ASTM D6159-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in Ethylene by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in Ethylene by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 High-purity ethylene is required as a feedstock for some manufacturing processes and the presence of trace amounts of certain hydrocarbon impurities can have deleterious effects. This test method is suitable for setting specifications, for use as an internal quality control tool, and for use in development or research work.
4.2 This test method does not detect such impurities as H2O, CO, CO2, and alcohols that may be present in the sample. Hydrocarbons higher than n-decane cannot be analyzed by this test method, if present in the sample. Test Method D2504 addresses the analysis of noncondensable gases and Test Method D2505 addresses the analysis of CO2. Guide D5234 describes all potential impurities present in ethylene. These standards should be consulted when determining the total concentration of impurities in ethylene.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of methane, ethane, propane, propene, acetylene, iso-butane, propadiene, butane, trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutene, cis-2-butene, methyl acetylene and 1,3-butadiene in high-purity ethylene. The purity of the ethylene can be calculated by subtracting the total percentage of all impurities from 100.00 %. Since this test method does not determine all possible impurities such as CO, CO2, H2O, alcohols, nitrogen oxides, and carbonyl sulfide, as well as hydrocarbons higher than decane, additional tests may be necessary to fully characterize the ethylene sample.
1.2 Data are reported in this test method as ppmV (parts per million by gaseous volume) and ppmMol (parts per million Mol). This test method was evaluated in an interlaboratory cooperative study in the concentration range of 4 ppmV to 340 ppmV (2 mg/kg to 204 mg/kg). The participants in the interlaboratory cooperative study reported the data in non-SI units. Wherever possible, SI units are included.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6159 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in Ethylene by Gas
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6159; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D2504 Test Method for Noncondensable Gases in C and
2
Lighter Hydrocarbon Products by Gas Chromatography
1.1 This test method covers the determination of methane,
D2505 Test Method for Ethylene, Other Hydrocarbons, and
ethane, propane, propene, acetylene, iso-butane, propadiene,
Carbon Dioxide in High-Purity Ethylene by Gas Chroma-
butane, trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutene, cis-2-butene,
tography
methyl acetylene and 1,3-butadiene in high-purity ethylene.
D5234 Guide for Analysis of Ethylene Product
The purity of the ethylene can be calculated by subtracting the
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analy-
total percentage of all impurities from 100.00 %. Since this test
sis
method does not determine all possible impurities such as CO,
CO , H O, alcohols, nitrogen oxides, and carbonyl sulfide, as
2 2
3. Summary of Test Method
well as hydrocarbons higher than decane, additional tests may
be necessary to fully characterize the ethylene sample.
3.1 A gaseous ethylene sample is analyzed as received. The
1.2 Data are reported in this test method as ppmV (parts per
gaseous sample is injected into a capillary gas chromatograph.
million by gaseous volume) and ppmMol (parts per million
Sample may be introduced by direct valve injection or by split
Mol). This test method was evaluated in an interlaboratory
valve injection. The gas chromatograph is provided with a
cooperative study in the concentration range of 4 ppmV to
6-port sampling valve and two wide bore capillary columns
340 ppmV (2 mg ⁄kg to 204 mg ⁄kg). The participants in the
connected in series. These columns are a dimethyl polysi-
interlaboratory cooperative study reported the data in non-SI
loxane column and a porous layer open tubular column (PLOT)
units. Wherever possible, SI units are included.
Al O /KCl column. (See Note 1.) A flame ionization detector is
2 3
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the used for detection. The integrated detector signal (peak areas)
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the are corrected for detector response. The hydrocarbon impuri-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ties are determined and the total impurities are used to
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
determine the ethylene content.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—This column is supplied by major column manufacturers.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 High-purity ethylene is required as a feedstock for some
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
manufacturing processes and the presence of trace amounts of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
certain hydrocarbon impurities can have deleterious effects.
This test method is suitable for setting specifications, for use as
2. Referenced Documents
an internal quality control tool, and for use in development or
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
research work.
4.2 This test method does not detect such impurities as H O,
2
1
CO, CO , and alcohols that may be present in the sample.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
2
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Hydrocarbons higher than n-decane cannot be analyzed by this
Subcommittee D02.D0.02 on Ethylene.
test method, if present in the sample. Test Method D2504
Current edition approved May 1, 2023. Published June 2023. Originally
addresses the analysis of noncondensable gases and Test
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D6159 – 17. DOI:
10.1520/D6159-23.
Method D2505 addresses the analysis of CO . Guide D5234
2
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
describes all potential impurities present in ethylene. These
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
standards should be consulted when determining the total
Standards volume information, refer t
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6159 − 17 D6159 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in Ethylene by Gas
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6159; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of methane, ethane, propane, propene, acetylene, iso-butane, propadiene, butane,
trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutene, cis-2-butene, methyl acetylene and 1,3-butadiene in high-purity ethylene. The purity of the
ethylene can be calculated by subtracting the total percentage of all impurities from 100.00 %. Since this test method does not
determine all possible impurities such as CO, CO , H O, alcohols, nitrogen oxides, and carbonyl sulfide, as well as hydrocarbons
2 2
higher than decane, additional tests may be necessary to fully characterize the ethylene sample.
1.2 Data are reported in this test method as ppmV (parts per million by gaseous volume) and ppmMol (parts per million Mol).
This test method was evaluated in an interlaboratory cooperative study in the concentration range of 4 ppmV to 340 ppmV
(2 mg ⁄kg to 204 mg ⁄kg). The participants in the interlaboratory cooperative study reported the data in non-SI units. Wherever
possible, SI units are included.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2504 Test Method for Noncondensable Gases in C and Lighter Hydrocarbon Products by Gas Chromatography
2
D2505 Test Method for Ethylene, Other Hydrocarbons, and Carbon Dioxide in High-Purity Ethylene by Gas Chromatography
D5234 Guide for Analysis of Ethylene Product
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analysis
3. Summary of Test Method
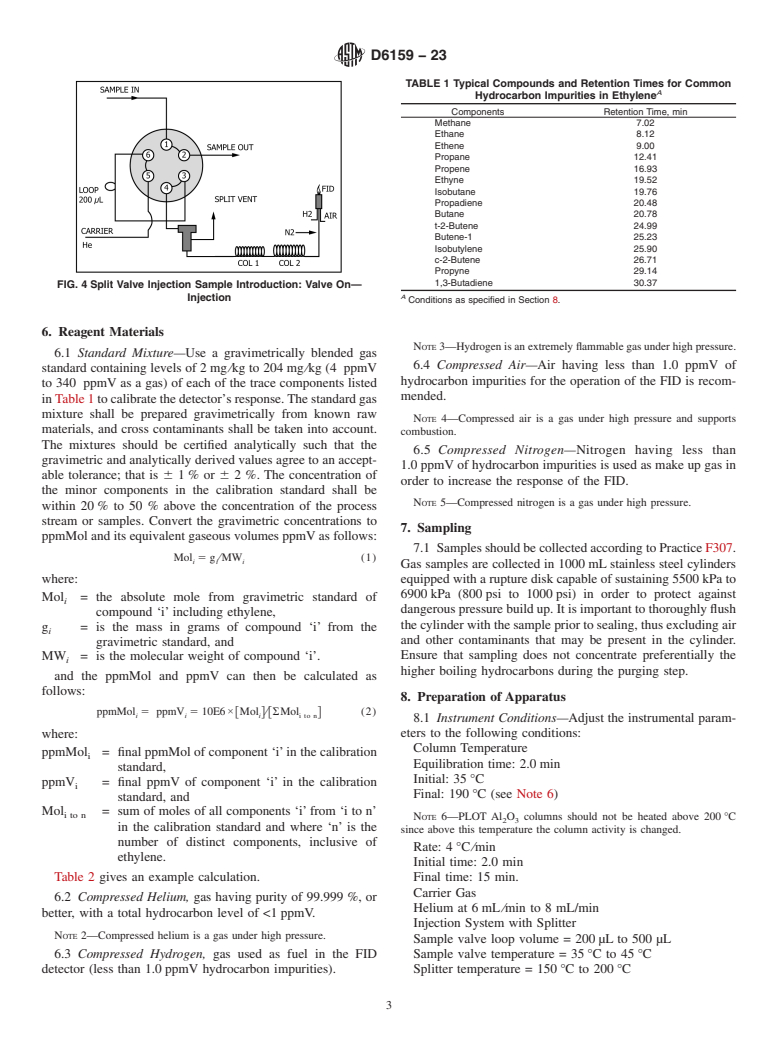
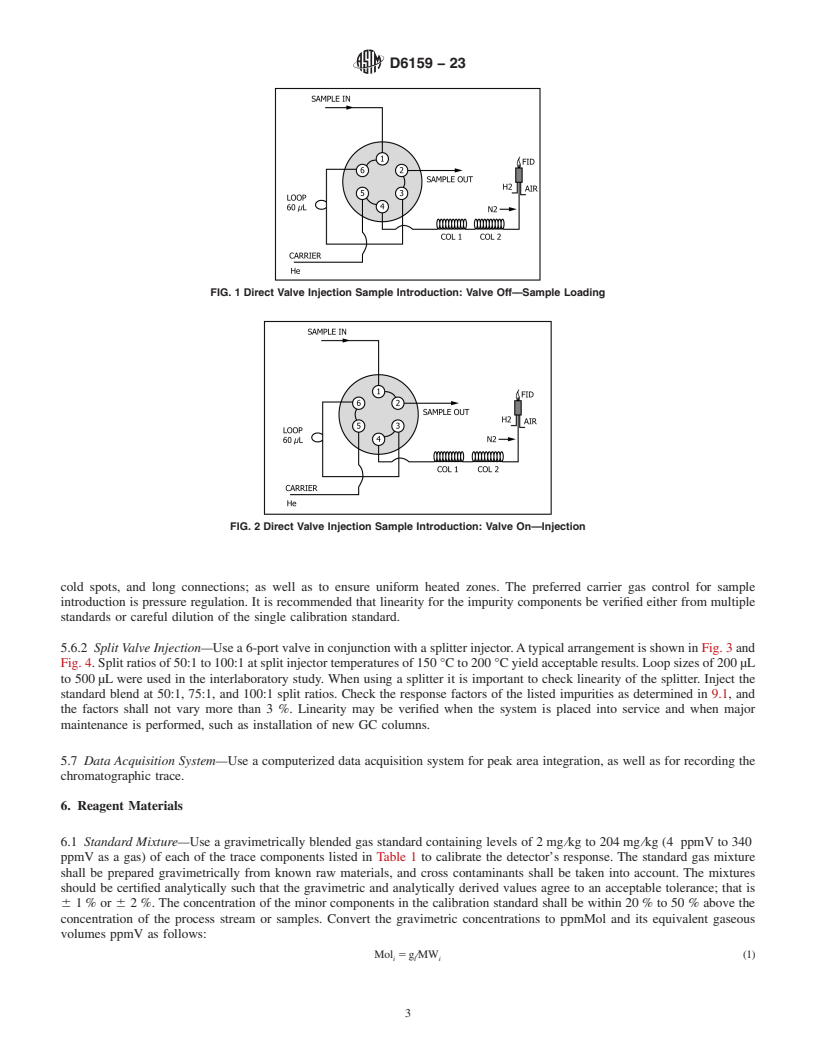
3.1 A gaseous ethylene sample is analyzed as received. The gaseous sample is injected into a capillary gas chromatograph. Sample
may be introduced by direct valve injection or by split valve injection. The gas chromatograph is provided with a 6-port sampling
valve and two wide bore capillary columns connected in series. These columns are a dimethyl polysiloxane column and a porous
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.D0.02 on Ethylene.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2017May 1, 2023. Published February 2017June 2023. Originally approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 20122017 as
D6159 – 97 (2012).D6159 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/D6159-17.10.1520/D6159-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6159 − 23
layer open tubular column (PLOT) Al O /KCl column. (See Note 1.) A flame ionization detector is used for detection. The
2 3
integrated detector signal (peak areas) are corrected for detector response. The hydrocarbon impurities are determined and the total
impurities are used to determine the ethylene content.
NOTE 1—This column is supplied by major column manufacturers.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 High-purity ethylene is required as a feedstock for some manufacturing processes and the presence of trace amounts of certain
hydrocarbon impurities can have deleterious effects. This test method is suitable for setting specifications, for use as an internal
quality control tool, and for u
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.