ASTM G2-88(2002)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Corrosion Testing of Products of Zirconium, Hafnium, and Their Alloys in Water at 680°F or in Steam at 750°F
Standard Test Method for Corrosion Testing of Products of Zirconium, Hafnium, and Their Alloys in Water at 680°F or in Steam at 750°F
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers (1) the determination of mass gain, and (2) the surface inspection of products of zirconium, hafnium, and their alloys when corrosion tested in water at 680°F or in steam at 750°F.
1.2 This test method is to be utilized in its entirety to the extent specified herein as a product acceptance test.
1.3 This test method may be used on wrought products, castings, powder metallurgy products, and weld metals.
1.4 A complete metric companion to this test method has been developed, Test Method G 2M. Therefore, no metric equivalents are shown. However, since the mass gain and surface area of the specimen and the electrical resistivity of water are always measured or calculated in SI units, these are given in SI units.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:G2–88(Reapproved2002)
Standard Test Method for
Corrosion Testing of Products of Zirconium, Hafnium, and
Their Alloys in Water at 680°F or in Steam at 750°F
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G2; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers (1) the determination of mass 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
gain, and (2) the surface inspection of products of zirconium, 3.1.1 control coupons, n—zirconium alloy specimens of
hafnium, and their alloys when corrosion tested in water at known performance used to monitor the validity of the test.
680°F or in steam at 750°F. 3.1.2 etching, n—a process for removal of surface metal by
1.2 This test method is to be utilized in its entirety to the action of acids in water.
extent specified herein as a product acceptance test. 3.1.3 Grade A water, n—purified water having a pH of 5.0
1.3 This test method may be used on wrought products, to 8.0 and an electrical resistivity of not less than 1.0 MV·cm.
castings, powder metallurgy products, and weld metals. 3.1.4 Grade B water, n—water prepared with deionized or
1.4 A complete metric companion to this test method has demineralized water having a minimum electrical resistivity of
been developed, Test Method G2M. Therefore, no metric 0.5 MV·cm.
equivalents are shown. However, since the mass gain and 3.1.5 ThestatedvaluesofpHandelectricalresistivityareto
surface area of the specimen and the electrical resistivity of be met after the measured values are corrected to 77°F.
water are always measured or calculated in SI units, these are 3.1.6 high mass gain coupons, n—zirconium alloy speci-
given in SI units. mens that have been specially heat-treated to produce a mass
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the gain higher than the maximum specified as acceptable value
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the used for verifying the severity of the test.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1.7 reagent grade, n—The grade of chemicals normally
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- used for analytical purposes.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
4. Summary of Test Method
precautionary statements, see Section 9.
4.1 Specimens of zirconium, hafnium, or their alloys are
2. Referenced Documents
exposed to high-pressure water or steam at elevated tempera-
2.1 ASTM Standards: tures for 72 or 336 h. The corrosion is normally measured by
D888 Test Methods for Dissolved Oxygen in Water thegaininmassofthespecimensandbytheappearanceofthe
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to oxidefilmonthespecimensurfaces.Insomeinstances,suchas
Determine Conformance with Specifications weld evaluation, mass gain measurements are either impracti-
G2M Test Method for Corrosion Testing of Products of cal to make or not required. When so specified, appearance of
Zirconium, Hafnium, and Their Alloys in Water at 633°K the specimen shall be the sole criterion for acceptance.
or in Steam at 673°K [Metric]
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is primarily used as an acceptance test
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB10onReactive
for products of zirconium, hafnium, and their alloys. This
and Refractory Metals andAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
standard has been widely used in the development of new
B10.02 on Zirconium and Hafnium.
Current edition approved Jan. 29, 1988. Published March 1988. Originally
alloys, heat treating practices, and for evaluation of welding
published as G2–67. Last previous edition G2–81. DOI: 10.1520/G0002-88R02.
techniques.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
5.2 Specimens are normally tested after careful etching and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on rinsing. Specimens with as-manufactured surfaces may also be
the ASTM website.
tested without further surface removal.
Withdrawn.
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
G2–88 (2002)
5.3 When tubing with a second material clad on the inner organiccompounds,acidsandproductsofzirconium,hafnium,
surface is to be tested, the inner cladding shall be removed and their alloys should be obtained from competent sources.
prior to the test. 9.2 High-temperature, high-pressure autoclave operation
must be in accordance with government regulations and
6. Interferences
manufacturer’s instructions.
6.1 Autoclave loads that have one or more specimens 9.3 Hydrogen gas used for addition to the autoclave steam
supply must be handled in accordance with guidelines for
showing gross oxidation may affect results on other specimens
in the autoclave by contamination of the environment. explosives and flammables.
9.4 Donotaddcoldwaterdirectlytotheautoclavevesselin
7. Apparatus
order to accelerate cooling upon completion of testing.
7.1 The apparatus consists of equipment for (1) etching the
10. Sampling, Test Specimens, and Test Units
specimens when required, (2) measuring the specimen surface
area and mass, the water resistivity and pH, test temperature
10.1 The size and the quantity of the test specimens, the
and pressure, etch and rinse temperature, and (3) performing
method of selection, surface preparation, and test acceptance
the water or steam corrosion test at elevated temperature and
criteria shall be specified in the product specification or by
pressure.
agreement between the purchaser and the seller as stated in the
7.1.1 Etching—An acid bath, a flowing rinse, and a deion-
purchase contract.
ized water rinse are needed for proper metal removal and
10.2 Each specimen and control coupons shall be individu-
stain-free rinsing. Polyethylene or polypropylene tanks are
ally identified.
commonly used with a bottom feed for flowing water rinses.
Specimen hangers are generally made of Type 300 series
11. Preparation of Apparatus
stainless steel. When many specimens are processed, a me-
11.1 General requirements for new or reworked autoclaves
chanical dipper for the etching process is useful.
and parts of autoclaves previously used for testing materials
7.1.2 Autoclaves, constructed of Type 300 series stainless
other than to this standard are as follows:
steel or nickel base alloys such as UNS grade N06600 or
11.1.1 Before specimens are tested in a new or reworked
N06690andaremanufacturedtoconformtoASME(American
autoclave, or in one having new valves, tubing, gaskets, etc.,
SocietyforMechanicalEngineers)andgovernmentregulations
which contact the test specimen, clean the apparatus thor-
governingunfiredpressurevessels.Theautoclaveisfittedwith
oughly, wipe with reagent grade ethanol or acetone, and rinse
devices for measurement and control of pressure and tempera-
twice with Grade B water. Dry the autoclave or auxiliary
ture, safety devices, and venting valves. Control systems for
equipmentbyvacuumcleaningordrainandwipewithaclean,
pressure and temperature adequate to meet the requirements of
lint-free cloth, and inspect carefully to ensure freedom from
this standard are needed. Sample holders and other internal
contamination.Thereshallbenovisiblecontamination,suchas
accessories are also constructed of Type 300 or 400 series
lubricant, residues, dust or dirt, loose oxides or rust, and oil or
stainless steel, or nickel-base alloys such as UNS grade
grease film on the water surface, internal surface, gasket, or
N06600 or N06690.
head surfaces.
NOTE 1—Ifautoclaveheatingisperformedinanoven,theovenandnot 11.1.2 Clean all new and reworked fixtures and jigs to be
the autoclave will have the automatic temperature-control equipment.
usedintheautoclave,rinseinhotGradeBwater.Autoclavethe
fixtures and jigs for at least 1 day at 750°F in 1500 psi steam
7.1.3 Measuring Equipment, capable of measuring speci-
or at 680°F in water. Inspect the parts for corrosion product. If
mendimensionsto0.002in.andabalancecapableofweighing
−4
corrosion product is found or electrical resistivity of the
specimens to 1 310 g are needed.
residualwaterafterthetestmeasureslessthan0.1MV·cm,the
8. Reagents and Materials parts should be cleaned and autoclaved again.
11.2 General requirements for autoclaves and parts in con-
8.1 Argon Gas, welding grade.
tinuous use for corrosion testing under this standard are as
8.2 Grade A Water.
follows:
8.3 Grade B Water.
11.2.1 With Grade B water rinse all autoclaves, fixtures,
8.4 Detergents and Solvents, for specimen cleaning includ-
parts, and jigs that have been in continuous use and have
ing reagent grade ethanol and reagent grade acetone.
shown satisfactory behavior in prior tests. Inspect the fixtures
8.5 Hydrofluoric Acid (HF), reagent grade.
and jigs for corrosion products after each test and rework and
8.6 Nitric Acid (HNO ), reagent grade.
re-prepare items showing loose corrosion product.
8.7 Sulfuric Acid (H SO ), reagent grade.
2 4
8.8 Nitrogen Gas, for purging or controlling oxygen con-
12. Calibration and Standardization
tent.
8.9 Argon-Hydrogen Mixed Gas, for purging or controlling
12.1 High Mass Gain Coupon Preparation—Thesecoupons
oxygen content.
shall be selected from a previously tested lot. The selected
material shall be heat treated to produce the desired mass gain.
9. Hazards
Heating for8hat 1652 6 5°F and cooling to 572 6 5°F at a
9.1 The chemicals used in preparing specimens for this test rate not exceeding 6°F/min will normally produce the desired
are hazardous. Detailed information on safe handling of mass gain.
G2–88 (2002)
12.2 Autoclaves: established in 12.2.2.6 or may be calculated periodically using
12.2.1 Prior to use for product acceptance testing, an auto- all accepted values determined over the preceding 3-month
clave shall be profiled thermally as in 12.4.2 and shall period but not less than 21 values.
demonstrate acceptability by testing at least three control 12.2.3 An alternative method for establishing the mass gain
coupons, one each at the top, middle, and bottom of useful
meanandstandarddeviationforthecontrolcouponswhichare
volume. The test results shall be incorporated in the certifica- used repeatedly is:
tiondocumentfortheautoclaveacceptancetest.Whendesired,
12.2.3.1 Expose the control coupons to be used in three
high mass gain coupons may also be used.
different tests, once each in the top, middle, and bottom of an
12.2.2 Establishing Mass Gain Mean and Standard Devia-
autoclave, and determine mass gain.
tion of Control Coupons—The control coupon lot and, when
12.2.3.2 Themeanvalueofeachcontrolcouponisthemean
desired, the high mass gain coupon lot mass gain mean and
for the three tests.
standard deviation shall be established by a minimum of one
12.2.3.3 Thestandarddeviationforthecontrolcouponlotis
autoclave test as follows:
calculated by the (n-1) method using the data from all of the
12.2.2.1 Randomly select 12 specimens from the control
control coupons taken from the same material lot.
coupon lot or the high mass gain coupon lot respectively.
12.2.4 The new or used autoclave is considered acceptable
12.2.2.2 Prepare all specimens per the pretest requirements
if each control coupon mass gain is reproducible within the
of this test method.
previously established control coupon mean mass gain 63
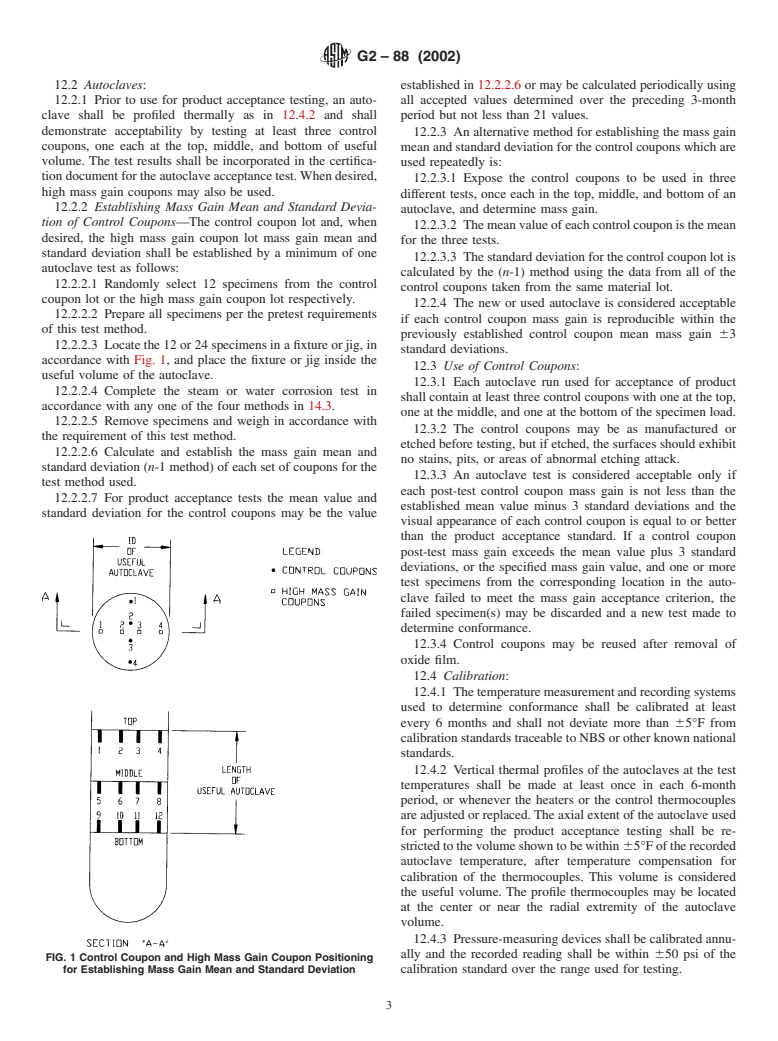
12.2.2.3 Locatethe12or24specimensinafixtureorjig,in
standard deviations.
accordance with Fig. 1, and place the fixture or jig inside the
12.3 Use of Control Coupons:
useful volume of the autoclave.
12.3.1 Each autoclave run used for acceptance of product
12.2.2.4 Complete the steam or water corrosion test in
shall contain at least three control coupons with one at the top,
accordance with any one of the four methods in 14.3.
one at the middle, and one at the bottom of the specimen load.
12.2.2.5 Remove specimens and weigh in accordance with
12.3.2 The control coupons may be as manufactured or
the requirement of this test method.
etched before testing, but if etched, the surfaces should exhibit
12.2.2.6 Calculate and establish the mass gain mean and
no stains, pits, or areas of abnormal etching attack.
standard deviation (n-1 method) of each set of coupons for the
12.3.3 An autoclave test is considered acceptable only if
test method used.
each post-test control coupon mass gain is not less than the
12.2.2.7 For product acceptance tests the mean value and
established mean value minus 3 standard deviations and the
standard deviation for the control coupons may be the value
visual appearance of each control coupon is equal to or better
than the product acceptance standard. If a control coupon
post-test mass gain exceeds the mean value plus 3 standard
deviations, or the specified mass gain value, and one or more
test specimens from the corresponding location in the auto-
clave failed to meet the mass gain acceptance criterion, the
failed specimen(s) may be discarded and a new test made to
determine conformance.
12.3.4 Control coupons may be reused after removal of
oxide film.
12.4 Calibration:
12.4.1 Thetemperaturemeasurementandrecordingsystems
used to determine conformance shall be calibrated at least
every 6 months and shall not deviate more than 65°F from
calibrationstandardstraceabletoNBSorotherknownnational
standards.
12.4.2 Vertical thermal profiles of the autoclaves at the test
temperatures shall be made at least once in each 6-month
period, or whenever the heaters or the control thermocouples
areadjustedorreplaced.Theaxialextentoftheautoclaveused
for performing the product acceptance testing shall be re-
strictedtothevolumeshowntobewithin 65°Foftherecorded
autoclave temperature, after temperature compensation for
calibration of the thermocouples. This volume is considered
the useful volume. The profile thermocouples may be located
at the center or near the radial extremity of the autoclave
volume.
12.4.3 Pressure-measuring devices shall be calibrated annu-
ally and the recorded reading shall be within 650 psi of the
FIG. 1 Control Coupon and High Mass Gain Coupon Positioning
for Establishing Mass Gain Mean and Standard Deviation calibration standard over the range used for testing.
G2–88 (2002)
13. Conditioning washers or wire mesh grids may be used
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.