ASTM E100-17
(Specification)Standard Specification for ASTM Hydrometers
Standard Specification for ASTM Hydrometers
ABSTRACT
This specification covers glass hydrometers of various scale graduation systems, as required by the ASTM test methods in which they are used. Hydrometers shall be of the constant-mass, variable-displacement type. Hydrometers shall be made of glass, except for the scale, ballasting material, and the thermometric liquid of thermohydrometers. Material used for ballast shall be secured to the lower part of the body, and no loose material of any sort may be inside a hydrometer. The stem shall be uniform in cross section, with no perceptible irregularities. The preferred shapes for the bodies of hydrometers are presented. Graduation lines and inscriptions shall be in a permanent black marking material, such as India ink. All hydrometers shall be graduated to read correctly where the plane of the level liquid surface intersects the stem. The thermometer shall be of the mercury-in-glass type, unless otherwise specified. Hydrometers shall be inspected, tested, and standardized in accordance with the requirements prescribed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers glass hydrometers of various scale graduation systems, as required by the ASTM Test Methods in which they are used.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E100 −17
Standard Specification for
1
ASTM Hydrometers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E100; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope E2877 Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
2.2 Other Standards:
1.1 This specification covers glass hydrometers of various
ISO 1768:1975 Glass Hydrometers—Conventional Value
scale graduation systems, as required by the ASTM Test
for the Thermal Cubic Expansion Coefficient (for Use in
Methods in which they are used.
the Preparation of Measurement Tables for Liquids)
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3. Terminology
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1 Definitions—The definitions given inTerminology E344
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
apply.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2.1 ledger paper, n—a paper characterized by strength,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
high tearing resistance, eraseability, water resistance, ink
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
receptivity, uniformity of surface, and smoothness.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.2.1.1 Discussion—Originally, ledger paper was used espe-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
cially for pen and ink records. Most ledger papers are surface
sized, frequently subjected to appreciable wear, and shall have
2. Referenced Documents
a high degree of permanence and durability.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.2 length of the scale, n—length of the nominal range in
D287 Test Method for API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and
the stem, not including graduations extending above and below
Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)
the nominal limits.
D3290 Specification for Bond and Ledger Papers for Perma-
3.2.3 relative density (formerly specific gravity), n—ratio of
3
nent Records (Withdrawn 2010)
the mass of a given volume of material at a stated temperature
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
tothemassofanequalvolumeofgas-freedistilledwateratthe
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
same or different temperature. Both reference temperatures
mometers
shall be explicitly stated.
E126 Test Method for Inspection, Calibration, and Verifica-
3.2.3.1 Discussion—Common reference temperatures in-
tion of ASTM Hydrometers
clude 60°F/60°F, 20°C/20°C, 20°C/4°C. The historic term
E344 Terminology Relating to Thermometry and Hydrom-
specific gravity may still be found.
etry
3.2.3.2 Discussion—The reference temperatures for ASTM
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
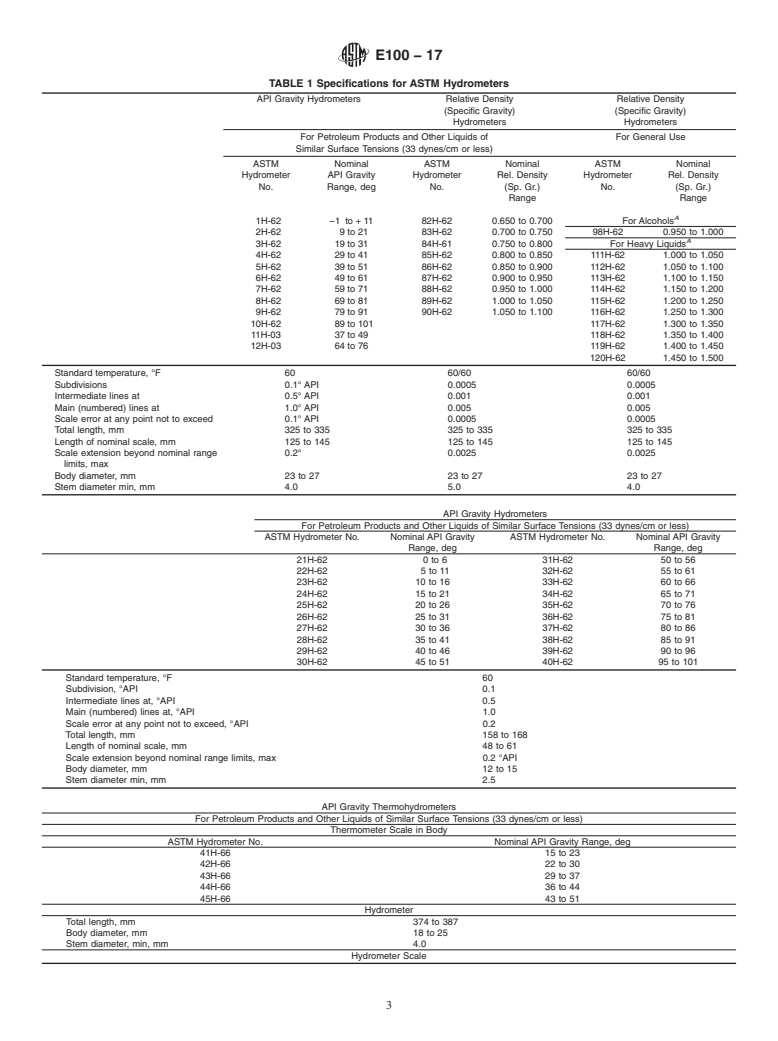
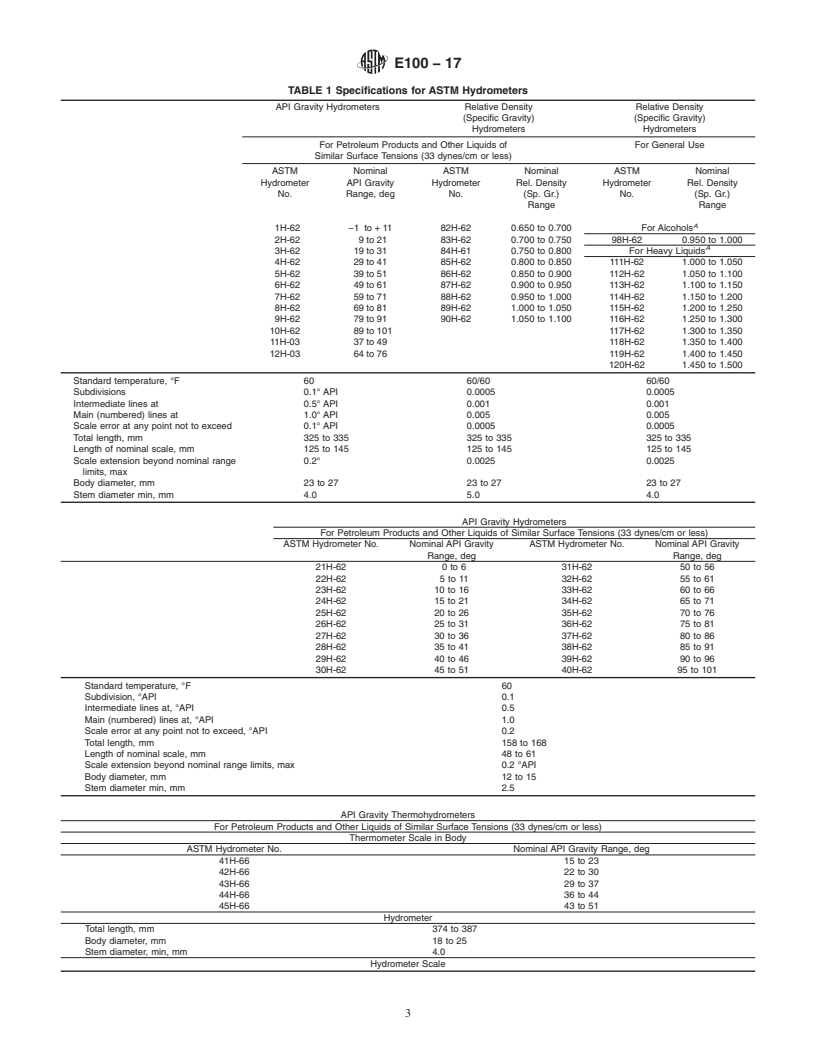
hydrometers and thermohydrometers are found in Table 1
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
under the heading “standard temperature”.
3.2.4 specific gravity, n—an historic term, replaced by
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E20 on
relative density.
Temperature Measurement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E20.05
3.2.4.1 Discussion—hydrometers manufactured to this stan-
on Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers and Hydrometers.
dard may be marked sp. gr., rel. density, or with both
Current edition approved May 1, 2017. Published May 2017. Originally
approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as E100 – 15a. DOI: designations. The two terms are both equally acceptable in this
10.1520/E0100-17.
standard and are used interchangeably.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.2.5 thermohydrometer, n—glass hydrometer having an
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
integral thermometer.
the ASTM website.
3
3.2.6 top of the hydrometer, n—top of the finished instru-
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. ment.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E100−17
3.2.7 total length, n—overall length of the finished instru- 6. Body
ment.
6.1 The preferred shapes for the bodies of hydrometers are
shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
4. Specifications
7. Ballast
4.1 Individual hy
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E100 − 15a E100 − 17
Standard Specification for
1
ASTM Hydrometers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E100; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers glass hydrometers of various scale graduation systems, as required by the ASTM Test Methods in
which they are used.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D287 Test Method for API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)
D1250 Guide for Use of the Petroleum Measurement Tables
3
D3290 Specification for Bond and Ledger Papers for Permanent Records (Withdrawn 2010)
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Thermometers
E126 Test Method for Inspection, Calibration, and Verification of ASTM Hydrometers
E344 Terminology Relating to Thermometry and Hydrometry
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermometers with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
E2877 Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
2.2 Other Standards:
ISO 1768:1975 Glass Hydrometers—Conventional Value for the Thermal Cubic Expansion Coefficient (for Use in the
Preparation of Measurement Tables for Liquids)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—The definitions given in Terminology E344 apply.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 ledger paper, n—a paper characterized by strength, high tearing resistance, eraseability, water resistance, ink receptivity,
uniformity of surface, and smoothness.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E20 on Temperature Measurement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E20.05 on
Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers and Hydrometers.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2015May 1, 2017. Published January 2016May 2017. Originally approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as
E100 – 15.E100 – 15a. DOI: 10.1520/E0100-15A.10.1520/E0100-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—
Originally, ledger paper was used especially for pen and ink records. Most ledger papers are surface sized, frequently subjected
to appreciable wear, and shall have a high degree of permanence and durability.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E100 − 17
3.2.2 length of the scale, n—length of the nominal range in the stem, not including graduations extending above and below the
nominal limits.
3.2.3 relative density (formerly specific gravity), n—ratio of the mass of a given volume of material at a stated temperature to
the mass of an equal volume of gas-free distilled water at the same or different temperature. Both reference temperatures shall be
explicitly stated.
3.2.3.1 Discussion—
Common reference temperatures include 60°F/60°F, 20°C/20°C, 20°C/4°C. The historic term specific gravity may still be found.
3.2.3.2 Discussion—
The reference temperatures for ASTM hydrometers and thermohydrometers are found in Table 1 under the heading “standard
temperature”.
3.2.4 specific gravity, n—an historic term, replaced by relative density.
3.2.4.1 Discussion—
hydrometers manufactured to this standard may be marked sp. gr., rel. density, or with both designations. The two terms are both
equally accept
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.