ASTM D5819-05
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selecting Test Methods for Experimental Evaluation of Geosynthetic Durability
Standard Guide for Selecting Test Methods for Experimental Evaluation of Geosynthetic Durability
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers a designer/specifier through a systematic determination of those factors of the appropriate application environment that may affect the post-construction service life of a geosynthetic. Subsequently, test methods are recommended to facilitate an experimental evaluation of the durability of geosynthetics in a specified environment so that the durability can be considered in the design process.
1.2 This guide is not intended to address durability issues associated with the manufacturing, handling, transportation, or installation environments.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5819 − 05
StandardGuide for
Selecting Test Methods for Experimental Evaluation of
1
Geosynthetic Durability
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5819; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D4716 Test Method for Determining the (In-plane) Flow
Rate per Unit Width and Hydraulic Transmissivity of a
1.1 This guide covers a designer/specifier through a system-
Geosynthetic Using a Constant Head
atic determination of those factors of the appropriate applica-
D4886 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Geotextiles
tion environment that may affect the post-construction service
(Sand Paper/Sliding Block Method)
life of a geosynthetic. Subsequently, test methods are recom-
D5101 Test Method for Measuring the Soil-Geotextile Sys-
mended to facilitate an experimental evaluation of the durabil-
tem Clogging Potential by the Gradient Ratio
ity of geosynthetics in a specified environment so that the
D5262 Test Method for Evaluating the Unconfined Tension
durability can be considered in the design process.
Creep and Creep Rupture Behavior of Geosynthetics
1.2 This guide is not intended to address durability issues
D5322 Practice for Laboratory Immersion Procedures for
associated with the manufacturing, handling, transportation, or
Evaluating the Chemical Resistance of Geosynthetics to
installation environments.
Liquids
D5397 Test Method for Evaluation of Stress Crack Resis-
2. Referenced Documents
tance of Polyolefin Geomembranes Using Notched Con-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
stant Tensile Load Test
D1204 Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of
D5496 Practice for In Field Immersion Testing of Geosyn-
Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated
thetics
Temperature
D5567 Test Method for Hydraulic Conductivity Ratio
D1987 TestMethodforBiologicalCloggingofGeotextileor
(HCR) Testing of Soil/Geotextile Systems
Soil/Geotextile Filters
D5885 Test Method for Oxidative Induction Time of Poly-
D2990 Test Methods for Tensile, Compressive, and Flexural
olefin Geosynthetics by High-Pressure Differential Scan-
Creep and Creep-Rupture of Plastics
ning Calorimetry
D3083 Specification for Flexible Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Plas-
D5970 Test Method for Deterioration of Geotextiles from
tic Sheeting for Pond, Canal, and Reservoir Lining (With-
Outdoor Exposure
3
drawn 1998)
D3895 Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Poly-
3. Summary of Guide
olefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
D4355 Test Method for Deterioration of Geotextiles by
3.1 The effects of a given application environment on the
Exposure to Light, Moisture and Heat in a Xenon Arc
durability of a geosynthetic must be determined through
Type Apparatus
appropriate testing. Selection of appropriate tests requires a
D4594 Test Method for Effects of Temperature on Stability
systematic determination of the primary function(s) to be
of Geotextiles
performedandtheassociateddegradationprocessesthatshould
be considered. This guide provides a suitable systematic
approach.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on Geosynthet-
3.2 Primary functions of geosynthetics are listed and de-
icsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD35.02onEnduranceProperties.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2005.PublishedJuly2005.Originallyapproved
fined in Table 1. With knowledge of the specific geosynthetic
in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D5819 – 99. DOI: 10.1520/
application area and end use, the corresponding primary
D5819-05.
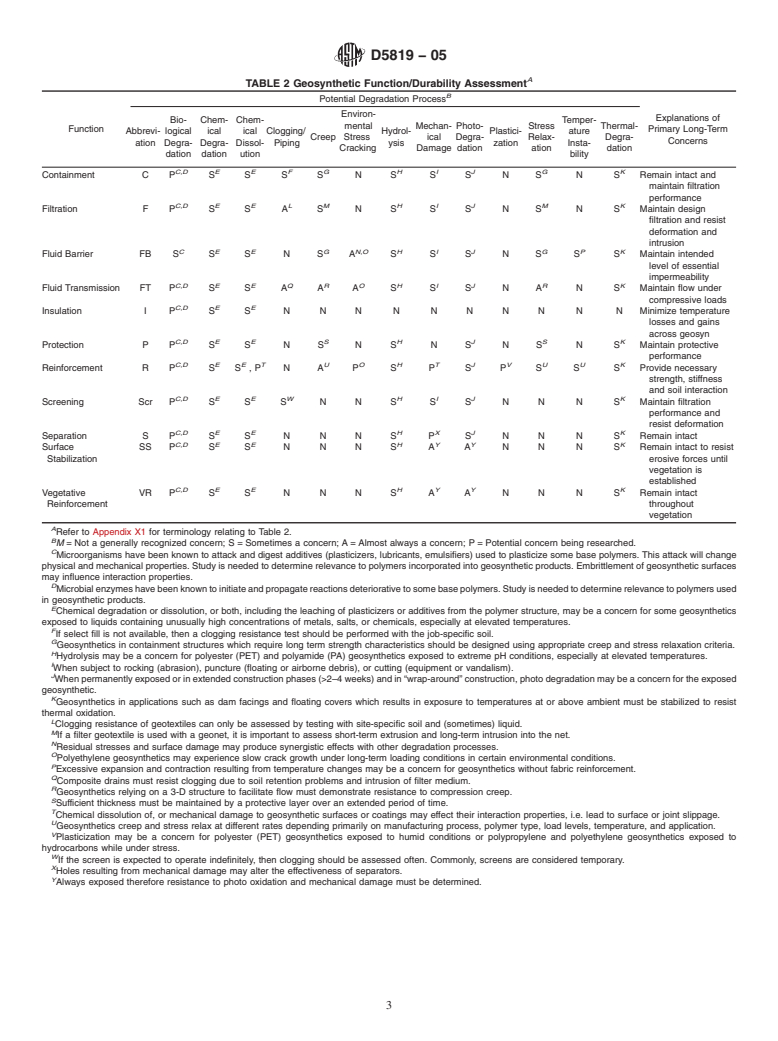
2 function(s) is (are) identified. Table 2 gives degradation con-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
cerns as they relate to geosynthetic functions. Table 3 gives the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
environmental elements that relate to the various degradation
the ASTM website.
3 processes and the currently available ASTM Committee D-35
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. test method for the experimental evaluation of specific types of
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5819 − 05
A B
TABLE 1 Functions and Other Performance Characteristics
B C
Containment (C)—A geosynthetic provides containment when it encapsulates or surrounds materials such as sand, rocks, and fresh concrete.
A
Filtration (F)—A geosynthetic performs the filtration function when th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.