ISO 3674:1976
(Main)Shipbuilding — Inland vessels — Deck rail
Shipbuilding — Inland vessels — Deck rail
Specifies the types, designs and basic dimensions of ship deck handrail. Does not apply to special deck rails designed for particular purposes.
Construction navale — Bateaux de navigation intérieure — Garde-corps
General Information
- Status
- Withdrawn
- Publication Date
- 30-Apr-1976
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 8/SC 7 - Inland navigation vessels
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 8/SC 7 - Inland navigation vessels
- Current Stage
- 9599 - Withdrawal of International Standard
- Start Date
- 16-Jun-2025
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 3674:1976 - Shipbuilding: Inland vessels - Deck rail defines standard types, basic designs and principal dimensions for deck handrails (garde-corps) used on inland waterway vessels. The standard covers common rail types (tube, trellis/mesh, chain, cable) and their variants (fixed, demountable, foldable) and excludes special-purpose rails (for example rails intended specifically for cargo restraint or timber lashing).
Key topics and technical requirements
Scope and classification
- Applies to deck rails used on all types of inland navigation vessels.
- Classifies rails by construction: tube, trellis (mesh), chain and cable; each can be fixed, demountable or foldable where applicable.
Materials and strength
- Steel sections must be made of weldable steel with a minimum strength of 350 N/mm² for all steel rail sections.
Tube rails
- Construction follows specified component layout and dimensional tables. Typical tube sizes referenced include 33.7 mm (1") and 21.3 mm (1/2") for different elements.
- Mounting choices depend on whether the rail is fixed (ferrure K) or demountable (ferrure L).
Trellis (mesh) rails
- Two construction variants are specified with corresponding dimensional limits and fixing options.
Chain rails
- Chains must have a minimum breaking/limit load of 9 kN.
- Chain sag (deflection) must not exceed 50 mm; chain span guidance (max spacing) is illustrated (e.g., up to 2000 mm between supports in the standard diagrams).
- Chains should be suspended with spring hooks or simple hooks and terminate on stanchions (chandeliers) with pegs.
Cable rails
- Minimum steel cable diameter: 6 mm.
- Typical span ranges shown: 2,000–4,000 mm; for 900 mm rail height a single top cable may be acceptable.
- Cable guides and turnbuckle (ridoirs) arrangements are specified.
Fixings and fittings
- Fixing types are standardized:
- Ferrure K - rigid (fixed) mounting;
- Ferrure L - demountable mounting;
- Ferrure M - foldable mounting.
- Demountable sections must be easily removed and stowed horizontally; removable sections must include devices to prevent unintended separation. Socket/receiver details (e.g., sockets for 33.7 mm posts made from 42.4 mm tube) are specified.
- Fixing types are standardized:
Applications and users
ISO 3674 is used by:
- Shipbuilders and shipyards constructing inland vessels
- Naval architects and designers specifying deck safety systems
- Classification societies and flag authorities reviewing compliance
- Fabricators, welders and riggers installing deck handrails
- Port operators and safety officers updating vessel safety equipment
Practical benefits include consistent safety performance, interchangeable fittings and clear fabrication/installation guidance for common guardrail systems.
Related standards
For comprehensive ship safety and structural requirements, refer to broader shipbuilding and maritime safety standards and classification rules used by national and international authorities (consult classification societies and current ISO maritime standards for updates or complementary guidance).
ISO 3674:1976 - Shipbuilding -- Inland vessels -- Deck rail
ISO 3674:1976 - Construction navale -- Bateaux de navigation intérieure -- Garde-corps
ISO 3674:1976 - Construction navale -- Bateaux de navigation intérieure -- Garde-corps
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

DNV
DNV is an independent assurance and risk management provider.

Lloyd's Register
Lloyd's Register is a global professional services organisation specialising in engineering and technology.

ABS Quality Evaluations Inc.
American Bureau of Shipping quality certification.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 3674:1976 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Shipbuilding — Inland vessels — Deck rail". This standard covers: Specifies the types, designs and basic dimensions of ship deck handrail. Does not apply to special deck rails designed for particular purposes.
Specifies the types, designs and basic dimensions of ship deck handrail. Does not apply to special deck rails designed for particular purposes.
ISO 3674:1976 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 47.060 - Inland navigation vessels. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 3674:1976 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION +lEXAYHAPO~HAJl OPI-AHM3AUMJl no CTAH~AP-IM3A4WW.ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Shipbuilding - Inland vessels - Deck rail
- Bateaux de navigation intkieure - Garde-Corps
Constfuction navale
First edition - 1976-05-01
iii
-
UDC 629.12.011.74 : 629.122 Ref. No. ISO 3674-1976 (E)
Descriptors : shipbuilding, inland navigation, ships, parapets, stanchions, chains, classification, dimensions.
-
Price based on 6 pages
FOREWORD
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worlwide federation
of national Standards institutes (ISO Member Bodies). The work of developing
International Standards is carried out through ISO Technical Committees. Every
Member Body interested in a subject for which a Technical Committee has been set
up has the right to be represented on that Committee. International organizations,
governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the Technical Committees are circulated
to the Member Bodies for approval before their acceptance as International
Standards by the ISO Council.
International Standard ISO 3674 was drawn up by Technical Committee ISO/TC 8,
Shipbuilding, and circulated to the Member Bodies in February 1975.
lt has been approved by the Member Bodies of the following countries :
Austria Israel Romania
Belgium I taly Spain
Brazil Japan Turkey
Bulgaria Mexico United Kingdom
Czechoslovakia Netherlands
France Poland
The Member Bodies of the following countries expressed disapproval of the
docu ment on technical grounds :
Germany
I reland
0 International Organkation for Standardkation, 1976 l
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 36744976 (E)
Shipbuilding - Inland vessels - Deck rail
1 SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION
4.3 Tiltable deck rail should be easy to release and tilt on
the deck.
This International Standard specifies the types, designs and
basic dimensions of ship deck handrail (hereinafter called
deck rail).
4.4 In passageways, detachable sections shall be fitted
with devices which secure against spontaneous release.
Chains may also be used instead of detachable sections.
2 FIELD OF APPLICATION
2.1 The deck rails specified are intended for use on
4.5 Weldable steel with a minimum tensile strength of
vessels of all types for inland waterways.
350 N/mm2 shall be used for all steel sections of deck rail.
2.2 The International Standard does not apply to special
TABLE 1
deck rails designed for particular purposes, for example
for fastening of wood loaded on the deck of a ship, solid
deck rail formed by overlapping plating, etc.
Tube
3 CLASSIFICATION
Network
Deck rails are classified in conformity with table 1.
4 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Chain
4.1 As a rule, solid deck rail is fitted to the deck or the
plating of a ship by welding.
Rope 111
4.2 Detachable deck rail is fitted to the deck by means
of clamps or receptacles so that it may be easily dismantled.
ISO 3674-1976 (E)
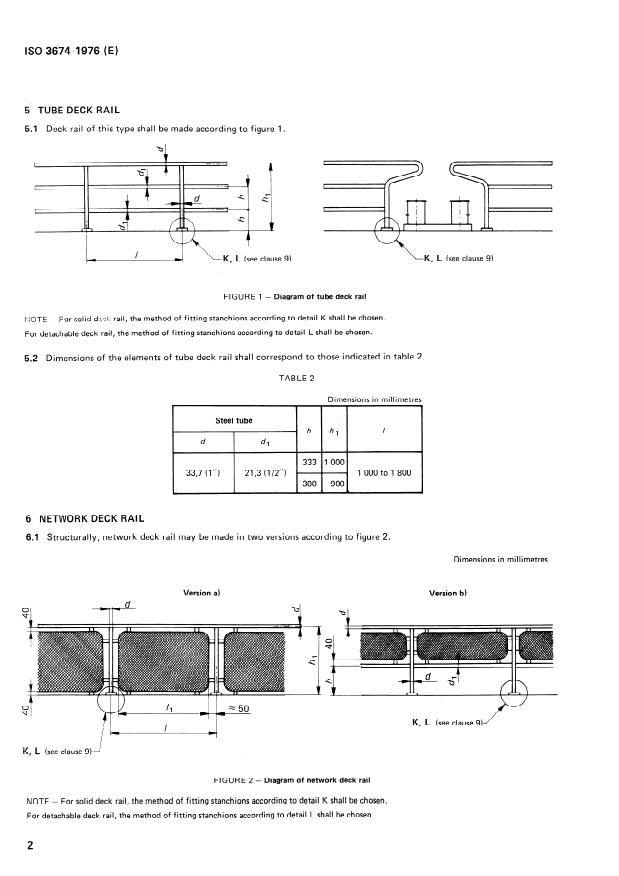
5- TUBE DECK RAIL
5.1 Deck rail of this type shall be made according to figure 1.
. IM
1 1
c: i I ‘)
1’ !
Y
K, L (sec clause 9) K, L (sec clause 9)
FIGURE 1 - Diagram of tube deck rail
NOTE - For solid dx!,:. rail, the method of fitting stanchions according to detail K shall be Chosen.
For detachable deck rail, the method of fitting stanchions according to detail L shall be Chosen.
5.2 Dimensions of the elements of tube deck rail shall correspond to those indicated in table 2.
TABLE 2
Dimensions in millimetres
I
Steel tube
h hl /
d
dl
333 1 000
33,7 (1”) 21,3 (1/2”) 1 000 to 1 800
300 900
6 NETW
...
NORME INTERNATIONALE
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION .ME)+(ayHAP(jflHAA OPrAHM3ALIMR l-l0 CTAH~!&4PT~ï3AL~MM .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Construction navale - Bateaux de navigation intérieure -
Garde-corps
Shipbuilding - lnland Vesse/s - Deck rail
Première édition - 1976-05-01
CDU 629.12.011.74 : 629.122 Réf. no : ISO 3674-1976 (F)
Descripteurs : construction navale, navigation intérieure, navire, garde-corps, chandelier de garde-corps, chaîne, classification, dimension.
Prix basé sur 6 pages
AVANT-PROPOS
ISO (Organisation Internationale de Normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (Comités Membres ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes Internationales est confiée aux Comités Techniques ISO. Chaque
Comité Membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du Comité
Technique correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et
non gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les Projets de Normes Internationales adoptés par les Comités Techniques sont
soumis aux Comités Membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme
Normes Internationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme Internationale ISO 3674 a été établie par le Comité Technique ISO/TC 8,
Construction navale, et soumise aux Comités Membres en février 1975.
Elle a été approuvée par les Comités Membres des pays suivants :
Autriche Israël Roumanie
Belgique Italie Royaume-Uni
Brésil Japon Tchécoslovaquie
Bulgarie Mexique Turquie
Espagne Pays-Bas
France Pologne
Les Comités Membres des pays suivants ont désapprouvé le document pour des
raisons techniques :
Allemagne
Irlande
0 Organisation Internationale de Normalisation, 1976 l
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 36744976 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Bateaux de navigation intérieure -
Construction navale -
Garde-corps
1 OBJET 4.3 Les garde-corps rabattables doivent pouvoir être
facilement démontés et placés horizontalement sur le pont.
La présente Norme Internationale spécifie les types, cons-
tructions et dimensions principales de garde-corps de
4.4 Aux points de raccordement, les sections démontables
bateaux (nommés par la suite simplement ((garde-corps))).
doivent être munies de dispositifs interdisant leur sépara-
tion. II est admissible d’utiliser des chaînes au lieu des
2 DOMAINE D’APPLICATION
sections détachables.
2.1 Les garde-corps spécifiés sont destinés à l’utilisation à
bord des bateaux de tous types de navigation intérieure.
4.5 Un acier soudable, ayant une résistance minimale de
350 N/mm2, doit être utilisé pour toutes les sections en
acier du garde-corps.
2.2 La présente Norme Internationale n’est pas applicable
aux garde-corps spéciaux destinés aux cas particuliers, par
TABLEAU 1
exemple aux matières en bois chargées à bord du bateau,
aux gardes-corps fixes formés par le bordage, etc.
3 CLASSIFICATION
fixe
Les garde-corps sont classés d’après le tableau 1.
Treillis
démontable
4 CARACTÉRISTIQUES GÉNÉRALES
démontable
4.1 En règle générale, les garde-corps fixes sont soudés au Chaîne
rabattable
pont ou au bordé du bateau.
démontable
4.2 Les garde-corps démontables sont fixés sur le pont à
Câble
l’aide d’étriers ou d’emboîtement assurant leur démontage
rabattable
rapide.
ISO 3674-1976 (F)
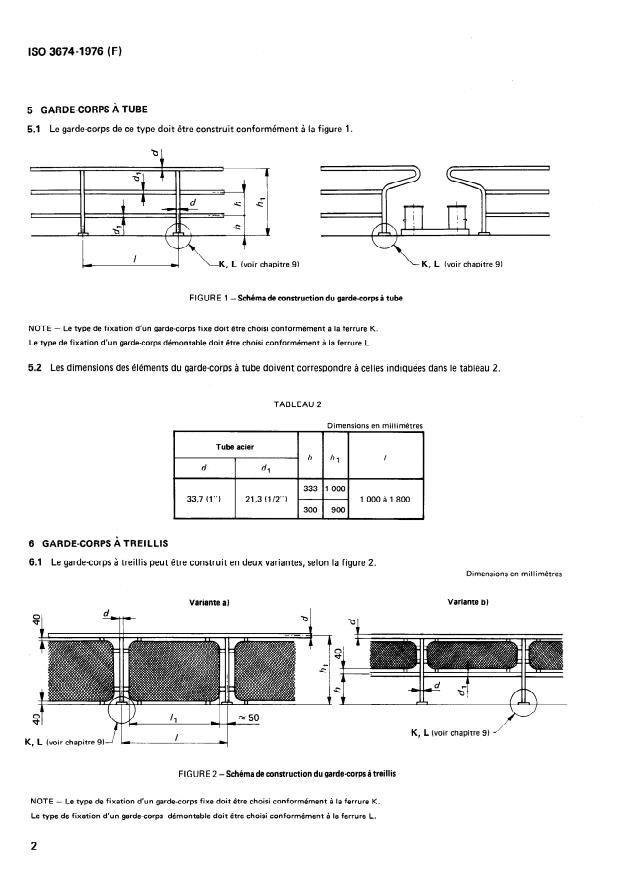
5 GARDE-CORPS À TUBE
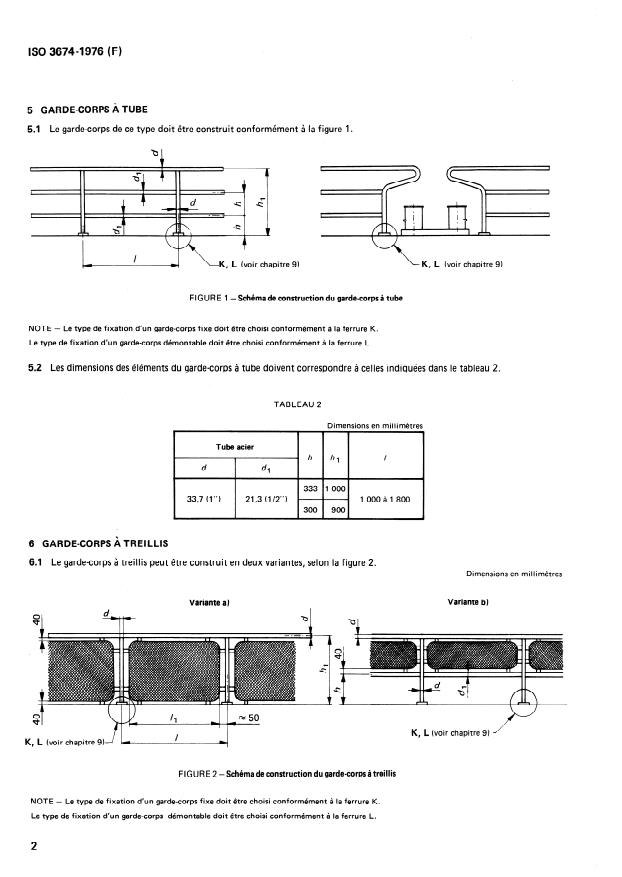
5.1 Le garde-corps de ce type doit être construit conformément à la figure 1.
1 I
. , 4
b , 4
I
I y;
L: i
I
1 I
Y
K, L (voir chapitre 9) K, L (voir chapitre 9)
FIGURE 1 -Schémade construction du garde-corpsà tube
NOTE - Le type de fixation d’un garde-corps fixe doit être choisi conformément à la ferrure K.
Le type de fixation d’un garde-corps démontable doit être choisi conformément à la ferrure L.
5.2 Les dimensions des éléments du garde-corps à tube doivent correspondre à celles indiquées dans le tableau 2.
TABLEAU 2
Dimensions en millimètrt
Tube acier
/
1 h hl
d 4
333 1 000
33,7 (1”) 21,3 (1/2”) 7 1 000 à 1 800
300 900
6 GARDE-CORPS À TREILLIS
6.1 Le garde-corps à treillis peut être construit en deux variantes, selon la figure 2.
...
NORME INTERNATIONALE
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION .ME)+(ayHAP(jflHAA OPrAHM3ALIMR l-l0 CTAH~!&4PT~ï3AL~MM .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Construction navale - Bateaux de navigation intérieure -
Garde-corps
Shipbuilding - lnland Vesse/s - Deck rail
Première édition - 1976-05-01
CDU 629.12.011.74 : 629.122 Réf. no : ISO 3674-1976 (F)
Descripteurs : construction navale, navigation intérieure, navire, garde-corps, chandelier de garde-corps, chaîne, classification, dimension.
Prix basé sur 6 pages
AVANT-PROPOS
ISO (Organisation Internationale de Normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (Comités Membres ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes Internationales est confiée aux Comités Techniques ISO. Chaque
Comité Membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du Comité
Technique correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et
non gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les Projets de Normes Internationales adoptés par les Comités Techniques sont
soumis aux Comités Membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme
Normes Internationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme Internationale ISO 3674 a été établie par le Comité Technique ISO/TC 8,
Construction navale, et soumise aux Comités Membres en février 1975.
Elle a été approuvée par les Comités Membres des pays suivants :
Autriche Israël Roumanie
Belgique Italie Royaume-Uni
Brésil Japon Tchécoslovaquie
Bulgarie Mexique Turquie
Espagne Pays-Bas
France Pologne
Les Comités Membres des pays suivants ont désapprouvé le document pour des
raisons techniques :
Allemagne
Irlande
0 Organisation Internationale de Normalisation, 1976 l
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 36744976 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Bateaux de navigation intérieure -
Construction navale -
Garde-corps
1 OBJET 4.3 Les garde-corps rabattables doivent pouvoir être
facilement démontés et placés horizontalement sur le pont.
La présente Norme Internationale spécifie les types, cons-
tructions et dimensions principales de garde-corps de
4.4 Aux points de raccordement, les sections démontables
bateaux (nommés par la suite simplement ((garde-corps))).
doivent être munies de dispositifs interdisant leur sépara-
tion. II est admissible d’utiliser des chaînes au lieu des
2 DOMAINE D’APPLICATION
sections détachables.
2.1 Les garde-corps spécifiés sont destinés à l’utilisation à
bord des bateaux de tous types de navigation intérieure.
4.5 Un acier soudable, ayant une résistance minimale de
350 N/mm2, doit être utilisé pour toutes les sections en
acier du garde-corps.
2.2 La présente Norme Internationale n’est pas applicable
aux garde-corps spéciaux destinés aux cas particuliers, par
TABLEAU 1
exemple aux matières en bois chargées à bord du bateau,
aux gardes-corps fixes formés par le bordage, etc.
3 CLASSIFICATION
fixe
Les garde-corps sont classés d’après le tableau 1.
Treillis
démontable
4 CARACTÉRISTIQUES GÉNÉRALES
démontable
4.1 En règle générale, les garde-corps fixes sont soudés au Chaîne
rabattable
pont ou au bordé du bateau.
démontable
4.2 Les garde-corps démontables sont fixés sur le pont à
Câble
l’aide d’étriers ou d’emboîtement assurant leur démontage
rabattable
rapide.
ISO 3674-1976 (F)
5 GARDE-CORPS À TUBE
5.1 Le garde-corps de ce type doit être construit conformément à la figure 1.
1 I
. , 4
b , 4
I
I y;
L: i
I
1 I
Y
K, L (voir chapitre 9) K, L (voir chapitre 9)
FIGURE 1 -Schémade construction du garde-corpsà tube
NOTE - Le type de fixation d’un garde-corps fixe doit être choisi conformément à la ferrure K.
Le type de fixation d’un garde-corps démontable doit être choisi conformément à la ferrure L.
5.2 Les dimensions des éléments du garde-corps à tube doivent correspondre à celles indiquées dans le tableau 2.
TABLEAU 2
Dimensions en millimètrt
Tube acier
/
1 h hl
d 4
333 1 000
33,7 (1”) 21,3 (1/2”) 7 1 000 à 1 800
300 900
6 GARDE-CORPS À TREILLIS
6.1 Le garde-corps à treillis peut être construit en deux variantes, selon la figure 2.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...