ASTM D943-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D943 − 17 BS 2000-280:1999
Standard Test Method for
1
Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D943; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the oxidation
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
stability of inhibited steam-turbine oils in the presence of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
oxygen, water, and copper and iron metals at an elevated
temperature. This test method is limited to a maximum testing
2. Referenced Documents
time of 10 000 h.This test method is also used for testing other
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
oils,suchashydraulicoilsandcirculatingoilshavingaspecific
A510 Specification for General Requirements forWire Rods
gravitylessthanthatofwaterandcontainingrustandoxidation
and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel
inhibitors.
B1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D664 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
by Potentiometric Titration
standard.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
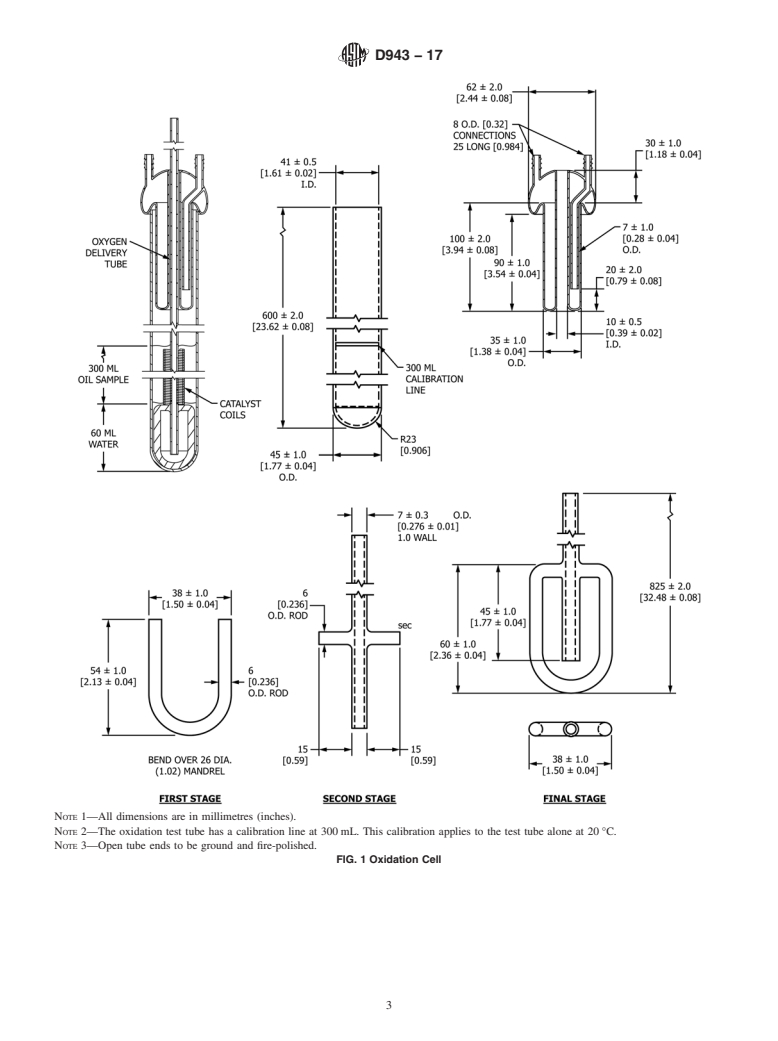
1.2.1 Exception—The values in parentheses in the figures
D3244 Practice for Utilization of Test Data to Determine
are provided for information for those using old equipment
Conformance with Specifications
based on non-SI units.
D3339 Test Method forAcid Number of Petroleum Products
1.3 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or Petroleum Products
its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to D4310 Test Method for Determination of Sludging and
materials.Cautionshouldbetakenwhenhandlingmercuryand Corrosion Tendencies of Inhibited Mineral Oils
mercury containing products. See the applicable product Ma-
D5770 Test Method for Semiquantitative Micro Determina-
terial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s tion of Acid Number of Lubricating Oils During Oxida-
website—http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm—for addi-
tion Testing
tional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
and/or mercury containing products into your state or country
E2877 Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
3
may be prohibited by law. 2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4
2.3 British Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
BS 1829
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3. Summary of Test Method
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
3.1 The oil sample is contacted with oxygen in the presence
warning statements, see Section 6.
of water and an iron-copper catalyst at 95 °C. The test
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
continuesuntilthemeasuredacidnumberoftheoilis2.0 mg⁄g
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Subcommittee D02.09.0C on Oxidation of Turbine Oils. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved June 15, 2017. Published August 2017. Originally Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, W1G 7AR,
ɛ1
approved in 1947. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D943 – 04a (2010) . U.K., http://www.energyinst.org.
4
DOI: 10.1520/D0943-17. Available from British Standards Institution (BSI), 389 Chiswick High Rd.,
In 1976, this test method ceased to be a joint ASTM-IP standard. London W4 4AL, U.K., http://www.bsigroup.com.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D943 − 04a (Reapproved 2010) D943 − 17 BS 2000-280:1999
Standard Test Method for
1
Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D943; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Updated Scope with regard to SI units and added mercury caveat editorially in October 2010.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the oxidation stability of inhibited steam-turbine oils in the presence of oxygen,
water, and copper and iron metals at an elevated temperature. This test method is limited to a maximum testing time of 10 000
h. 10 000 h. This test method is also used for testing other oils, such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils having a specific gravity
less than that of water and containing rust and oxidation inhibitors.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
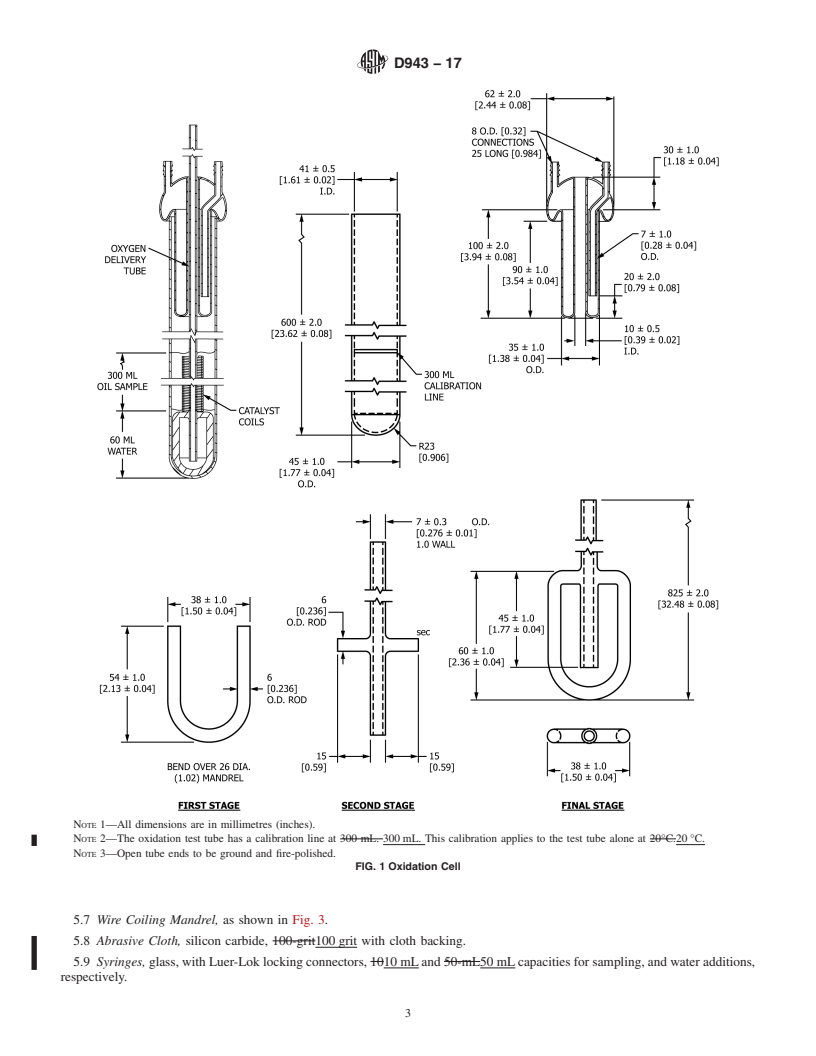
1.2.1 Exception—The values in parentheses in the figures are provided for information for those using old equipment based on
non-SI units.
1.3 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central
nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS) for details and EPA’s website—http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm—for additional information. Users should be aware
that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Section 6.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A510 Specification for General Requirements for Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel
B1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
D664 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Potentiometric Titration
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D3244 Practice for Utilization of Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
D3339 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4310 Test Method for Determination of Sludging and Corrosion Tendencies of Inhibited Mineral Oils
D5770 Test Method for Semiquantitative Micro Determination of Acid Number of Lubricating Oils During Oxidation Testing
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E2877 Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.09.0C on Oxidation of Turbine Oils.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010June 15, 2017. Published December 2010August 2017. Originally approved in 1947. Last previous edition approved in 20042010
ɛ1
as D943D943 – 04a (2010) –04a. . DOI: 10.1520/D0943-17.
In 1976, this test method ceased to be a joint ASTM-IP standard. DOI: 10.1520/D0943-10.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.