ASTM D6560-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Asphaltenes (Heptane Insolubles) in Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products
Standard Test Method for Determination of Asphaltenes (Heptane Insolubles) in Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Asphaltenes are the organic molecules of highest molecular mass and carbon-hydrogen ratio normally occurring in crude petroleum and petroleum products containing residual material. They may give problems during storage and handling if the suspension of asphaltene molecules is disturbed through excess stress or incompatibility. They are also the last molecules in a product to combust completely, and thus may be one indicator of black smoke propensity. Their composition normally includes a disproportionately high quantity of the sulfur, nitrogen, and metals present in the crude petroleum or petroleum product.
SCOPE
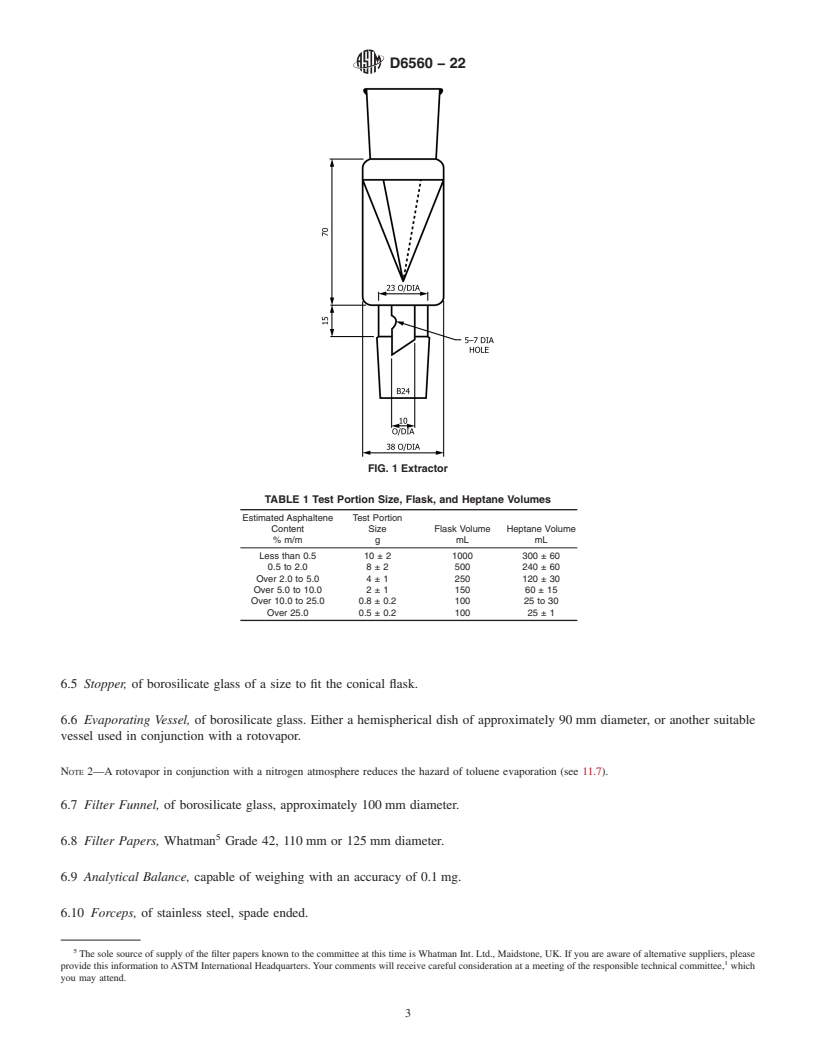
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for the determination of the heptane insoluble asphaltene content of gas oil, diesel fuel, residual fuel oils, lubricating oil, bitumen, and crude petroleum that has been topped to an oil temperature of 260 °C (see A1.2.1.1).
1.2 The precision is applicable to values between 0.50 % m/m and 30.0 % m/m. Values outside this range may still be valid but may not give the same precision values.
1.3 Oils containing additives may give erroneous results.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6560 −22
Designation: IP 143⁄21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Asphaltenes (Heptane Insolubles) in Crude
1,2
Petroleum and Petroleum Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
3
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for the determina-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tion of the heptane insoluble asphaltene content of gas oil,
D86Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and
diesel fuel, residual fuel oils, lubricating oil, bitumen, and
Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
crude petroleum that has been topped to an oil temperature of
D1298Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
260°C (see A1.2.1.1).
Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
ucts by Hydrometer Method
1.2 The precision is applicable to values between
D4052Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
0.50%m⁄m and 30.0%m⁄m. Values outside this range may
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
still be valid but may not give the same precision values.
D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
1.3 Oils containing additives may give erroneous results.
Petroleum Products
D4175Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Fuels, and Lubricants
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
D4177Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
standard.
Petroleum Products
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4
2.2 Energy Institute Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3. Terminology
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1 Definitions:
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
to Terminology D4175.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.2 asphaltenes, n—(rarely used in the singular) — in
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
petroleum technology, represent an oil fraction that is soluble
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
in a specified aromatic solvent but separates upon addition of
an excess of a specified paraffinic solvent.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In this test method, the aromatic sol-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM International Committee
vent is hot toluene and the paraffinic solvent is heptane.
D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct
3.1.2.2 Discussion—Historically, benzene was the aromatic
responsibility of ASTM Subcommittee D02.14 on Stability, Cleanliness and
Compatibility of Liquid Fuels. The technically equivalent standard as referenced is
solvent, but benzene is not typically used now for health
under the jurisdiction of the Energy Institute Subcommittee SC-B-5.
reasons. The precision of this test method when using toluene
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2022.PublishedJuly2022.Originallyapproved
has been found to be the same as when using benzene.
in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D6560–17. DOI: 10.1520/
D6560-22.
2
This standard is based on material published in the IP Standard methods for
Analysis and Testing of Petroleum and Related Products and British Standard 2000
3
Parts, copyright Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish Street, London, W1M 8AR. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Adapted with permission of Energy Institute. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
This test method has been developed through the cooperative effort between Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ASTMandtheEnergyInstitute,London.ASTMandIPstandardswereapprovedby the ASTM website.
4
ASTMandEItechnicalcommitteesasbeingtechnicallyequivalentbutthatdoesnot Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIM 8AR,
imply both standards are identical. UK.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocke
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6560 − 17 D6560 − 22
Designation: IP 143 ⁄01⁄21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Asphaltenes (Heptane Insolubles) in Crude
1,2
Petroleum and Petroleum Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for the determination of the heptane insoluble asphaltene content of gas oil, diesel fuel,
residual fuel oils, lubricating oil, bitumen, and crude petroleum that has been topped to an oil temperature of 260 °C (see A1.2.1.1).
1.2 The precision is applicable to values between 0.50 % m ⁄m and 30.0 % m ⁄m. Values outside this range may still be valid but
may not give the same precision values.
1.3 Oils containing additives may give erroneous results.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM International Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility
of ASTM Subcommittee D02.14 on Stability, Cleanliness and Compatibility of Liquid Fuels. The technically equivalent standard as referenced is under the jurisdiction of
the Energy Institute Subcommittee SC-B-5.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017June 1, 2022. Published March 2018July 2022. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20122017 as
D6560 – 12.D6560 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/D6560-17.10.1520/D6560-22.
2
This standard is based on material published in the IP Standard methods for Analysis and Testing of Petroleum and Related Products and British Standard 2000 Parts,
copyright Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish Street, London, W1M 8AR. Adapted with permission of Energy Institute.
This test method has been developed through the cooperative effort between ASTM and the Energy Institute, London. ASTM and IP standards were approved by ASTM
and EI technical committees as being technically equivalent but that does not imply both standards are identical.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6560 − 22
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
4
2.2 Energy Institute Standard:
Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.1.2 asphaltenes, n—(rarely used in the singular) — in petroleum technology, represent an oil fraction that is soluble in a specified
aromatic solvent but separates upon addition of an excess of a specified paraffinic solvent.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
In this test method, the aromatic solvent is hot toluene and the paraffini
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.