ASTM G170-01a
(Guide)Standard Guide for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors in the Laboratory
Standard Guide for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors in the Laboratory
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers some generally accepted laboratory methodologies that are used for evaluating corrosion inhibitors for oilfield and refinery applications in well defined flow conditions.
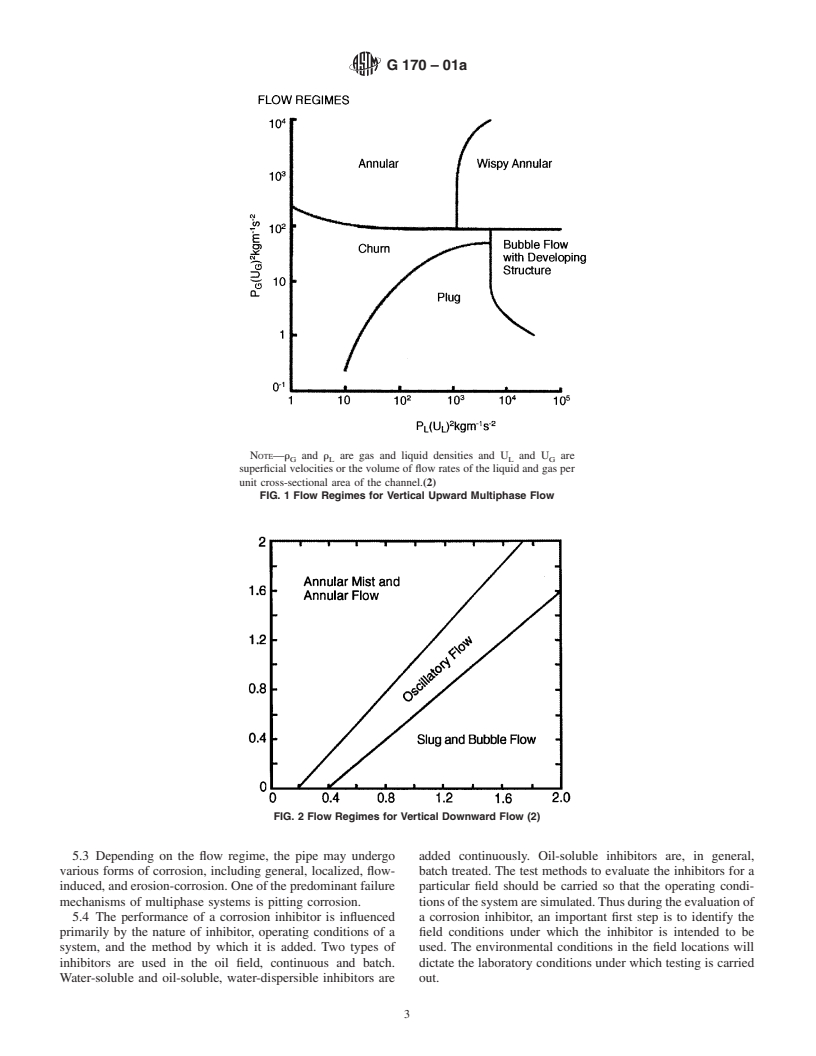
1.2 This guide does not cover detailed calculations and methods, but rather covers a range of approaches which have found application in inhibitor evaluation.
1.3 Only those methodologies that have found wide acceptance in inhibitor evaluation are considered in this guide.
1.4 This guide is intended to assist in the selection of methodologies that can be used for evaluating corrosion inhibitors.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G 170 – 01a
Standard Guide for
Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and Refinery Corrosion
1
Inhibitors in the Laboratory
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G 170; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope G 46 Guide for Examination and Evaluation of Pitting
4
Corrosion
1.1 This guide covers some generally accepted laboratory
G 59 Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polar-
methodologies that are used for evaluating corrosion inhibitors
4
ization Resistance Measurements
for oilfield and refinery applications in well defined flow
G 96 Guide for On-Line Monitoring of Corrosion in Plant
conditions.
4
Equipment (Electrical and Electrochemical Methods)
1.2 This guide does not cover detailed calculations and
G 102 Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and
methods, but rather covers a range of approaches which have
4
Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements
found application in inhibitor evaluation.
G 106 PracticeforVerificationofAlgorithmandEquipment
1.3 Only those methodologies that have found wide accep-
4
for Electrochemical Impedance Measurements
tance in inhibitor evaluation are considered in this guide.
G 111 Guide for Corrosion Tests in High Temperature or
1.4 This guide is intended to assist in the selection of
4
High Pressure Environment, or Both
methodologies that can be used for evaluating corrosion
5
2.2 NACE Standards:
inhibitors.
NACE-5A195 State-of-the-Art Report on Controlled-Flow
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Laboratory Corrosion Test, Houston, TX, NACE Interna-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tional Publication, Item No. 24187, December 1995
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
NACE-ID196 Laboratory Test Methods for Evaluating Oil-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Field Corrosion Inhibitors, Houston, TX, NACE Interna-
bility of regulatory requirements prior to use.
tional Publication, Item No. 24192, December 1996
2. Referenced Documents NACE-TM0196 Standard Test Method “Chemical Resis-
tance of Polymeric Materials by Periodic Evaluation,”
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
Houston, TX, NACE International Publication, Item No.
D 1141 Practice for Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water
3
21226, 1996
D 4410 Terminology for Fluvial Sediment
6
2.3 ISO Standards:
G 1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Cor-
4
ISO 696 SurfaceActiveAgents — Measurements of Foam-
rosion Test Specimens
ing Power Modified Ross-Miles Method
G 3 PracticeforConventionsApplicabletoElectrochemical
4
ISO 6614 Petroleum Products — Determination of Water
Measurements in Corrosion Testing
Separability of Petroleum Oils and Synthetic Fluids
G 5 Reference Test Method for Making Potentiostatic and
4
Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements
3. Terminology
G 15 Terminology Relating to Corrosion and Corrosion
4
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Testing
3.1.1 atmospheric pressure experiment—an experiment
G 16 Guide forApplying Statistics toAnalysis of Corrosion
4
conducted at the ambient atmospheric pressure (typically less
Data
than 0.07 MPa (10 psig)), using normal laboratory glassware.
G 31 Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing
4
3.1.2 batch inhibitor—an inhibitor that forms a film on the
of Metals
metal surface that persists to effect inhibition.
3.1.3 batch treatment—amethodofapplyingabatchinhibi-
1
tor. Batch inhibitors are applied as a plug between pigs or as
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee G01 on Corrosion of
Metals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.05 on Laboratory
Corrosion Tests.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2001. Published December 2001. Originally
5
published as G 170 - 01. Last previous edition G 170 - 01. Available from National Assoc. of Corrosion Engineers, P.O. Box 218340,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.02. Houston, TX 77218.
3 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street,
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02. 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G 170 – 01a
slugs of chemical poured down the well bore. The batch 3.1.18 Schmidt Number (Sc)—a measure of the ratio of the
inhibitor is dissolved or dispersed in a medium, usually hydrodynamic boundary layer to the diffusion boundary layer.
hydrocarbon and the inhi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.