ASTM F2096-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Detecting Gross Leaks in Medical Packaging by Internal Pressurization (Bubble Test)
Standard Test Method for Detecting Gross Leaks in Medical Packaging by Internal Pressurization (Bubble Test)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The internal pressurization test method provides a practical way to examine packages for gross leaks, which may render the product non-sterile.
This test method is extremely useful in a test laboratory environment where no common package material/size exists.
This test method may apply to very large or long packages, which do not fit into any other package integrity test method apparatus.
This test method may be used as a means to evaluate package integrity. Package integrity is crucial to consumer safety since heat sealed packages are designed to provide a contamination free and sterile environment to the product.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the detection of gross leaks in medical packaging. Method sensitivity is down to 250 μm with an 81 % probability (see Section 11). This test method may be used for tray and pouch packages.
1.2 The sensitivity of this test method has not been evaluated for use with porous materials other than spunbonded polyolefin or with nonporous packaging.
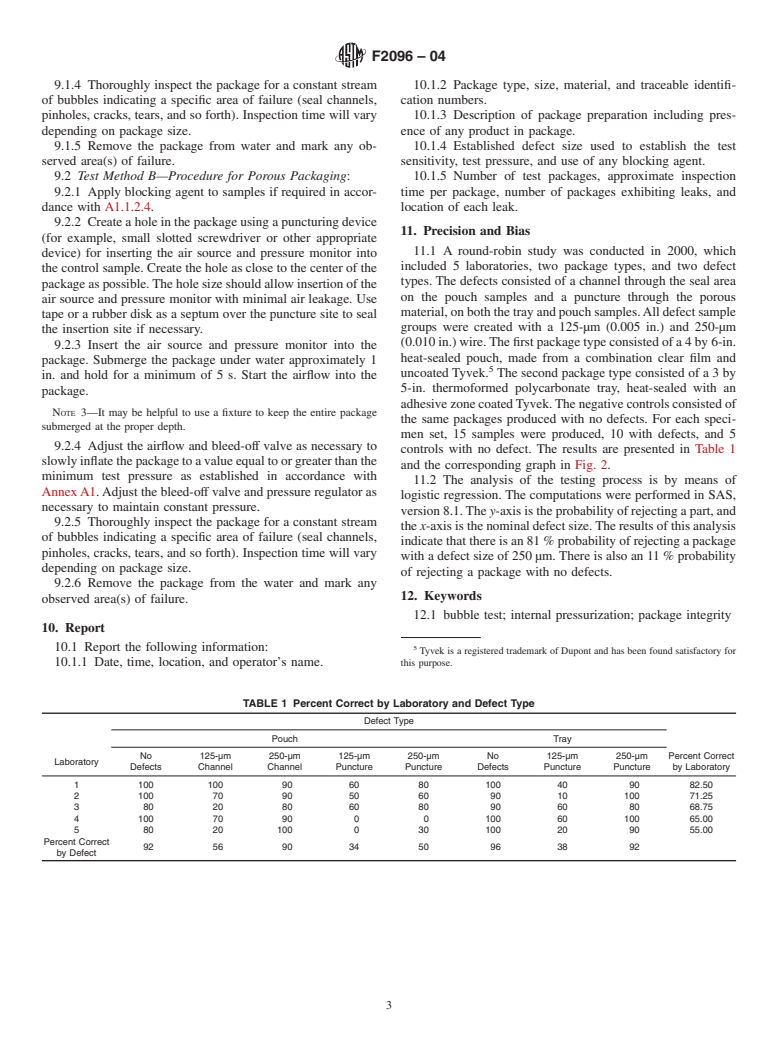
1.3 This test method is destructive in that it requires entry into the package to supply an internal air pressure
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2096–04
Standard Test Method for
Detecting Gross Leaks in Medical Packaging by Internal
1
Pressurization (Bubble Test)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2096; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.1 breathing point pressure, n—pressureatwhichperme-
4
ation of air through the porous material begins.
1.1 This test method covers the detection of gross leaks in
medical packaging. Method sensitivity is down to 250 µm with
4. Summary of Test Method
an 81 % probability (see Section 11). This test method may be
4.1 The package is inflated underwater to a predetermined
used for tray and pouch packages.
pressure. The package is then observed for a steady stream of
1.2 The sensitivity of this test method has not been evalu-
air bubbles indicating a failure area.
ated for use with porous materials other than spunbonded
4.2 The sensitivity of this test method is dependent on the
polyolefin or with nonporous packaging.
differential pressure and method of pressurization. Establish-
1.3 This test method is destructive in that it requires entry
ment of a test pressure for each package material/size is critical
into the package to supply an internal air pressure
for obtaining repeatable results (see Annex A1 for the proce-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
dure on establishing test pressure). Inadequate pressurization
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
of the package can significantly reduce the sensitivity of this
only.
test method. Higher differential pressures will increase the test
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sensitivity. However, excessive pressurization of the package
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
may rupture seals or cause misinterpretation of bubble patterns
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
emanating from porous packaging. This may result in an
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
erroneous conclusion regarding the presence or absence of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
package defects. While not required, use of a bleed-off control
2. Referenced Documents valve in line with the pressure monitoring device, will aid in
2
stabilizing the test pressure, and help eliminate excessive
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3 pressurization of the package (see Fig. 1).
D1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
4.3 Two different test methods are presented for the testing
F1327 Terminology Relating to Barrier Materials for Medi-
3 of porous and nonporous packaging. The key difference
cal Packaging
between the test methods (as described in Annex A1)isin
3. Terminology allowing time for the water to saturate the porous material.
3.1 Definitions—General terms relating to barrier materials
5. Significance and Use
for medical packaging are found in Terminology F1327.
5.1 The internal pressurization test method provides a prac-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
tical way to examine packages for gross leaks, which may
render the product non-sterile.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F02 on Flexible 5.2 This test method is extremely useful in a test laboratory
Barrier Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.40 on
environment where no common package material/size exists.
Package Integrity.
5.3 This test method may apply to very large or long
CurrenteditionapprovedJan.3,2006.PublishedJune2004.Originallyapproved
´1
packages, which do not fit into any other package integrity test
in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as F2096 – 02 . DOI: 10.1520/
F2096-04.
method apparatus.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on All porous packaging by definition will permit the passage of air. At a given
the ASTM website. internal pressure it will therefore exhibit an emanating stream of air bubbles
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced dependent on the pore size. A stream of bubbles identified at a lower internal
on www.astm.org. pressure than the breathing pressure point may indicate a defect in the packaging.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2096–04
FIG. 1 Sample Test Apparatus
5.4 This tes
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.