board. All thermal insulation shall be of uniform density and shall contain sufficient flame retardants to meet the oxygen index of requirements. They shall also meet the physical requirements such as thermal resistance, compressive resistance, flexural strength, water vapor permeance, water absorption, dimensional stability, and oxygen index specified herein.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the types, physical properties, and dimensions of cellular polystyrene boards with or without facings or coatings made by molding (EPS) or extrusion (XPS) of expandable polystyrene. Products manufactured to this specification are intended for use as thermal insulation for temperatures from -65 to +165°F (-53.9 to +73.9°C). This specification does not apply to laminated products manufactured with any type of rigid board facer including fiberboard, perlite board, gypsum board, or oriented strand board.
1.1.1 For Type XIII only, this specification covers the physical properties, and dimensions of cellular polystyrene intended for use as thermal insulation for temperatures from −297 to +165°F (−183 to +73.9°C).
1.2 Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations and properties in cryogenic conditions.
1.2.1 This specification does not cover cryogenic properties except for the k-factors for Type XIII in Appendix X1. For Type XIII in specific cryogenic applications, the manufacturer and purchaser shall agree upon the actual temperature limits and physical property requirements in addition to the k-factors in Appendix X1.
1.3 The use of thermal insulation materials covered by this specification may be regulated by building codes that address fire performance. For some end uses, specifiers should also address the effect of moisture and wind pressure resistance. Guidelines regarding these end use considerations are included in Appendix X1.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C578 – 11a
Standard Specification for
1
Rigid, Cellular Polystyrene Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C578; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 Thisspecification coversthetypes,physicalproperties,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
and dimensions of cellular polystyrene boards with or without
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
facingsorcoatingsmadebymolding(EPS)orextrusion(XPS)
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of expandable polystyrene. Products manufactured to this
specification are intended for use as thermal insulation for
2. Referenced Documents
temperatures from -65 to +165°F (-53.9 to +73.9°C). This
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specification does not apply to laminated products manufac-
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties
tured with any type of rigid board facer including fiberboard,
of Thermal Insulations
perlite board, gypsum board, or oriented strand board.
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
1.1.1 For Type XIII only, this specification covers the
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
physical properties, and dimensions of cellular polystyrene
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
intended for use as thermal insulation for temperatures from
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
−297 to +165°F (−183 to +73.9°C).
C203 Test Methods for Breaking Load and Flexural Prop-
1.2 Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations
erties of Block-Type Thermal Insulation
and properties in cryogenic conditions.
C272 Test Method for Water Absorption of Core Materials
1.2.1 This specification does not cover cryogenic properties
for Structural Sandwich Constructions
except for the k-factors for Type XIII in Appendix X1. For
C303 Test Method for Dimensions and Density of Pre-
Type XIII in specific cryogenic applications, the manufacturer
formed Block and Board−Type Thermal Insulation
and purchaser shall agree upon the actual temperature limits
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Proper-
and physical property requirements in addition to the k-factors
ties of Pipe Insulation
in Appendix X1.
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal
1.3 The use of thermal insulation materials covered by this
Insulation Lots
specification may be regulated by building codes that address
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
fire performance. For some end uses, specifiers should also
Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
address the effect of moisture and wind pressure resistance.
C550 Test Method for Measuring Trueness and Squareness
Guidelinesregardingtheseenduseconsiderationsareincluded
of Rigid Block and Board Thermal Insulation
in Appendix X1.
C870 Practice for Conditioning of Thermal Insulating Ma-
1.4 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
terials
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
C1045 PracticeforCalculatingThermalTransmissionProp-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
erties Under Steady-State Conditions
and are not considered standard.
C1058 Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating
and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
C1114 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
Properties by Means of the Thin-Heater Apparatus
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on
C1303 Test Method for Predicting Long-Term Thermal
Organic and Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
Resistance of Closed-Cell Foam Insulation
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011. Published October 2011. Originally
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C578–11. DOI:
10.1520/C0578-11A.
2
ThisspecificationissimilartoISO4898-1984,“CellularPlastics–Specification
3
for Rigid Cellular Materials Used in the Thermal Insulation of Buildings,” in title For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
only. The scope and technical content are significantly different. contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM
ISO standards are available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
25 W. 43
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C578–11 Designation: C578 – 11a
Standard Specification for
1
Rigid, Cellular Polystyrene Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C578; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
2
1.1 This specification covers the types, physical properties, and dimensions of cellular polystyrene boards with or without
facings or coatings made by molding (EPS) or extrusion (XPS) of expandable polystyrene. Products manufactured to this
specification are intended for use as thermal insulation for temperatures from -65 to +165°F (-53.9 to +73.9°C).This specification
does not apply to laminated products manufactured with any type of rigid board facer including fiberboard, perlite board, gypsum
board, or oriented strand board.
1.1.1 For Type XIII only, this specification covers the physical properties, and dimensions of cellular polystyrene intended for
use as thermal insulation for temperatures from −297 to +165°F (−183 to +73.9°C).
1.2 Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations and properties in cryogenic conditions.
1.2.1 This specification does not cover cryogenic properties except for the k-factors for Type XIII in Appendix X1. For Type
XIIIinspecificcryogenicapplications,themanufacturerandpurchasershallagreeupontheactualtemperaturelimitsandphysical
property requirements in addition to the k-factors in Appendix X1.
1.3 The use of thermal insulation materials covered by this specification may be regulated by building codes that address fire
performance. For some end uses, specifiers should also address the effect of moisture and wind pressure resistance. Guidelines
regarding these end use considerations are included in Appendix X1.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C165 Test Method for Measuring Compressive Properties of Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
C203 Test Methods for Breaking Load and Flexural Properties of Block-Type Thermal Insulation
C272 Test Method for Water Absorption of Core Materials for Structural Sandwich Constructions
C303 Test Method for Dimensions and Density of Preformed Block and BoardType Thermal Insulation
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Properties of Pipe Insulation
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal Insulation Lots
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
C550 Test Method for Measuring Trueness and Squareness of Rigid Block and Board Thermal Insulation
C870 Practice for Conditioning of Thermal Insulating Materials
C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Properties Under Steady-State Conditions
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on Organic and
Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
Current edition approved JuneOct. 1, 2011. Published AugustOctober 2011. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20102011 as
C578–10a.C578–11. DOI: 10.1520/C0578-11A.
2
This specification is similar to ISO 4898-1984, “Cellular Plastics–Specification for Rigid Cellular Materials Used in the Thermal Insulation of Buildings,” in title only.
The scope and technical content are significantly different.
ISO standards are available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
3
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume inf
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.