ASTM D7078/D7078M-20e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Shear Properties of Composite Materials by V-Notched Rail Shear Method
Standard Test Method for Shear Properties of Composite Materials by V-Notched Rail Shear Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This shear test is designed to produce shear property data for material specifications, research and development, quality assurance, and structural design and analysis. Either in-plane or interlaminar shear properties may be evaluated, depending upon the orientation of the material coordinate system relative to the loading axis. Factors that influence the shear response and should therefore be reported include: material, methods of material preparation and lay-up, specimen stacking sequence, specimen preparation, specimen conditioning, environment of testing, specimen alignment and gripping, speed of testing, time at temperature, void content, and volume percent reinforcement.
5.2 In anisotropic materials, properties may be obtained in any of the six possible shear planes by orienting the testing plane of the specimen with the desired material plane (1-2 or 2-1, 1-3 or 3-1, 2-3 or 3-2). Only a single shear plane may be evaluated for any given specimen. Properties, in the test direction, which may be obtained from this test method, include the following:
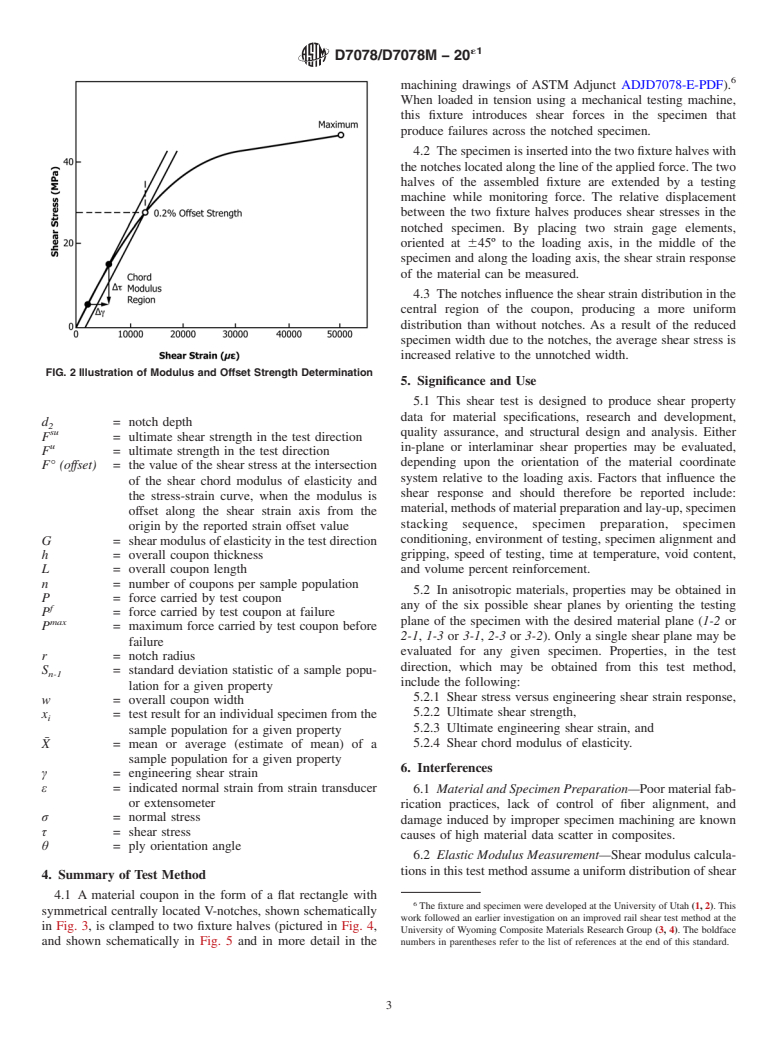
5.2.1 Shear stress versus engineering shear strain response,
5.2.2 Ultimate shear strength,
5.2.3 Ultimate engineering shear strain, and
5.2.4 Shear chord modulus of elasticity.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the shear properties of high-modulus fiber-reinforced composite materials by clamping the ends of a V-notched specimen between two pairs of loading rails. When loaded in tension, the rails introduce shear forces into the specimen through the specimen faces. In comparison, the specimen of Test Method D5379/D5379M is loaded through its top and bottom edges. Face loading allows higher shear forces to be applied to the specimen, if required. Additionally, the present test method utilizes a specimen with a larger gage section than the V-notched specimen of Test Method D5379/D5379M. In both test methods, the use of a V-notched specimen increases the gage section shear stresses in relation to the shear stresses in the vicinity of the grips, thus localizing the failure within the gage section while causing the shear stress distribution to be more uniform than in a specimen without notches. In comparison, Test Method D4255/D4255M utilizes an unnotched specimen clamped between two pairs of loading rails that are loaded in tension. Also, in contrast to Test Method D4255/D4255M, the present test method provides specimen gripping without the need for holes in the specimen.
The composite materials are limited to continuous-fiber or discontinuous-fiber-reinforced composites in the following material forms:
1.1.1 Laminates composed only of unidirectional fibrous laminae, with the fiber direction oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the fixture rails.
1.1.2 Laminates of balanced and symmetric construction, with the 0° direction oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the fixture rails.
1.1.3 Laminates composed of woven, braided, or knitted fabric filamentary laminae.
1.1.4 Short-fiber-reinforced composites with a majority of the fibers being randomly distributed.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.2.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in brackets.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on stand...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: D7078/D7078M − 20
Standard Test Method for
Shear Properties of Composite Materials by V-Notched Rail
1
Shear Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7078/D7078M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorial corrections were made to the adjunct information in March 2021.
1. Scope 1.1.4 Short-fiber-reinforced composites with a majority of
the fibers being randomly distributed.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the shear
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
properties of high-modulus fiber-reinforced composite materi-
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The
alsbyclampingtheendsofaV-notchedspecimenbetweentwo
values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equiva-
pairs of loading rails. When loaded in tension, the rails
lents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each
introduce shear forces into the specimen through the specimen
system shall be used independently of the other, and values
faces. In comparison, the specimen of Test Method D5379/
from the two systems shall not be combined.
D5379M is loaded through its top and bottom edges. Face
1.2.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in
loading allows higher shear forces to be applied to the
brackets.
specimen, if required. Additionally, the present test method
utilizes a specimen with a larger gage section than the
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
V-notched specimen of Test Method D5379/D5379M. In both
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
test methods, the use of a V-notched specimen increases the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
gage section shear stresses in relation to the shear stresses in
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
the vicinity of the grips, thus localizing the failure within the
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
gage section while causing the shear stress distribution to be
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
more uniform than in a specimen without notches. In
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
comparison, Test Method D4255/D4255M utilizes an un-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
notched specimen clamped between two pairs of loading rails
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
that are loaded in tension. Also, in contrast to Test Method
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
D4255/D4255M, the present test method provides specimen
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
gripping without the need for holes in the specimen.
2. Referenced Documents
The composite materials are limited to continuous-fiber or
2
discontinuous-fiber-reinforcedcompositesinthefollowingma-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
terial forms: D792Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
1.1.1 Laminates composed only of unidirectional fibrous tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
laminae, with the fiber direction oriented either parallel or
perpendicular to the fixture rails. D2584Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced
Resins
1.1.2 Laminates of balanced and symmetric construction,
D2734TestMethodsforVoidContentofReinforcedPlastics
withthe0°directionorientedeitherparallelorperpendicularto
D3171Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite
the fixture rails.
Materials
1.1.3 Laminates composed of woven, braided, or knitted
D3878Terminology for Composite Materials
fabric filamentary laminae.
D4255/D4255MTest Method for In-Plane Shear Properties
of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by the Rail Shear
Method
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on
Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.04 on
2
Lamina and Laminate Test Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published April 2020. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D7078/D7078M–19. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D7078_D7078M-20E01. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-295
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.