ASTM F3592-23
(Guide)Standard Guide for Additive Manufacturing of Metals – Powder Bed Fusion – Guidelines for Feedstock Re-use and Sampling Strategies
Standard Guide for Additive Manufacturing of Metals – Powder Bed Fusion – Guidelines for Feedstock Re-use and Sampling Strategies
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The overall aim of this guide is to support AM users with the selection of the optimum re-use strategy for their AM process and end-use application, and provide guidance on how to implement re-use strategies in their organization.
4.2 This guide suggests possible control measures that AM users can use to maintain powder quality, and factors to consider when validating selected re-use strategies, including guidance on sampling techniques.
4.3 This guide is intended for metal powders used in Powder Bed Fusion processes.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide:
1.1.1 Defines key powder re-use variables and factors affecting powder re-use strategies.
1.1.2 Outlines implications associated with implementation of powder re-use strategies based on selection of powder re-use variables and factors.
1.1.3 Provides guidance to AM users in selection of factors in powder re-use variables depending on considered material type, AM process type and end-use application.
1.1.4 Provides guidance on key process variables affecting powder properties, and considerations to mitigate their effects.
1.1.5 Identifies key powder properties that may be affected by powder re-use and provides AM users guidance on control measures that can be exploited to ensure quality of re-used powder.
1.1.6 Provides recommendations and guidance on factors to consider when implementing powder re-use strategies.
1.1.7 Provides information on how to design a powder re-use study to validate the selected re-use variables.
1.1.8 Summarizes sampling techniques and provides recommendations to AM users on sampling technique selection, and suitability of sampling techniques for powder re-use strategies.
1.1.9 Provides factors to consider when designing a powder sampling study to validate the selected sampling technique.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard units. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F3592 − 23
Standard Guide for
Additive Manufacturing of Metals – Powder Bed Fusion –
1
Guidelines for Feedstock Re-use and Sampling Strategies
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3592; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This guide:
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1.1 Defines key powder re-use variables and factors af-
fecting powder re-use strategies.
2. Referenced Documents
1.1.2 Outlines implications associated with implementation
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of powder re-use strategies based on selection of powder re-use
B215 Practices for Sampling Metal Powders
variables and factors.
B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
1.1.3 Provides guidance to AM users in selection of factors
F2924 Specification for Additive Manufacturing Titanium-6
in powder re-use variables depending on considered material
Aluminum-4 Vanadium with Powder Bed Fusion
type, AM process type and end-use application.
F3001 Specification for Additive Manufacturing Titanium-6
1.1.4 Provides guidance on key process variables affecting
Aluminum-4 Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) with
powder properties, and considerations to mitigate their effects.
Powder Bed Fusion
1.1.5 Identifies key powder properties that may be affected
F3055 Specification for Additive Manufacturing Nickel Al-
by powder re-use and provides AM users guidance on control
loy (UNS N07718) with Powder Bed Fusion
measures that can be exploited to ensure quality of re-used
F3184 Specification for Additive Manufacturing Stainless
powder.
Steel Alloy (UNS S31603) with Powder Bed Fusion
1.1.6 Provides recommendations and guidance on factors to
F3318 for Additive Manufacturing – Finished Part Proper-
consider when implementing powder re-use strategies.
ties – Specification for AlSi10Mg with Powder Bed
1.1.7 Provides information on how to design a powder
Fusion – Laser Beam
re-use study to validate the selected re-use variables.
F3456 Guide for Powder Reuse Schema in Powder Bed
1.1.8 Summarizes sampling techniques and provides recom-
Fusion Processes for Medical Applications for Additive
mendations to AM users on sampling technique selection, and
Manufacturing Feedstock Materials
suitability of sampling techniques for powder re-use strategies.
2
2.2 ISO/ASTM Standards:
1.1.9 Provides factors to consider when designing a powder
sampling study to validate the selected sampling technique. ISO/ASTM FDIS 52900 Additive manufacturing — General
principles — Fundamentals and vocabulary
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
ISO/ASTM PWI 52928 Additive manufacturing of metals
as the standard units. No other units of measurement are
— Feedstock materials — Powder life cycle management
included in this standard.
ISO/ASTM 52907 Additive manufacturing — Feedstock
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
materials — Methods to characterize metal powders
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3. Terminology
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.1 Powder metallurgy terms can be found in Terminology
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
B243 and AM processes and terms can be found in ISO/ASTM
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
52900. Terms used frequently in this document are given
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
below.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2 Definitions:
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F42 on Additive
2
Manufacturing Technologies and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
F42.05 on Materials and Processes. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved July 15, 2023. Published September 2023. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/F3592-23. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F3592 − 23
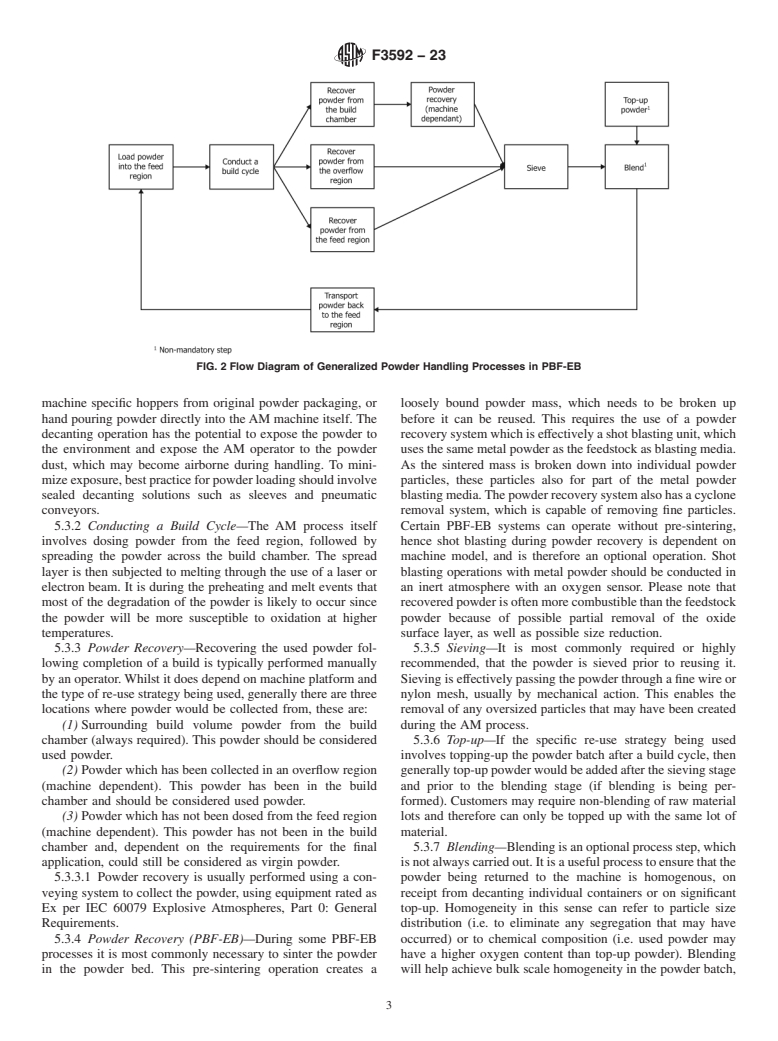
FIG. 1 Flow Diagram of Generalized Powder Handling Processes in PB
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.