ISO 13002:1998
(Main)Carbon fibre — Designation system for filament yarns
Carbon fibre — Designation system for filament yarns
1.1 This International Standard establishes a system of designation for filament yarns of carbon fibre which may be used as the basis for specifications. 1.2 This designation system is applicable to filament yarns used for the reinforcement of polymer composites. It does not apply to discontinuous fibre products pyrolized in the form of staple yarns, woven fabrics, braids, knits, mats, etc. 1.3 The types of filament yarns are differentiated from each other by a classification system based on appropriate levels of the designatory properties: a) tensile modulus of elasticity; b) tensile strength; c) linear density. 1.4 It is not intended to imply that materials having the same designation give the same performance. This International Standard does not provide engineering data, performance data or data on processing conditions which may be required to specify a material for a particular application and/or method of processing. 1.5 In order to specify a filament yarn for a particular application or to ensure reproducible processing, additional requirements may be given in data block 3 (see clause 3).
Fibres de carbone — Système de désignation des fils continus
1.1 La présente Norme internationale établit un système de désignation des fils continus de carbone, susceptible d'être utilisé comme base pour les spécifications. 1.2 Le présent système de désignation s'applique aux fils continus de carbone utilisés comme renforts dans les composites à matrice polymère. Il ne s'applique pas aux produits faits de fibres discontinues, pyrolisés sous forme de fils, tissus, tresses, tricots, mats, etc. 1.3 Les types de fils de carbone sont différenciés les uns des autres au moyen d'un système de classement basé sur différents niveaux des propriétés retenues pour la désignation: a) le module d'élasticité en traction; b) la résistance en traction; c) la masse linéique. 1.4 Le fait que des matériaux puissent avoir la même désignation n'impliquent pas qu'ils aient la même performance. La présente Norme internationale ne fournit pas de caractéristiques pour le dimensionnement, de données sur les performances ou de données sur les conditions de fabrication, qui peuvent être nécessaires pour spécifier un matériau pour une application particulière et/ou une méthode de fabrication. 1.5 Pour spécifier un fil de carbone pour une application particulière ou pour assurer une mise en œuvre reproductible, des exigences supplémentaires peuvent être données dans le bloc de données 3 (voir article 3).
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 11-Nov-1998
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 13 - Composites and reinforcement fibres
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 13/WG 1 - Reinforcements and reinforcement products
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 04-Mar-2031
Relations
- Consolidates
EN ISO 13002:1998 - Carbon fibre - Designation system for filament yarns (ISO 13002:1998) - Effective Date
- 12-Feb-2026
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
Overview
ISO 13002:1998, titled "Carbon fibre - Designation system for filament yarns," is an international standard developed by ISO to establish a consistent and clear system for the designation of carbon fibre filament yarns. This standard applies specifically to filament yarns used in reinforcing polymer composites and excludes discontinuous fibre products like staple yarns, woven fabrics, braids, and mats.
The designation system in ISO 13002 enables manufacturers, users, and specifiers to classify carbon filament yarns based on key designatory properties, making it foundational for creating specifications related to carbon fibre materials.
Key Topics
Scope and Application
The standard’s scope targets filament yarns in carbon fibre for polymer composite reinforcement but does not cover discontinuous fibres or other fabric forms.Designation System Structure
The system uses a structured designation consisting of:- An optional description block (e.g., "Reinforcing fibre")
- An identity block referencing the International Standard number (ISO 13002)
- An individual-item block subdivided into three data blocks:
- Data block 1: Carbon fibre precursor yarn and product form (e.g., AC for acrylic fibre filament yarn)
- Data block 2: Key mechanical properties and linear density specified via coded numbers
- Data block 3 (optional): Additional application-specific requirements such as filament diameter, twist, surface treatment, or thermal stability
Designatory Properties
Distinctions among filament yarns rely on:- Tensile modulus of elasticity, coded with a three-digit number representing gigapascal (GPa) ranges
- Tensile strength, coded by a two-digit number representing strength in megapascals (MPa)
- Linear density, coded by a four-digit number representing tex (mass per unit length)
Standardized Testing Methods
Tensile modulus is measured according to ISO 10618 (Method B), and linear density according to ISO 1889, ensuring reproducibility and global alignment.Designation Example
A carbon filament yarn from an acrylic precursor with a tensile modulus of 233 GPa, tensile strength of 3,540 MPa, and linear density of 198 tex would be designated as:ISO 13002-CF-AC,225-35-200,,
Applications
This designation system is critical for industries involved in manufacturing and utilizing carbon fibre reinforced polymer composites, including:
- Aerospace and Automotive: For selecting appropriate carbon fibre filament yarns that meet safety and performance requirements.
- Sports Equipment: Ensuring consistency and quality in high-strength, lightweight composite materials.
- Construction and Civil Engineering: Standardizing reinforcement fibres that influence structural integrity and durability.
- Composite Material Suppliers and Manufacturers: Facilitating clear communication and specification compliance throughout the supply chain.
By applying ISO 13002, stakeholders can achieve:
- Improved material traceability
- Enhanced specification accuracy for design and processing
- Streamlined compliance with international quality requirements
- Better alignment of manufacturer and end-user expectations
Related Standards
- ISO 10618 - Carbon fibre: Determination of tensile properties of resin-impregnated yarns (test methods related to tensile modulus).
- ISO 1889 - Reinforcement yarns: Determination of linear density (measurement of yarn mass per unit length).
These complementary standards are referenced in ISO 13002 to define the testing and measurement protocols necessary for accurate designation and classification of carbon filament yarns.
Keywords: ISO 13002, carbon fibre designation, filament yarns, tensile modulus, tensile strength, linear density, polymer composites, carbon fibre standards, composite reinforcement, fibre classification, carbon fibre specifications.
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Control Union Certifications
Global certification for agriculture and sustainability.

Bureau Veritas Bangladesh
Bureau Veritas certification services in Bangladesh.

ECOCERT France
Leader in organic and sustainability certification worldwide.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 13002:1998 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Carbon fibre — Designation system for filament yarns". This standard covers: 1.1 This International Standard establishes a system of designation for filament yarns of carbon fibre which may be used as the basis for specifications. 1.2 This designation system is applicable to filament yarns used for the reinforcement of polymer composites. It does not apply to discontinuous fibre products pyrolized in the form of staple yarns, woven fabrics, braids, knits, mats, etc. 1.3 The types of filament yarns are differentiated from each other by a classification system based on appropriate levels of the designatory properties: a) tensile modulus of elasticity; b) tensile strength; c) linear density. 1.4 It is not intended to imply that materials having the same designation give the same performance. This International Standard does not provide engineering data, performance data or data on processing conditions which may be required to specify a material for a particular application and/or method of processing. 1.5 In order to specify a filament yarn for a particular application or to ensure reproducible processing, additional requirements may be given in data block 3 (see clause 3).
1.1 This International Standard establishes a system of designation for filament yarns of carbon fibre which may be used as the basis for specifications. 1.2 This designation system is applicable to filament yarns used for the reinforcement of polymer composites. It does not apply to discontinuous fibre products pyrolized in the form of staple yarns, woven fabrics, braids, knits, mats, etc. 1.3 The types of filament yarns are differentiated from each other by a classification system based on appropriate levels of the designatory properties: a) tensile modulus of elasticity; b) tensile strength; c) linear density. 1.4 It is not intended to imply that materials having the same designation give the same performance. This International Standard does not provide engineering data, performance data or data on processing conditions which may be required to specify a material for a particular application and/or method of processing. 1.5 In order to specify a filament yarn for a particular application or to ensure reproducible processing, additional requirements may be given in data block 3 (see clause 3).
ISO 13002:1998 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 59.100.20 - Carbon materials. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 13002:1998 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to EN ISO 13002:1998, ISO 5889:1983. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 13002:1998 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL ISO
STANDARD 13002
First edition
1998-11-15
Carbon fibre — Designation system for
filament yarns
Fibres de carbone — Système de désignation des fils continus
A
Reference number
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO
member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical
committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in
liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member bodies for voting.
Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting a vote.
International Standard ISO 13002 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 61, Plastics, Subcommittee
SC 13, Composites and reinforcement fibres.
© ISO 1998
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic
or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Switzerland
Internet iso@iso.ch
Printed in Switzerland
ii
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD © ISO ISO 13002:1998(E)
Carbon fibre — Designation system for filament yarns
1 Scope
1.1 This International Standard establishes a system of designation for filament yarns of carbon fibre which may be
used as the basis for specifications.
1.2 This designation system is applicable to filament yarns used for the reinforcement of polymer composites.
It does not apply to discontinuous fibre products pyrolized in the form of staple yarns, woven fabrics, braids, knits,
mats, etc.
1.3 The types of filament yarns are differentiated from each other by a classification system based on appropriate
levels of the designatory properties:
a) tensile modulus of elasticity;
b) tensile strength;
c) linear density.
1.4 It is not intended to imply that materials having the same designation give the same performance. This
International Standard does not provide engineering data, performance data or data on processing conditions which
may be required to specify a material for a particular application and/or method of processing.
1.5 In order to specify a filament yarn for a particular application or to ensure reproducible processing, additional
requirements may be given in data block 3 (see clause 3).
2 Normative references
The following standards contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this
International Standard. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards are subject to
revision, and parties to agreements based on this International Standard are encouraged to investigate the
possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below. Members of IEC and ISO maintain
registers of currently valid International Standards.
ISO 1889:1997, Reinforcement yarns — Determination of linear density.
1)
ISO 10618:— , Carbon fibre — Determination of tensile properties of resin-impregnated yarns.
1) To be published.
© ISO
3 Designation system
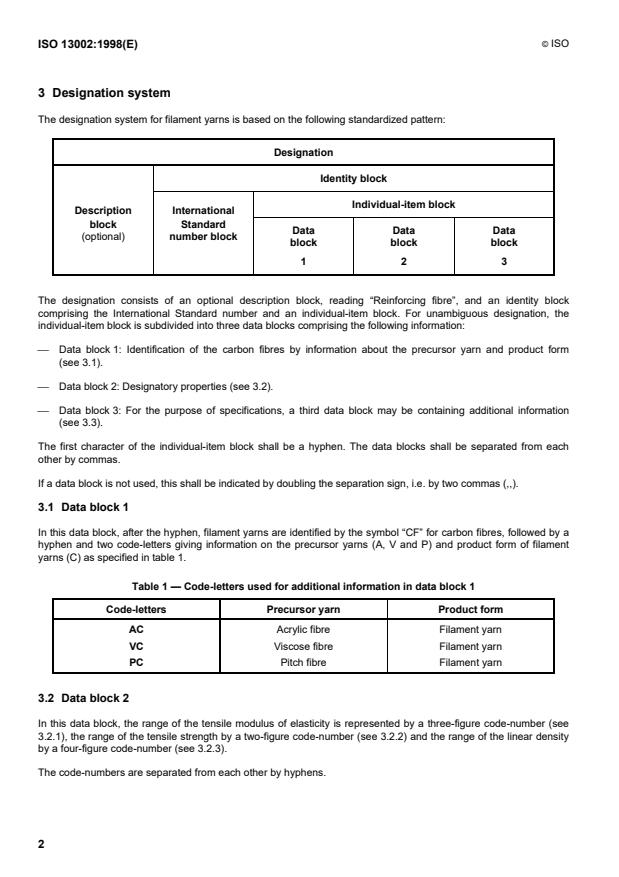
The designation system for filament yarns is based on the following standardized pattern:
Designation
Identity block
Individual-item block
Description International
block Standard
Data Data Data
(optional) number block
block block block
The designation consists of an optional description block, reading “Reinforcing fibre”, and an identity block
comprising the International Standard number and an individual-item block. For unambiguous designation, the
individual-item block is subdivided into three data blocks comprising the following information:
Data block 1: Identification of the carbon fibres by information about the precursor yarn and product form
(see 3.1).
Data block 2: Designatory properties (see 3.2).
Data block 3: For the purpose of specifications, a third data block may be containing additional information
(see 3.3).
The first character of the individual-item block shall be a hyphen. The data blocks shall be separated from each
other by commas.
If a data block is not used, this shall be indicated by doubling the separation sign, i.e. by two
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 13002
Première édition
1998-11-15
Fibres de carbone — Système de
désignation des fils continus
Carbon fibre — Designation system for filament yarns
A
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L'ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
l'ISO). L'élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de l'ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales,
en liaison avec l'ISO participent également aux travaux. L'ISO collabore
étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en
ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l'approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 13002 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 61, Plastiques, sous-comité SC 13, Composites et fibres de
renforcement.
© ISO 1998
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l'accord
écrit de l'éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Suisse
Internet iso@iso.ch
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
©
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO ISO 13002:1998(F)
Fibres de carbone — Système de désignation des fils
continus
1 Domaine d'application
1.1 La présente Norme internationale établit un système de désignation des fils continus de carbone, susceptible
d'être utilisé comme base pour les spécifications.
1.2 Le présent système de désignation s'applique aux fils continus de carbone utilisés comme renforts dans les
composites à matrice polymère.
Il ne s'applique pas aux produits faits de fibres discontinues, pyrolisés sous forme de fils, tissus, tresses, tricots,
mats, etc.
1.3 Les types de fils de carbone sont différenciés les uns des autres au moyen d'un système de classement basé
sur différents niveaux des propriétés retenues pour la désignation:
a) le module d'élasticité en traction;
b) la résistance en traction;
c) la masse linéique.
1.4 Le fait que des matériaux puissent avoir la même désignation n'impliquent pas qu'ils aient la même
performance. La présente Norme internationale ne fournit pas de caractéristiques pour le dimensionnement, de
données sur les performances ou de données sur les conditions de fabrication, qui peuvent être nécessaires pour
spécifier un matériau pour une application particulière et/ou une méthode de fabrication.
1.5 Pour spécifier un fil de carbone pour une application particulière ou pour assurer une mise en œuvre
reproductible, des exigences supplémentaires peuvent être données dans le bloc de données 3 (voir article 3).
2 Références normatives
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions qui, par suite de la référence qui en est faite constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente Norme internationale. Au moment de la publication, les éditions indiquées
étaient en vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision, et les parties prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente
Norme internationale sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d'appliquer les éditions les plus récentes des normes
indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CEI et de l'ISO possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en vigueur
à un moment donné.
©
ISO 1889:1997, Fils de renfort — Détermination de la masse linéique.
1)
ISO 10618:— , Fibres de carbone — Détermination des propriétés en traction sur fils imprégnés de résine.
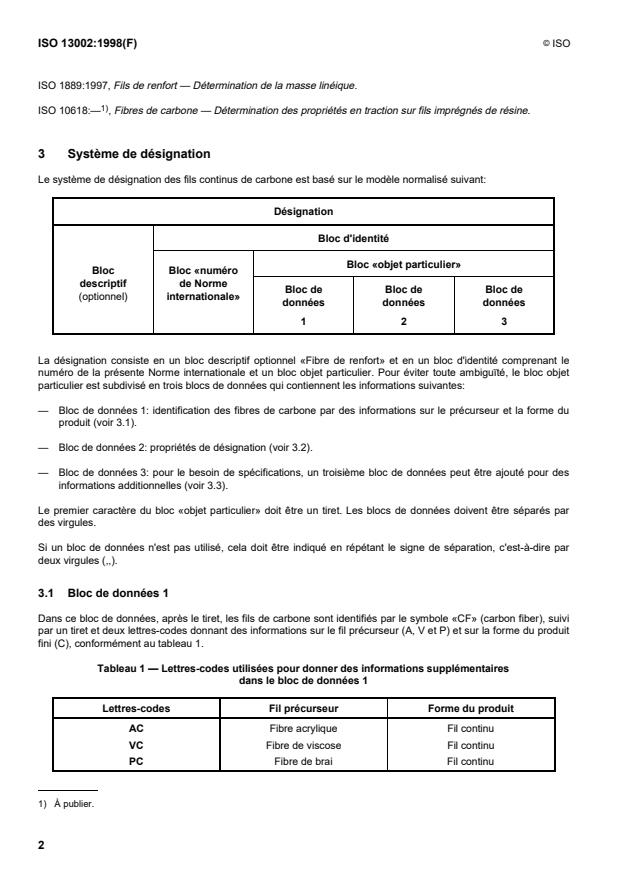
3 Système de désignation
Le système de désignation des fils continus de carbone est basé sur le modèle normalisé suivant:
Désignation
Bloc d'identité
Bloc «objet particulier»
Bloc Bloc «numéro
descriptif de Norme
Bloc de Bloc de Bloc de
(optionnel) internationale»
données données données
La désignation consiste en un bloc descriptif optionnel «Fibre de renfort» et en un bloc d'identité comprenant le
numéro de la présente Norme internationale et un bloc objet particulier. Pour éviter toute ambiguïté, le bloc objet
particulier est subdivisé en trois blocs de données qui contiennent les informations suivantes:
— Bloc de données 1: identification des fibres de carbone par des informations sur le précurseur et la forme du
produit (voir 3.1).
— Bloc de données 2: propriétés de désignation (voir 3.2).
— Bloc de données 3: pour le besoin de spécifications, un troisième bloc de données peut être ajouté pour des
informations additionnelles (voir 3.3).
Le premier caractère du bloc «objet particulier» doit être un tiret. Les blocs de données doivent être séparés par
des virgules.
Si un bloc de données n'est pas utilisé, cela doit être indiqué en répétant le signe de séparation, c'est-à-dire par
deux virgules (,,).
3.1 Bloc de données 1
Dans ce bloc de données
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...