ASTM E1786-08
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine by On-Line Infrared Spectrophotometry
Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine by On-Line Infrared Spectrophotometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Trace amounts of water may be detrimental to the use of chlorine in some applications. The amount of water in the chlorine must be known to prevent problems during its use.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is designed for the on-line determination of the content of water in liquid chlorine in the concentration range of 0.5 to 15 mg/kg (ppm).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Review the current Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 and Note 3.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1786 − 08
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine by
1
On-Line Infrared Spectrophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1786; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 173.315Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable
Tank Containers
1.1 This test method is designed for the on-line determina-
4
2.3 Other Document:
tion of the content of water in liquid chlorine in the concen-
tration range of 0.5 to 15 mg/kg (ppm). Chlorine Institute Pamphlet No. 77—Sampling Liquid
Chlorine
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3. Summary of Test Method
only.
3.1 Liquid chlorine continuously flows through a special
1.3 ReviewthecurrentMaterialSafetyDataSheets(MSDS)
infrared cell where it is maintained as a liquid under its own
for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid
pressure. A process infrared spectrometer scans from 400 to
procedures, and safety precautions.
4400 wavenumbers of the infrared transmission spectrum of
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
liquid chlorine. This spectrum then is ratioed to one obtained
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
from the nitrogen-filled infrared cell previously. The ratioed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
spectrumisconvertedtoabsorbance,andthenetabsorbanceof
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
water band at 1596 wavenumbers, relative to a reference at
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards
1663 wavenumbers, is determined.
statements are given in Section 7 and Note 3.
3.2 The amount of water corresponding to this net absor-
banceisdeterminedfromacalibrationcurvepreparedfromthe
2. Referenced Documents
infrared absorbencies of standards which contain concentra-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tions of water in liquid chlorine. These standards are prepared
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
from manual samples of liquid chlorine in tantalum cylinders.
E806TestMethodforCarbonTetrachlorideandChloroform
Sample from each cylinder is introduced into a calibration
in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromato-
infraredcellandmaintainedasaliquidunderitsownpressure.
graphic Procedure)
3
2.2 Federal Standards:
4. Significance and Use
49 CFR 173Code of Federal RegulationsTitle 49Transpor-
4.1 Traceamountsofwatermaybedetrimentaltotheuseof
tation:Shippers’GeneralRequirementsforShipmentsand
chlorine in some applications. The amount of water in the
Packaging, including the following sections:
chlorine must be known to prevent problems during its use.
173.304Charging of Cylinders with Liquefied Compressed
Gas
5. Apparatus
173.314Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
5.1 Process Infrared Spectrometer, capable of measure-
ments in the 1600 wavenumber region. An FTIR with four
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
wavenumber resolution is the instrument of choice, but disper-
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
sive instruments also may be used to achieve similar results.
Subcommittee D16.16 on Industrial and Specialty Product Standards.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally
5.2 Special Infrared Calibration Cell (Fig. 1), as used for
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as E1786–02. DOI:
calibration. Neither cell size nor pathlength are critical to the
10.1520/E1786-08.
2
analysis,butsensitivityandlimitofdetectionaredependenton
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
Code of Federal Regulations, available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Available from The Chlorine Institute, Inc., 2001 L St. NW, Washington, DC
Washington, DC 20402. 20036-4919.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1786 − 08
FIG. 2 Pipe Adapter
FIG. 1 Infrared Cell (Drawing Not to Scale)
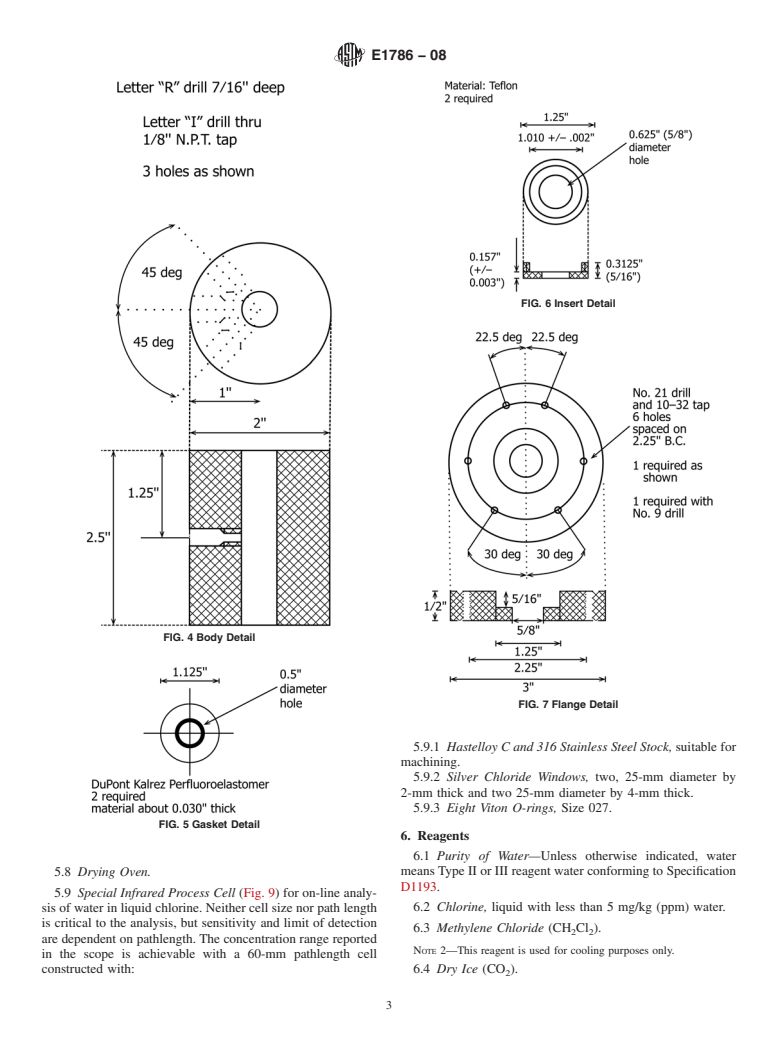
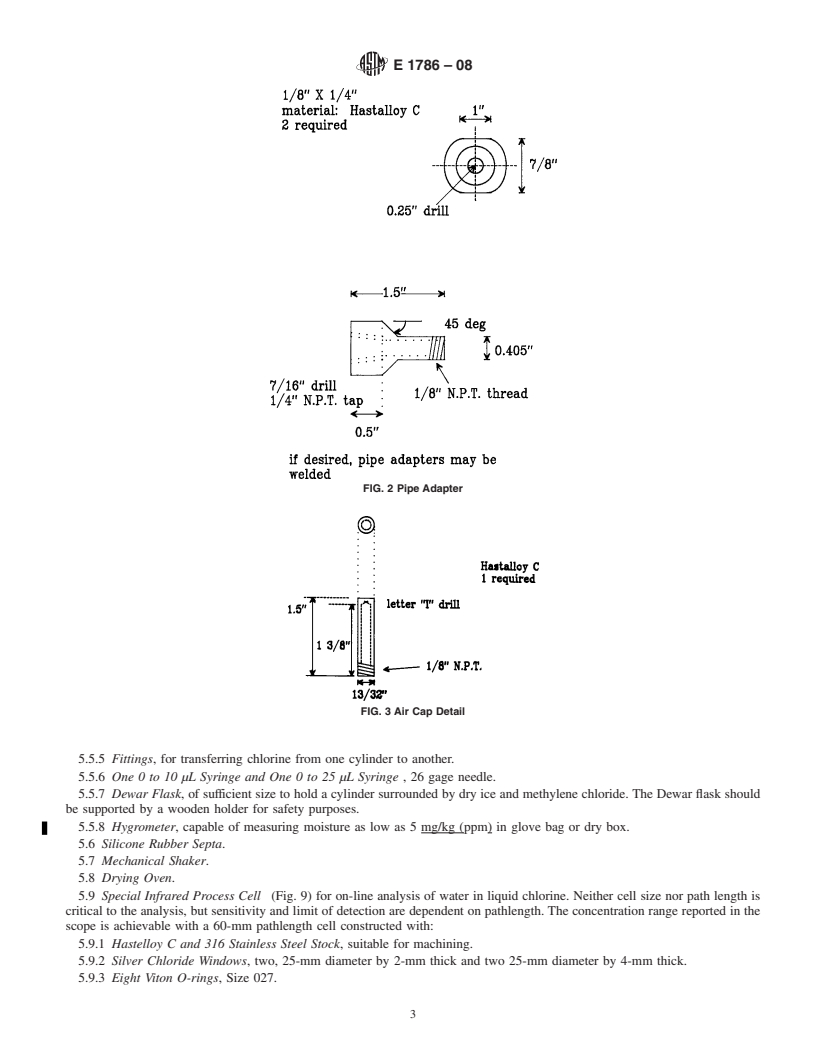
pathlength.TheconcentrationrangereportedintheSection1is
achievable with a 60-mm pathlength cell constructed with the
following: Figs. 2-7
5.2.1 Hastelloy C and 316 Stainless Steel Stock,suitablefor
ma
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E1786–02 Designation:E1786–08
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine by
1
On-Line Infrared Spectrophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1786; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method is designed for the on-line determination of the content of water in liquid chlorine in the concentration
range of 0.5 to 15 mg/kg (ppm).
1.2
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Review the current Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures,
and safety precautions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 and Note 2. Note 3.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
D1193Specifications for Reagent Water
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E 806 Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographyic
Procedure)
3
2.2 Federal Standards:
49CFR173CFR173 CodeofFederalRegulationsTitle49Transportation:Shippers’GeneralRequirementsforShipmentsand
Packaging, including the following sections:
173.304 Charging of Cylinders with Liquefied Compressed Gas
173.314 Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
173.315 Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable Tank Containers
4
2.3 Other Document:
Chlorine Institute Pamphlet No. 77 —Sampling Liquid Chlorine
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Liquid chlorine continuously flows through a special infrared cell where it is maintained as a liquid under its own pressure.
A process infrared spectrometer scans from 400 to 4400 wavenumbers of the infrared transmission spectrum of liquid chlorine.
This spectrum then is ratioed to one obtained from the nitrogen-filled infrared cell previously. The ratioed spectrum is converted
to absorbance, and the net absorbance of water band at 1596 wavenumbers, relative to a reference at 1663 wavenumbers, is
determined.
3.2 The amount of water corresponding to this net absorbance is determined from a calibration curve prepared from the infrared
absorbencies of standards which contain concentrations of water in liquid chlorine. These standards are prepared from manual
samples of liquid chlorine in tantalum cylinders. Sample from each cylinder is introduced into a calibration infrared cell and
maintained as a liquid under its own pressure.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.02 on
Product Standards.
Current edition approved March 10, 2002. Published May 2002. Originally published as E1786-96. Last previous edition E1786-96.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as E 1786 - 02.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 11.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05.Code of Federal Regulations, available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402.
4
Code of Federal Regulations, available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402.
4
Available from The Chlorine Institute, Inc., 2001 L St. NW, Washington, DC 20036-4919.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1786–08
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Trace amounts of water may be detrimental to the use of chlorine in some applications.The amount of water in the chlorine
must be known to prevent problems during its use.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Process Infrared Spectrometer , capable of measurements in
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.