ASTM D6296-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Olefins in Spark-ignition Engine Fuels by Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Total Olefins in Spark-ignition Engine Fuels by Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The quantitative determination of olefins in spark-ignition engine fuels is required to comply with government regulations.
5.2 Knowledge of the total olefin content provides a means to monitor the efficiency of catalytic cracking processes.
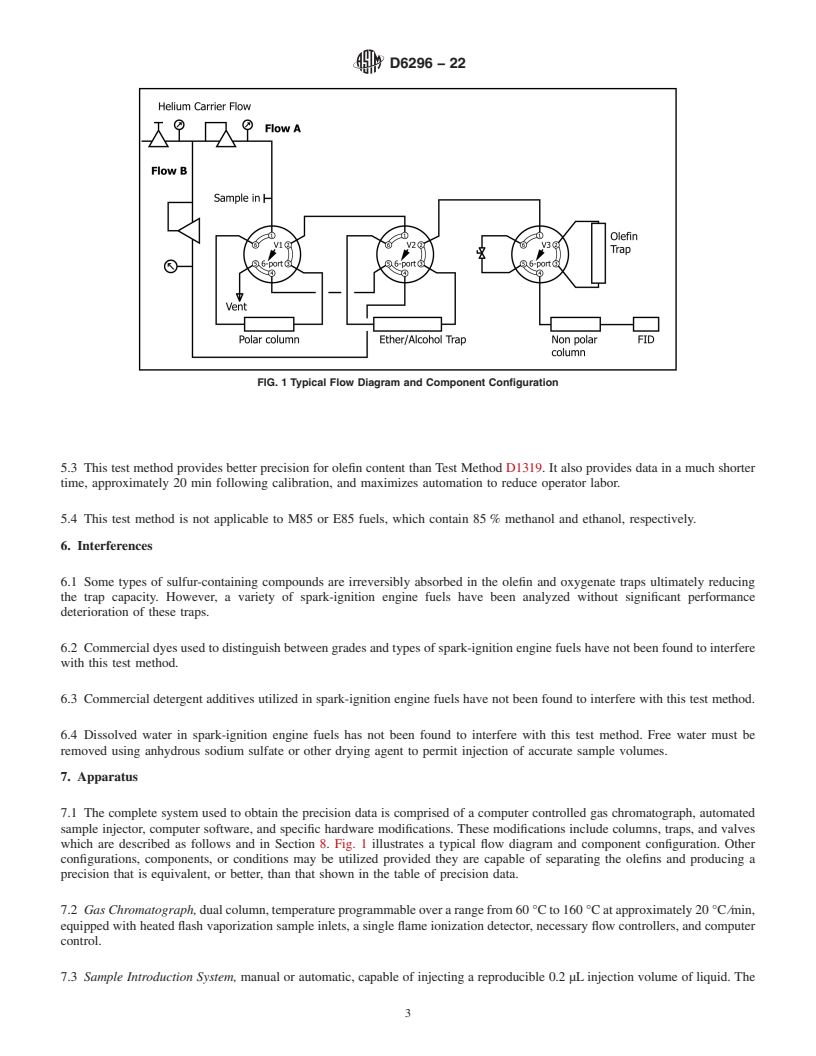
5.3 This test method provides better precision for olefin content than Test Method D1319. It also provides data in a much shorter time, approximately 20 min following calibration, and maximizes automation to reduce operator labor.
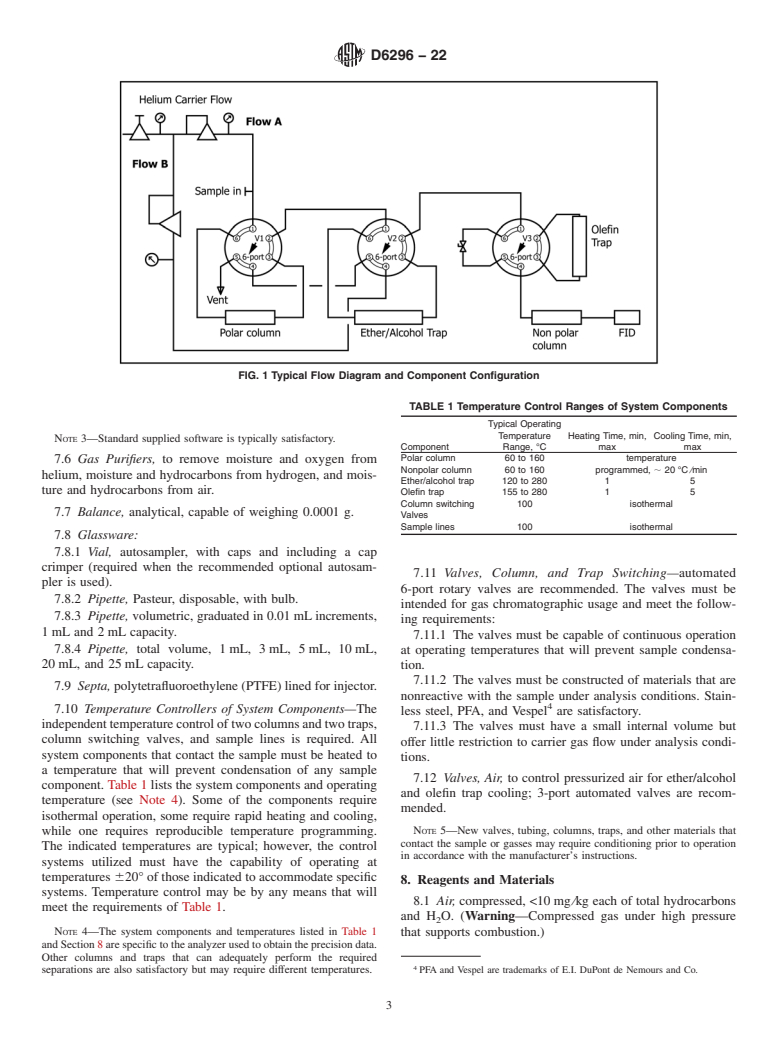
5.4 This test method is not applicable to M85 or E85 fuels, which contain 85 % methanol and ethanol, respectively.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determination of total olefins in the C4 to C10 range in spark-ignition engine fuels or related hydrocarbon streams, such as naphthas and cracked naphthas. Olefin concentrations in the range from 0.2 % by liquid-volume or mass to 5.0 % by liquid-volume or mass, or both, can be determined directly on the as-received sample whereas olefins in samples containing higher concentrations are determined after appropriate sample dilution prior to analysis.
1.2 This test method is applicable to samples containing alcohols and ethers; however, samples containing greater than 15 % alcohol must be diluted. Samples containing greater than 5.0 % ether must also be diluted to the 5.0 % or less level, prior to analysis. When ethyl-tert-butylether is present, only olefins in the C4 to C9 range can be determined.
1.3 This test method can not be used to determine individual olefin components.
1.4 This test method can not be used to determine olefins having higher carbon numbers than C10.
Note 1: Precision was determined only on samples containing MTBE and ethanol.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D6296 −22
Standard Test Method for
Total Olefins in Spark-ignition Engine Fuels by
1
Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6296; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determi-
nation of total olefins in the C to C range in spark-ignition
4 10
2. Referenced Documents
engine fuels or related hydrocarbon streams, such as naphthas
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and cracked naphthas. Olefin concentrations in the range from
D1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petro-
0.2 % by liquid-volume or mass to 5.0 % by liquid-volume or
leum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
mass, or both, can be determined directly on the as-received
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
sample whereas olefins in samples containing higher concen-
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
trations are determined after appropriate sample dilution prior
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
to analysis.
Fuels, and Lubricants
1.2 This test method is applicable to samples containing
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
alcohols and ethers; however, samples containing greater than
Analytical Standards
15 % alcohol must be diluted. Samples containing greater than
D4815 Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE,
5.0 %ethermustalsobedilutedtothe5.0 %orlesslevel,prior
TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C to C Alco-
1 4
to analysis. When ethyl-tert-butylether is present, only olefins
hols in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
in the C to C range can be determined.
4 9
D5599 Test Method for Determination of Oxygenates in
1.3 Thistestmethodcannotbeusedtodetermineindividual Gasoline by Gas Chromatography and Oxygen Selective
olefin components. Flame Ionization Detection
E355 Practice for Gas ChromatographyTerms and Relation-
1.4 This test method can not be used to determine olefins
ships
having higher carbon numbers than C .
10
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
NOTE 1—Precision was determined only on samples containing MTBE
in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
and ethanol.
3. Terminology
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1 This test method makes reference to common gas
standard.
chromatographicprocedures,terms,andrelationships.Detailed
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the definitions of these can be found in Practices E355 and E594
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the and Terminology D4175.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2.1 trap, n—a device utilized to selectively retain specific
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
portions (individual or groups of hydrocarbons or oxygenates)
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
of the test sample and to release the retained components by
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
increasing the trap temperature.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.3 Acronyms:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.3.1 ETBE—ethyl-tert-butylether.
3.3.2 MTBE—methyl-tert–butylether.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2022. Published May 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D6296 – 98 (2017). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D6296-22. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6296−22
4. Summary of Test Method 6. I
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6296 − 98 (Reapproved 2017) D6296 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Total Olefins in Spark-ignition Engine Fuels by
1
Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6296; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determination of total olefins in the C to C range in spark-ignition engine fuels
4 10
or related hydrocarbon streams, such as naphthas and cracked naphthas. Olefin concentrations in the range from 0.2 liquid-volume
%0.2 % by liquid-volume or mass % to 5.0 liquid-volume % or mass %, to 5.0 % by liquid-volume or mass, or both, can be
determined directly on the as-received sample whereas olefins in samples containing higher concentrations are determined after
appropriate sample dilution prior to analysis.
1.2 This test method is applicable to samples containing alcohols and ethers; however, samples containing greater than 15 %
alcohol must be diluted. Samples containing greater than 5.0 % ether must also be diluted to the 5.0 % or less level, prior to
analysis. When ethyl-tert-butylether is present, only olefins in the C to C range can be determined.
4 9
1.3 This test method can not be used to determine individual olefin components.
1.4 This test method can not be used to determine olefins having higher carbon numbers than C .
10
NOTE 1—Precision was determined only on samples containing MTBE and ethanol.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2017April 1, 2022. Published November 2017May 2022. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20132017 as
D6296 – 98 (2017).(2013). DOI: 10.1520/D6296-98R17.10.1520/D6296-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6296 − 22
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as Analytical Standards
D4815 Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C to C Alcohols in
1 4
Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
D5599 Test Method for Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame
Ionization Detection
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
3. Terminology
3.1 This test method makes reference to common gas chromatographic procedures, terms, and relationships. Detailed definitions
of these can be found in Practices E355 and E594 and Terminology D4175.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 trap, n—a device utilized to selectively retai
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.