ASTM D6888-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Available Cyanide with Ligand Displacement and Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
Standard Test Method for Available Cyanide with Ligand Displacement and Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
SCOPE
1.1 This method is used to determine the concentration of available inorganic cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or effluent. The method detects the cyanides that are free (HCN and CN-) and metal-cyanide complexes that are easily dissociated into free cyanide ions. The method does not detect the less toxic strong metal-cyanide complexes, cyanides that are not "amenable to chlorination."
1.2 This procedure is applicable over a range of approximately 2 to 400 μg/L (parts per billion) available cyanide. Higher concentrations can be analyzed by dilution or lower injection volume.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Note 2 and Section 8.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 6888 – 03
Standard Test Method for
Available Cyanide with Ligand Displacement and Flow
Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation
and Amperometric Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6888; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 6696 Guide for Understanding Cyanide Species
E 60 Practice for Photometric and Spectrophotometric
1.1 This method is used to determine the concentration of
Methods for Chemical Analysis of Metals
available inorganic cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or
E 275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance
effluent. The method detects the cyanides that are free (HCN
-
of Ultraviolet, Visible, and Near Infrared Spectrophotom-
and CN ) and metal-cyanide complexes that are easily disso-
eters
ciated into free cyanide ions. The method does not detect the
E 1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
less toxic strong metal-cyanide complexes, cyanides that are
Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
not “amenable to chlorination.”
1.2 This procedure is applicable over a range of approxi-
3. Terminology
mately 2 to 400 μg/L (parts per billion) available cyanide.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
Higher concentrations can be analyzed by dilution or lower
method, refer to Terminology D 1129 and Guide D 6696.
injection volume.
3.2 available cyanide—Inorganic cyanides that are free
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
-
(HCN and CN ) and metal-cyanide complexes that are easily
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
dissociated into free cyanide ions. Available cyanide does not
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
include the less toxic strong metal-cyanide complexes, cya-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
nides that are not “amenable to chlorination.”
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
statements are given in Note 2 and Section 9.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Complex cyanides bound with nickel or mercury are
2. Referenced Documents
released by ligand displacement by the addition of a ligand
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2 displacement agent prior to analysis.
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
2 4.2 Other weak and dissociable cyanide species do not
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3 require ligand displacement.
D 2036 Test Methods for Cyanides in Water
4.3 The treated sample is introduced into a flow injection
D 2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
2 analysis (FIA) system where it is acidified to form hydrogen
Applicable Methods of Committee D-19 on Water
2 cyanide (HCN). The hydrogen cyanide gas diffuses through a
D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water
hydrophobic gas diffusion membrane, from the acidic donor
D 3856 Guide for Good Laboratory Practices in Laborato-
2 stream into an alkaline acceptor stream.
ries Engaged in Sampling and Analysis of Water
-
4.4 The CN is captured in the alkaline acceptor stream
D 4210 Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Proce-
2 which then flows into an amperometric flowcell detector with
dures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
a silver working electrode.
D 4375 Terminology for Basic Statistics in Committee
2 4.5 The cyanide oxidizes the silver electrode causing an
D-19 on Water
amperometric current, which is detected. The current at any
D 5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
3 time is proportional to the concentration of cyanide flowing
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
past the detector.
4.6 Calibrations and data are processed with the instru-
ment’s data acquisition software.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis of
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published May 2003.
2 4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.02. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D6888–03
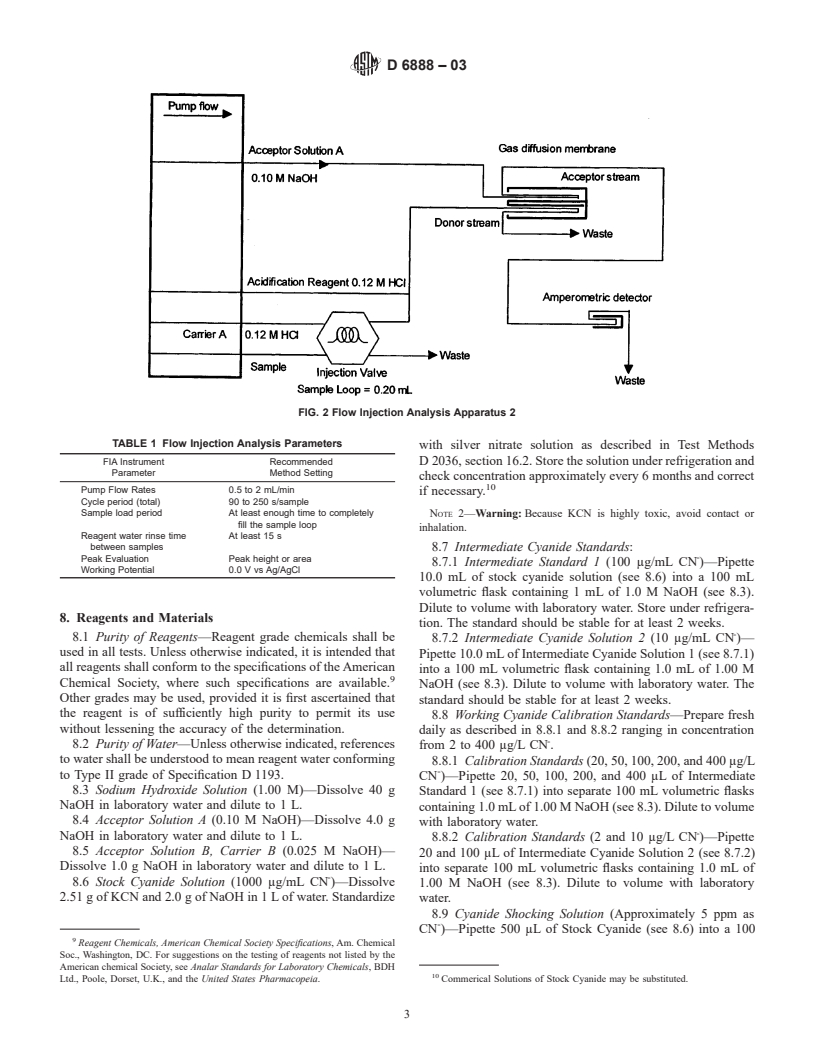
5. Significance and Use tem to include a silver working electrode, a Ag/AgCl reference
electrode, and a Pt or stainless steel counter electrode. Ex-
5.1 Cyanide and hydrogen cyanide are highly toxic. Regu-
amples of the apparatus schematics are shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
lations have been established to require the monitoring of
Example instrument settings are shown in Table 1.
cyanide in industrial and domestic wastes and surface waters.
5.2 This test method is applicable for natural water, saline
NOTE 1—The instrument settings in Table 1 are only examples. The
waters, and wastewater effluent. analyst may modify the settings as long as performance of the method has
not been degraded. Contact the instrument manufacturer for recommended
5.3 The method may be used for process control in waste-
instrument parameters.
water treatment facilities.
5.4 The spot test outlined in Test Methods D 2036, Annex
7.2 An autosampler is recommended but not required to
A1 can be used to detect cyanide and thiocyanate in water or
automate sample injections and increase throughput. Autosam-
wastewater, and to approximate its concentration.
plers are usually available as an option from the instrument’s
manufacturer.
6. Interferences
7.3 Data Acquisition System—Use the computer hardware
6.1 High levels of carbonate can release CO into the
and software recommended by the instrument manufacturer to
acceptor stream and cause an interference with the amperomet-
control the apparatus and to collect data from the detector.
ric detector that result in a slight masking effect (15 % negative
7.4 Pump Tubing—Use tubing recommended by instrument
bias with 20 ppb cyanide in 1500 ppm carbonate). Refer to 11.1
manufacturer. Replace pump tubing when worn, or when
for sample pretreatment.
precision is no longer acceptable.
6.2 Sulfide will diffuse through the gas diffusion membrane
7.5 Gas Diffusion Membranes—A hydrophobic membrane
and can be detected in the amperometric flowcell. Oxidized
which allows gaseous hydrogen cyanide to pervaporate from
- -
products of sulfide can also rapidly convert CN to SCN at a
the donor to the acceptor stream at a sufficient rate to allow
high pH. Refer to 11.3 for sulfide removal.
detection. The gas diffusion membrane should be replaced
6.3 Refer to section 6.1 of Test Methods D 2036 for 8
when the baseline becomes noisy or every 1 to 2 weeks.
additional information regarding interferences for the analysis
7.6 Use parts and accessories as directed by instrument
of cyanide and Section 11 of Test Methods D 2036 for
manufacturer.
elimination of interferences.
7. Apparatus
7.1 The instrument should be equipped with a precise
Both the ALPKEM CN Solution 3000 equipped with an amperometric flowcell,
Available from O.I. Analytical, and Lachat Instruments QuikChem Automated Ion
sample introduction system, a gas diffusion manifold with
Analyzer using Method 10-204-00-5-A have been found to be suitable for this
hydrophobic membrane, and an amperometric detection sys-
analysis.
Gelmen Sciences Part Number M5PU025, ALPKEM Part Number A0015200,
and Lachat Instruments Part Number 50398 have found to be suitable for this
analysis.
40 CFR Part 136.
FIG. 1 Flow Injection Analysis Apparatus 1
D6888–03
FIG. 2 Flow Injection Analysis Apparatus 2
TABLE 1 Flow Injection Analysis Parameters
with silver nitrate solution as described in Test Methods
FIA Instrument Recommended D 2036, section 16.2. Store the solution under refrigeration and
Parameter Method Setting
check concentration approximately every 6 months and correct
Pump Flow Rates 0.5 to 2 mL/min
if necessary.
Cycle period (total) 90 to 250 s/sample
Sample load period At least enough time to completely NOTE 2—Warning: Because KCN is highly toxic, avoid contact or
fill the sample loop
inhalation.
Reagent water rinse time At least 15 s
between samples 8.7 Intermediate Cyanide Standards:
-
Peak Evaluation Peak height or area
8.7.1 Intermediate Standard 1 (100 μg/mL CN )—Pipette
Working Potential 0.0 V vs Ag/AgCl
10.0 mL of stock cyanide solution (see 8.6) into a 100 mL
volumetric flask containing 1 mL of 1.0 M NaOH (see 8.3).
Dilute to volume with laboratory water. Store under refrigera-
8. Reagents and Materials
tion. The standard should be stable for at least 2 weeks.
-
8.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
8.7.2 Intermediate Cyanide Solution 2 (10 μg/mL CN )—
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
Pipette 10.0 mL of Intermediate Cyanide Solution 1 (see 8.7.1)
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the American
into a 100 mL volumetric flask containing 1.0 mL of 1.00 M
Chemical Society, where such specifications are available.
NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume with laboratory water. The
Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that
standard should be stable for at least 2 weeks.
the reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use
8.8 Working Cyanide Calibration Standards—Prepare fresh
without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
daily as described in 8.8.1 and 8.8.2 ranging in concentration
-
8.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
from 2 to 400 μg/L CN .
to water shall be understood to mean reagent water conforming
8.8.1 Calibration Standards (20, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/L
-
to Type II grade of Specification D 1193.
CN )—Pipette 20, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μL of Intermediate
8.3 Sodium Hydroxide Solution (1.00 M)—Dissolve 40 g
Standard 1 (see 8.7.1) into separate 100 mL volumetric flasks
NaOH in laboratory water and dilute to 1 L.
containing 1.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume
8.4 Acceptor Solution A (0.10 M NaOH)—Dissolve 4.0 g
with laboratory water.
-
NaOH in laboratory water and dilute to 1 L.
8.8.2 Calibration Standards (2 and 10 μg/L CN )—Pipette
8.5 Acceptor Solution B, Carrier B (0.025 M NaOH)—
20 and 100 μL of Intermediate Cyanide Solution 2 (see 8.7.2)
Dissolve 1.0 g NaOH in laboratory water and dilute to 1 L.
into separate 100 mL volumetric flasks containing 1.0 mL of
-
8.6 Stock Cyanide Solution (1000 μg/mL CN )—Dissolve
1.00 M NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume with laboratory
2.51 g of KCN and 2.0 g of NaOH in 1 L of water. Standardize
water.
8.9 Cyanide Shocking Solution (Approximately 5 ppm as
-
CN )—Pipette 500 μL of Stock Cyanide (see 8.6) into a 100
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, Am. Chemical
Soc., Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by the
American chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory Chemicals, BDH
Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia. Commerical Solutions of Stock Cyanide may be substituted.
D6888–03
mL volumetric flask containing 1.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH (see 8.18) into a 100 mL volumetric flask containing 1.0 mL of 1.00
8.3). Dilute to volume with laboratory water. The solution M NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume with laboratory water.
-
should be stored under refrigeration. K Ni(CN) as CN = 100 μg/L. Prepare fresh daily.
2 4
8.10 Acetate Buffer—Dissolve 410 g of sodium acetate 8.20 Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode Filling Solution—Fill
trihydrate (NaC H O ·3H O) in 500 mL of laboratory water. the reference electrode as recommended by the instrument
2 3 2 2
Add glacial acetic acid (approximately 500 mL) to yield a pH manufacturer.
of 4.5.
9. Hazards
8.11 Carrier A and Acidification Reagent (0.12 M HCl)—
Transfer 10 mL of Trace Metal Grade concentrated hydrochlo-
9.1 Caution—Because of the toxicity of cyanide, great care
ric acid intoa1L volumetric flask. Carefully, dilute to volume
must be exercised in its handling. Acidification of cyanide
with laboratory water.
solutions produces toxic hydrocyanic acid (HCN). All manipu-
8.12 Ligand Exchange Reagent 1 (TEP Solution)—Weigh
lations must be done in the hood so that any HCN gas that
0.10 g tetraethylenepentamine (TEP) into a 100 mL volumetric
might escape is safely vented.
flask. Dilute to volume with laboratory water. The solution
9.2 Warning—Many of the reagents used in these test
should be stored at room temperature.
methods are highly toxic. These reagents and their solutions
8.13 Ligand Exchange Reagent 2 (Dithizone Solution)—
must be disposed of properly.
Weigh 0.010 g of dithizone into a 100 mL volumetric flask
9.3 All reagents and standards should be prepared in vol-
containing 1.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume
umes consistent with laboratory use to minimize the generation
with laboratory water. Sonicate if necessary until all of the
of waste.
dithizone has dissolved. The solution should be stored at room
temperature.
10. Sample and Sample Preservation
NOTE 3—Commercially prepared or alternative ligand exchange re- 10.1 Collect the sample in accordance with Practices
agents can be used if equivalent results can be demonstrated. Commercial
D 3370 and D 3856.
reagents should be used in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions.
10.2 The sample must be stablized at time of collection with
the addition of sodium hydroxide (1 M is suitable for pH
8.14 Mercury (II) Cyanide Stock Solution—Weigh 0.4854 g
adjustment) until a pH of 12 to 12.5 is reached. See 11.1 if it
Hg(CN) into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Place 1.0 mL of 1.00
is suspected that high levels of carbonate (>1500 ppm) are
M NaOH (see 8.3) in the flask and dilute to volume with
-
present in the sample.
laboratory water. Hg(CN) as CN = 1000 mg/L. The solution
10.3 Samples should be stored in dark bottles to minimize
must be stored in an amber glass bottle under refrigeration at
exposure to ultraviolet radiation, refrigerated at 4°C, and
4°C.
analyzed as soon as possible.
8.15 Mercury (II) Cyanide Intermediate Solution—Pipet
10.0 mL of the mercury (II) cyanide stock solution (see 8.14)
11. Elimination of Interferences
into a 100 mL volumetric flask containing 1.0 mL of 1.00 M
2-
NaOH (see 8.3). Dilute to volume with laboratory grade water.
11.1 If samples are known to have high levels of CO
-
Hg(CN) as CN = 100 mg/L. The solution must be stored in an
2 (above 1500 ppm), preserve the sample by adding 2 g/L
amber glass bottle under r
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.