ASTM D5018-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Shear Viscosity of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches
Standard Test Method for Shear Viscosity of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is useful as one element in establishing the uniformity of shipments.
4.2 Viscosity is also valuable for rheological characterization of binder pitches. Binder pitch imparts consistency to carbonaceous mixes and affects their resistance to deformation. Binder pitch viscosity is important for assessing mix consistency and for evaluating the ease of mix extrusion or molding into artifacts.
SCOPE
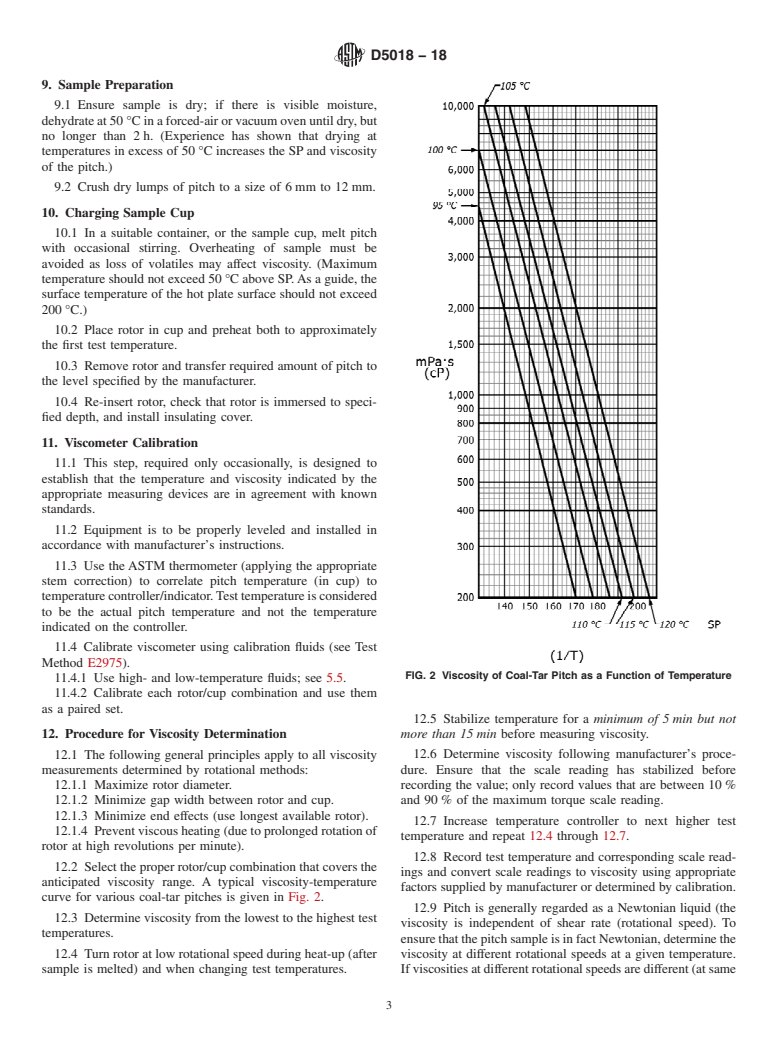
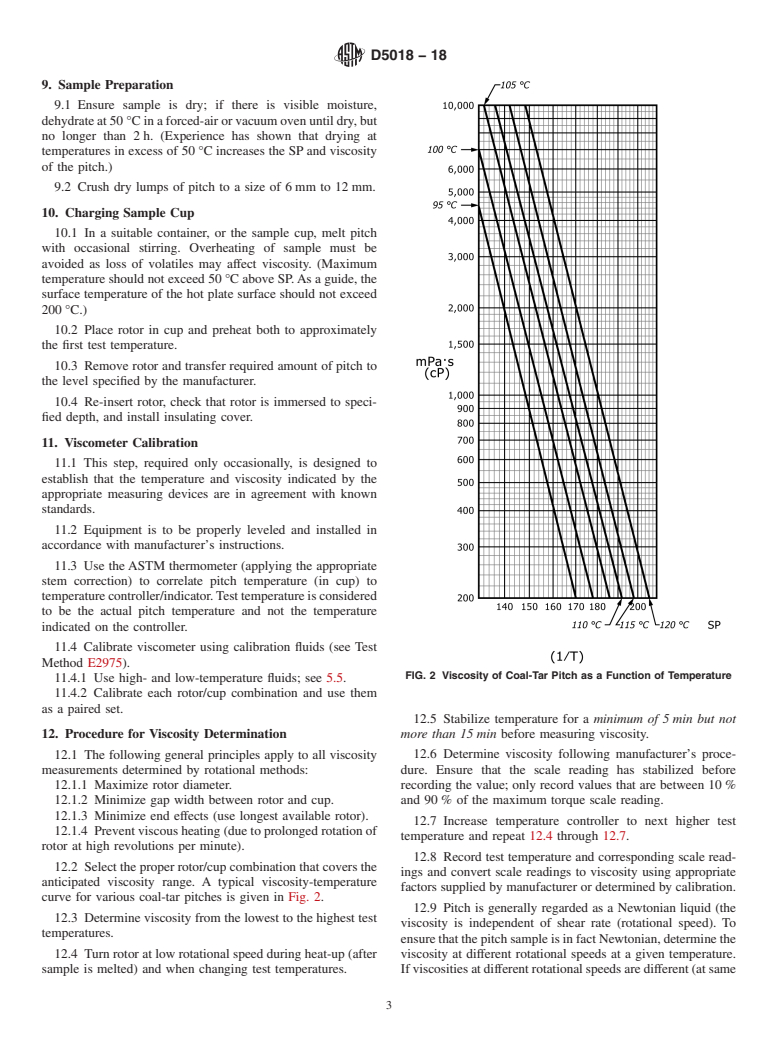
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent shear viscosity of coal-tar and petroleum-based pitches having a Mettler softening point (SP) range of approximately 95 °C to 120 °C (see Test Method D3104).
1.2 This test method is applicable only for rotational viscometers.
1.3 Since this test method is based on theoretical grounds, strict adherence to details of the procedure is necessary to comply with the theoretical requirements.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4.1 Exception—The values stated in conventional units (centipoise) are to be regarded as the standard for viscosity measurement only. The SI unit is the pascal second (Pa·s) and one millipascal second (mPa·s) = one centipoise (cP); centipoise is in cgs units.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5018 −18
Standard Test Method for
1
Shear Viscosity of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5018; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D3104Test Method for Softening Point of Pitches (Mettler
Softening Point Method)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the appar-
D4296Practice for Sampling Pitch
ent shear viscosity of coal-tar and petroleum-based pitches
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
having a Mettler softening point (SP) range of approximately
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
95°C to 120°C (see Test Method D3104).
E1953Practice for Description of Thermal Analysis and
1.2 This test method is applicable only for rotational vis-
Rheology Apparatus
cometers.
E2975Test Method for Calibration or Calibration Verifica-
1.3 Since this test method is based on theoretical grounds, tion of Concentric Cylinder Rotational Viscometers
strict adherence to details of the procedure is necessary to
3. Summary of Test Method
comply with the theoretical requirements.
3.1 The viscosity of a pitch, over the temperature range of
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
about 40°C to 100°C above the SP of the material, is
standard.
determined using a rotational viscometer.
1.4.1 Exception—The values stated in conventional units
3.2 The recommended specifications herein are for measur-
(centipoise) are to be regarded as the standard for viscosity
ing the apparent shear viscosity of binder pitches via a
measurement only. The SI unit is the pascal second (Pa·s) and
concentric cylinder viscometer.Apparent shear viscosity is the
one millipascal second (mPa·s)=one centipoise (cP); centi-
ratio of shear stress to shear rate in a unidirectional simple
poise is in cgs units.
shear flow field at steady state conditions. A concentric
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
cylinder viscometer is useful for measuring the apparent shear
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
viscosity, provided the sample temperature is adequately
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
controlled, the “end-effects” are negligible, and the gap be-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
tween rotor/cup is small and remains constant during the test.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
The extrapolated value of apparent shear viscosity at “zero”
Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
shear rate is called shear viscosity.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 Thistestmethodisusefulasoneelementinestablishing
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
the uniformity of shipments.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.2 Viscosity is also valuable for rheological characteriza-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
tion of binder pitches. Binder pitch imparts consistency to
carbonaceousmixesandaffectstheirresistancetodeformation.
2. Referenced Documents
Binder pitch viscosity is important for assessing mix consis-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tency and for evaluating the ease of mix extrusion or molding
into artifacts.
5. Apparatus
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of
5.1 Viscometer—Arotationalviscometercapableofmeasur-
SubcommitteeD02.05onPropertiesofFuels,PetroleumCokeandCarbonMaterial.
ing viscosity in the range of about 5 mPa·s (cP) to
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2018.PublishedJuly2018.Originallyapproved
ɛ1
15000mPa·s(cP);theviscometershouldbeequippedwiththe
in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D5018–89 (2015) . DOI:
10.1520/D5018-18.
appropriate accessories to allow measurements up to about
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
230°C. The essential instrumentation required providing the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
minimum rotational viscometer analytical capabilities include
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. (see Practice E1953):
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D5018 − 89 (Reapproved 2015) D5018 − 18
Standard Test Method for
1
Shear Viscosity of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5018; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—SI units formatting was corrected editorially in May 2015.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent shear viscosity of coal-tar and petroleum-based pitches having
a Mettler softening point (SP) range of approximately 95 °C to 120 °C.120 °C (see Test Method D3104).
1.2 This test method is applicable only for rotational viscometers.
1.3 Since this test method is based on theoretical grounds, strict adherence to details of the procedure is necessary to comply
with the theoretical requirements.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4.1 Exception—The values stated in conventional units (centipoise) are to be regarded as the standard for viscosity
measurement only. The SI unit is the pascal second (Pa·s) and one millipascal second (mPa·s) = one centipoise (cps);(cP);
centipoise is in cgs units.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D3104 Test Method for Softening Point of Pitches (Mettler Softening Point Method)
D4296 Practice for Sampling Pitch
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1953 Practice for Description of Thermal Analysis and Rheology Apparatus
E2975 Test Method for Calibration or Calibration Verification of Concentric Cylinder Rotational Viscometers
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The viscosity of a pitch, over the temperature range of about 40 °C to 100 °C above the SP of the material, is determined
using a rotational viscometer.
3.2 The recommended specifications herein are for measuring the apparent shear viscosity of binder pitches via a concentric
cylinder viscometer. Apparent shear viscosity is the ratio of shear stress to shear rate in a unidirectional simple shear flow field
at steady state conditions. A concentric cylinder viscometer is useful for measuring the apparent shear viscosity, provided the
sample temperature is adequately controlled, the “end-effects” are negligible, and the gap between rotor/cup is small and remains
constant during the test. The extrapolated value of apparent shear viscosity at “zero” shear rate is called shear viscosity.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.05 on Properties of Fuels, Petroleum Coke and Carbon Material.
Current edition approved April 1, 2015June 1, 2018. Published May 2015July 2018. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 20092015 as
ɛ1
D5018 – 89 (2009).(2015) . DOI: 10.1520/D5018-89R15E01.10.1520/D5018-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5018 − 18
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is useful as one element in establishing the uniformity of shipments.
4.2 Viscosity is also valuable for rheological characterization of binder pitches. Binder pitch imparts consistency to
carbonaceous mixes and affects their resi
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5018 − 18
Standard Test Method for
1
Shear Viscosity of Coal-Tar and Petroleum Pitches
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5018; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D3104 Test Method for Softening Point of Pitches (Mettler
Softening Point Method)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the appar-
D4296 Practice for Sampling Pitch
ent shear viscosity of coal-tar and petroleum-based pitches
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
having a Mettler softening point (SP) range of approximately
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
95 °C to 120 °C (see Test Method D3104).
E1953 Practice for Description of Thermal Analysis and
1.2 This test method is applicable only for rotational vis-
Rheology Apparatus
cometers.
E2975 Test Method for Calibration or Calibration Verifica-
tion of Concentric Cylinder Rotational Viscometers
1.3 Since this test method is based on theoretical grounds,
strict adherence to details of the procedure is necessary to
3. Summary of Test Method
comply with the theoretical requirements.
3.1 The viscosity of a pitch, over the temperature range of
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
about 40 °C to 100 °C above the SP of the material, is
standard.
determined using a rotational viscometer.
1.4.1 Exception—The values stated in conventional units
3.2 The recommended specifications herein are for measur-
(centipoise) are to be regarded as the standard for viscosity
ing the apparent shear viscosity of binder pitches via a
measurement only. The SI unit is the pascal second (Pa·s) and
concentric cylinder viscometer. Apparent shear viscosity is the
one millipascal second (mPa·s) = one centipoise (cP); cen-
ratio of shear stress to shear rate in a unidirectional simple
tipoise is in cgs units.
shear flow field at steady state conditions. A concentric
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
cylinder viscometer is useful for measuring the apparent shear
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
viscosity, provided the sample temperature is adequately
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
controlled, the “end-effects” are negligible, and the gap be-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
tween rotor/cup is small and remains constant during the test.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
The extrapolated value of apparent shear viscosity at “zero”
Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
shear rate is called shear viscosity.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 This test method is useful as one element in establishing
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
the uniformity of shipments.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.2 Viscosity is also valuable for rheological characteriza-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
tion of binder pitches. Binder pitch imparts consistency to
carbonaceous mixes and affects their resistance to deformation.
2. Referenced Documents
Binder pitch viscosity is important for assessing mix consis-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tency and for evaluating the ease of mix extrusion or molding
into artifacts.
5. Apparatus
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of
5.1 Viscometer—A rotational viscometer capable of measur-
Subcommittee D02.05 on Properties of Fuels, Petroleum Coke and Carbon Material.
ing viscosity in the range of about 5 mPa·s (cP) to
Current edition approved June 1, 2018. Published July 2018. Originally approved
ɛ1
15 000 mPa·s (cP); the viscometer should be equipped with the
in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D5018 – 89 (2015) . DOI:
10.1520/D5018-18.
appropriate accessories to allow measurements up to about
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
230 °C. The essential instrumentation required providing the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
minimum rotational viscometer analytical capabilities include
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. (see Practice E1953):
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, Wes
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.