ASTM D3339-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
Standard Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method measures the acid number of oils obtained from laboratory oxidation tests using smaller amounts of sample than Test Methods D974 or D664. It has specific application in Test Method D943 in which small aliquots of oil are periodically removed for testing by Test Method D3339. This test method, therefore, provides a means of monitoring the relative oxidation of oils, by measuring changes in acid number, at different time intervals and under the various oxidizing test conditions.
SCOPE
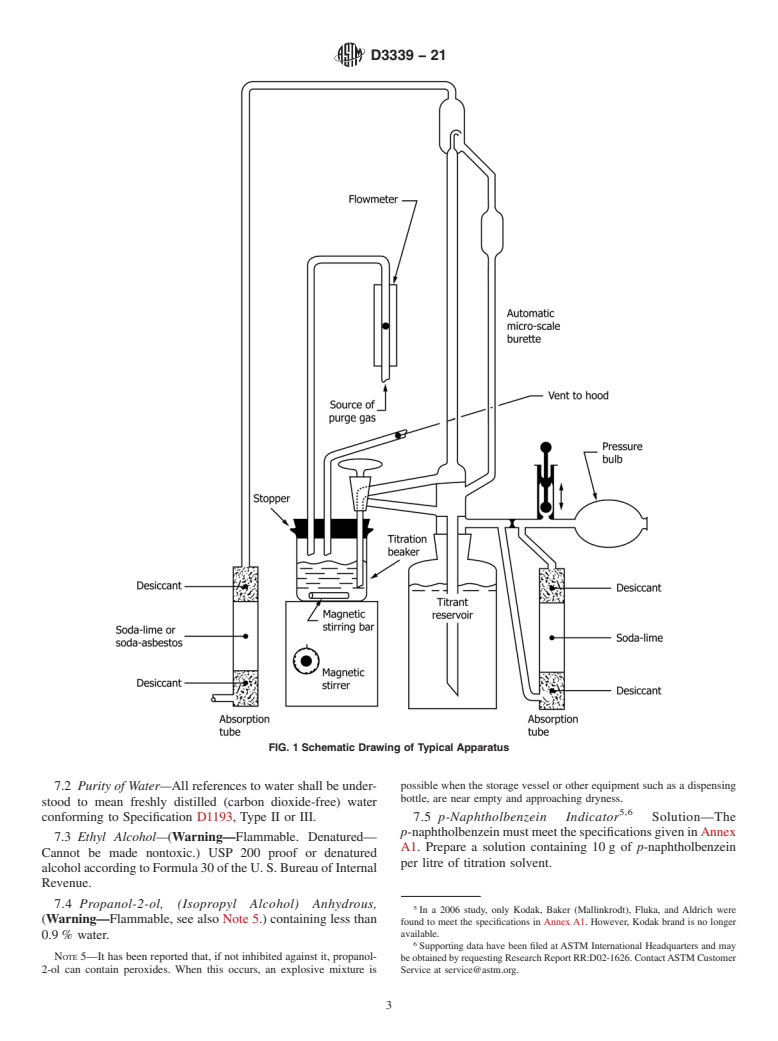
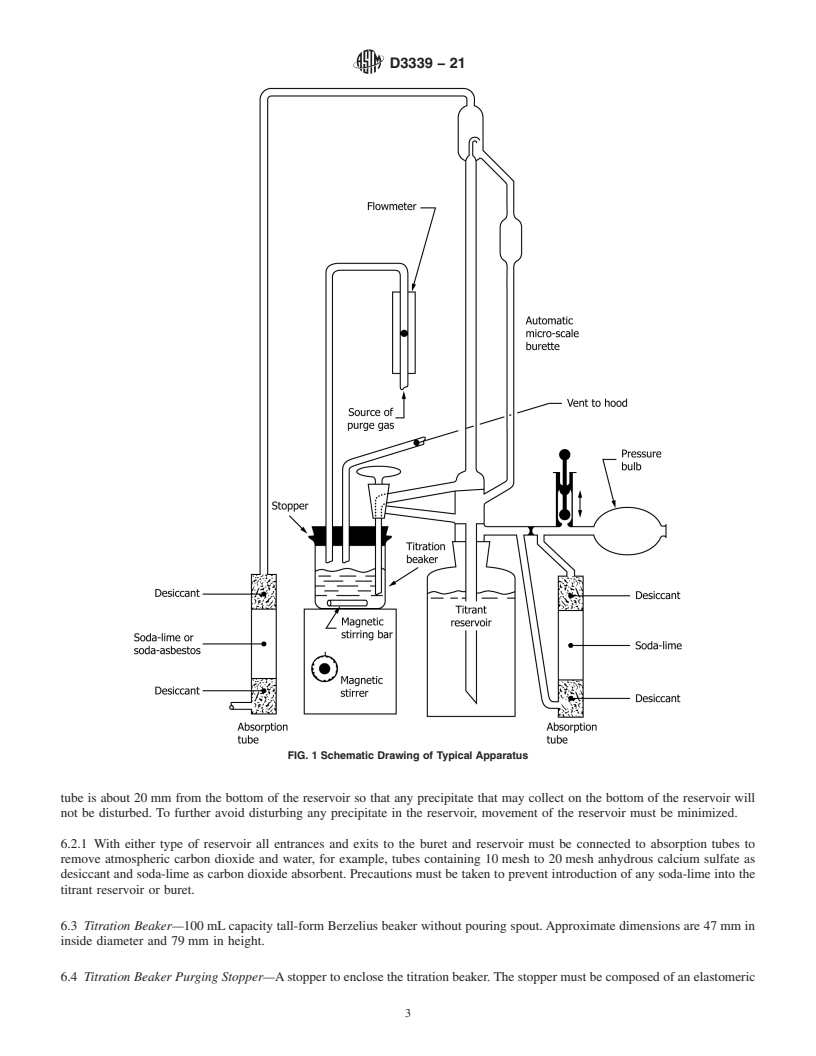
1.1 This test method covers the determination of acidic constituents in new or used petroleum products and lubricants soluble or nearly soluble in mixtures of toluene, and isopropyl alcohol. The test method is especially intended for cases in which the amount of sample available to be analyzed is too small to allow accurate analysis by Test Methods D974 or D664. It is applicable for the determination of acids having dissociation constants in water larger than 10−9. Extremely weak acids having dissociation constants smaller than 10−9 do not interfere. Salts titrate if their hydrolysis constants are larger than 10−9.
1.2 This test method can be used to indicate relative changes in acid number that occur in an oil during use under oxidizing conditions. Although the titration is made under definite equilibrium conditions, the method does not measure an absolute acidic property that can be used to predict performance of an oil under service conditions. No general relationship between bearing corrosion and acid number is known.
1.3 Since this test method requires substantially less sample than Test Methods D974 or D664, it provides an advantageous means of monitoring an oxidation test by changes in acid number by (1) minimizing test sample depletion for acid number analyses and thus minimizing the disturbance of the test or (2) allowing additional acid number analyses to be made while maintaining the same test sample depletion and thus providing additional data.
Note 1: Some oils, such as many cutting oils, rust-proofing oils, and similar compounded oils, or excessively dark-colored oils, may be more difficult to analyze by this test method due to obscurity of the color-indicator end point. These oils can be analyzed by Test Method D664 provided sufficient sample is available. However, this situation is much less likely using Test Method D3339 than using Test Method D974 due to the use of a more highly dilute sample during the titration and due to the greater stability of the end point color change. The acid numbers obtained by Test Method D3339 may or may not be numerically the same as those obtained by Test Method D664 but they should be of the same order of magnitude.
Note 2: The results obtained using this method have been found to be numerically the same as those obtained using Test Method D974, within the precision of the two methods, for new or oxidized lubricants of the type primarily intended for hydraulic or steam turbine type service. The oxidized lubricants were obtained using the Test Method D943 oxidation test. This correlation is shown by the correlation coefficient r = 0.989 with slope s = + 1.017 and intercept y = + 0.029, calculated using the acid numbers obtained using both titration methods for the samples used for the precision statement (12.2).2
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Sections 7 and 9, A1.1.4, A2.3.1, and A2.10.1.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on sta...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3339 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Semi-Micro Color
1
Indicator Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3339; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
obtained by Test Method D664 but they should be of the same order of
1. Scope*
magnitude.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of acidic
NOTE 2—The results obtained using this method have been found to be
constituents in new or used petroleum products and lubricants numerically the same as those obtained using Test Method D974, within
the precision of the two methods, for new or oxidized lubricants of the
soluble or nearly soluble in mixtures of toluene, and isopropyl
type primarily intended for hydraulic or steam turbine type service. The
alcohol. The test method is especially intended for cases in
oxidized lubricants were obtained using the Test Method D943 oxidation
which the amount of sample available to be analyzed is too
test.Thiscorrelationisshownbythecorrelationcoefficient r=0.989with
small to allow accurate analysis by Test Methods D974 or
slope s=+1.017 and intercept y=+0.029, calculated using the acid
D664. It is applicable for the determination of acids having numbersobtainedusingbothtitrationmethodsforthesamplesusedforthe
2
−9
precision statement (12.2).
dissociation constants in water larger than 10 . Extremely
−9
weak acids having dissociation constants smaller than 10 do
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
notinterfere.Saltstitrateiftheirhydrolysisconstantsarelarger
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
−9
than 10 .
standard.
1.2 Thistestmethodcanbeusedtoindicaterelativechanges 1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in acid number that occur in an oil during use under oxidizing safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
conditions. Although the titration is made under definite responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
equilibrium conditions, the method does not measure an priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
absolute acidic property that can be used to predict perfor- mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
mance of an oil under service conditions. No general relation- For specific warning statements, see Sections 7 and 9, A1.1.4,
ship between bearing corrosion and acid number is known. A2.3.1, and A2.10.1.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
1.3 Since this test method requires substantially less sample
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
thanTest Methods D974 or D664, it provides an advantageous
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
means of monitoring an oxidation test by changes in acid
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
number by (1) minimizing test sample depletion for acid
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
number analyses and thus minimizing the disturbance of the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
testor(2)allowingadditionalacidnumberanalysestobemade
while maintaining the same test sample depletion and thus
2. Referenced Documents
providing additional data.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—Some oils, such as many cutting oils, rust-proofing oils, and
D664Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products
similar compounded oils, or excessively dark-colored oils, may be more
by Potentiometric Titration
difficult to analyze by this test method due to obscurity of the color-
D943TestMethodforOxidationCharacteristicsofInhibited
indicator end point. These oils can be analyzed by Test Method D664
provided sufficient sample is available. However, this situation is much Mineral Oils
less likely usingTest Method D3339 than usingTest Method D974 due to
D974Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-
the use of a more highly dilute sample during the titration and due to the
Indicator Titration
greaterstabilityoftheendpointcolorchange.Theacidnumbersobtained
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
by Test Method D3339 may or may not be numerically the same as those
2
Use of the correlation coefficient is given in Mack, C., Essentials of Statistics
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on for Scientists and Technologists, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1967, or other
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the d
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3339 − 12 (Reapproved 2017) D3339 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Semi-Micro Color
1
Indicator Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3339; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of acidic constituents in new or used petroleum products and lubricants soluble or
nearly soluble in mixtures of toluene, and isopropyl alcohol. The test method is especially intended for cases in which the amount
of sample available to be analyzed is too small to allow accurate analysis by Test Methods D974 or D664. It is applicable for the
−9
determination of acids having dissociation constants in water larger than 10 . Extremely weak acids having dissociation constants
−9 −9
smaller than 10 do not interfere. Salts titrate if their hydrolysis constants are larger than 10 .
1.2 This test method can be used to indicate relative changes in acid number that occur in an oil during use under oxidizing
conditions. Although the titration is made under definite equilibrium conditions, the method does not measure an absolute acidic
property that can be used to predict performance of an oil under service conditions. No general relationship between bearing
corrosion and acid number is known.
1.3 Since this test method requires substantially less sample than Test Methods D974 or D664, it provides an advantageous means
of monitoring an oxidation test by changes in acid number by (1) minimizing test sample depletion for acid number analyses and
thus minimizing the disturbance of the test or (2) allowing additional acid number analyses to be made while maintaining the same
test sample depletion and thus providing additional data.
NOTE 1—Some oils, such as many cutting oils, rust-proofing oils, and similar compounded oils, or excessively dark-colored oils, may be more difficult
to analyze by this test method due to obscurity of the color-indicator end point. These oils can be analyzed by Test Method D664 provided sufficient
sample is available. However, this situation is much less likely using Test Method D3339 than using Test Method D974 due to the use of a more highly
dilute sample during the titration and due to the greater stability of the end point color change. The acid numbers obtained by Test Method D3339 may
or may not be numerically the same as those obtained by Test Method D664 but they should be of the same order of magnitude.
NOTE 2—The results obtained using this method have been found to be numerically the same as those obtained using Test Method D974, within the
precision of the two methods, for new or oxidized lubricants of the type primarily intended for hydraulic or steam turbine type service. The oxidized
lubricants were obtained using the Test Method D943 oxidation test. This correlation is shown by the correlation coefficient r = 0.989 with slope
s = + 1.017 and intercept y = + 0.029, calculated using the acid numbers obtained using both titration methods for the samples used for the precision
2
statement (12.2).
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.06 on Analysis of Liquid Fuels and Lubricants.
Current edition approved May 1, 2017Nov. 1, 2021. Published June 2017November 2021. Originally approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 20122017 as
D3339 – 12.D3339 – 12 (2017). DOI: 10.1520/D3339-12R17.10.1520/D3339-21.
2
Use of the correlation coefficient is given in Mack, C., Essentials of Statistics for Scientists and Technologists, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1967, or other publications
on statistics.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3339 − 21
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.