ASTM D2549-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Separation of Representative Aromatics and Nonaromatics Fractions of High-Boiling Oils by Elution Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Separation of Representative Aromatics and Nonaromatics Fractions of High-Boiling Oils by Elution Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The determination of compound types by mass spectrometry requires, in some instances, a preliminary separation of the petroleum sample into representative aromatics and nonaromatics fractions, as in Test Methods D2425, D2786, and D3239. This test method provides a suitable separation technique for this application.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the separation and determination of representative aromatics and nonaromatics fractions from hydrocarbon mixtures that boil between 232 °C and 538 °C (450 °F and 1000 °F). Alternative procedures are provided for the separation of 2 g or 10 g of hydrocarbon mixture.
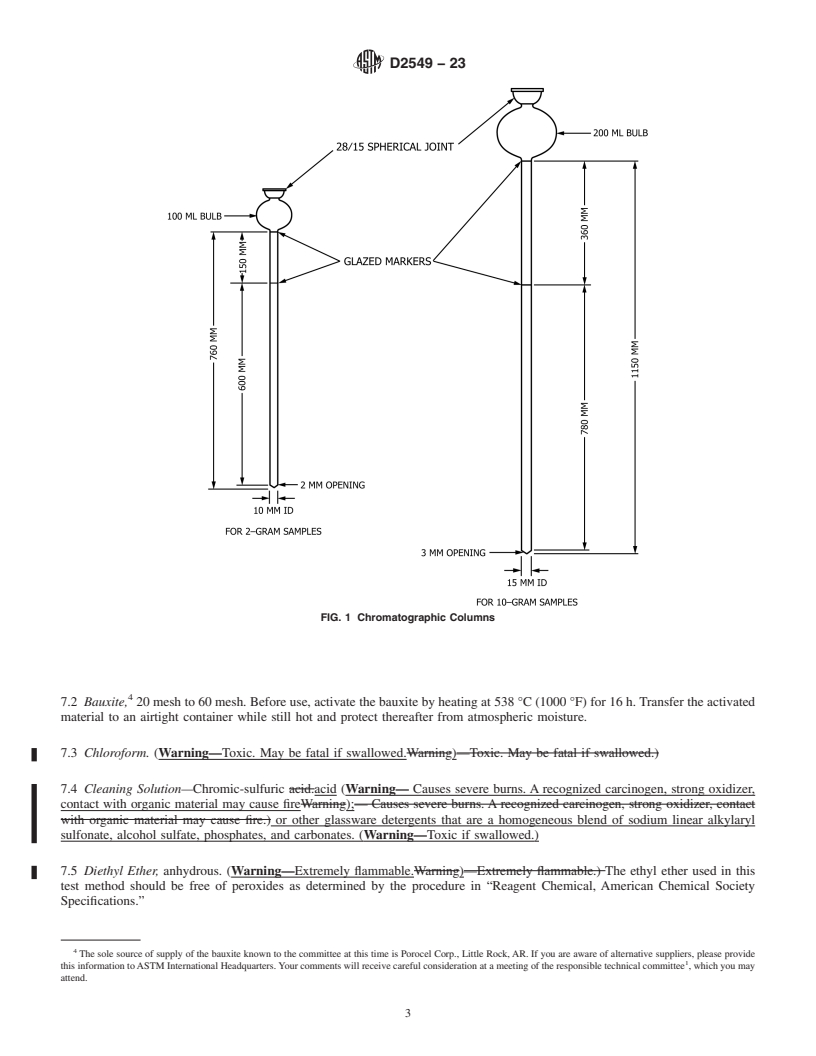
Note 1: Some components may not be eluted from the chromatographic column for some types of samples under the conditions used in this method.
Note 2: Test Method D2007 is an alternative method of separating high-boiling oils into polar compounds, aromatics, and saturates fractions.
1.2 An alternative procedure is provided to handle samples boiling below 232 °C (450 °F), but whose 5 % point is above 178 °C (350 °F) as determined by Test Method D2887. This procedure is given in Appendix X1.
1.3 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2549 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Separation of Representative Aromatics and Nonaromatics
1
Fractions of High-Boiling Oils by Elution Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2549; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D2007 Test Method for Characteristic Groups in Rubber
Extender and Processing Oils and Other Petroleum-
1.1 This test method covers the separation and determina-
Derived Oils by the Clay-Gel Absorption Chromato-
tion of representative aromatics and nonaromatics fractions
graphic Method
from hydrocarbon mixtures that boil between 232 °C and
D2425 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Middle Dis-
538 °C (450 °F and 1000 °F). Alternative procedures are pro-
tillates by Mass Spectrometry
vided for the separation of 2 g or 10 g of hydrocarbon mixture.
D2786 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types Analysis of
NOTE 1—Some components may not be eluted from the chromato-
Gas-Oil Saturates Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage
graphic column for some types of samples under the conditions used in
Mass Spectrometry
this method.
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe-
NOTE 2—Test Method D2007 is an alternative method of separating
high-boiling oils into polar compounds, aromatics, and saturates fractions. troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
D3239 Test Method for Aromatic Types Analysis of Gas-Oil
1.2 An alternative procedure is provided to handle samples
Aromatic Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spec-
boiling below 232 °C (450 °F), but whose 5 % point is above
trometry
178 °C (350 °F) as determined by Test Method D2887. This
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
procedure is given in Appendix X1.
Fuels, and Lubricants
1.3 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be
regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are
3. Terminology
provided for information purposes only.
3.1 Definitions:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to Terminology D4175.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.2.1 aromatics fraction, n—the portion of the sample
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor- desorbed with the polar eluants. The aromatics fraction may
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- contain aromatics, condensed naphthenic-aromatics, aromatic
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the olefins, and compounds containing sulfur, nitrogen, and oxy-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- gen atoms.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.2.2 nonaromatics fraction, n—the portion of the sample
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
eluted with n-pentane. The nonaromatics fraction is a mixture
of paraffinic and naphthenic hydrocarbons if the sample is a
2. Referenced Documents
straight-run material. If the sample is a cracked stock, the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
nonaromatics fraction will also contain aliphatic and cyclic
olefins.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
4. Summary of Test Method
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.04.0C on Liquid Chromatography.
4.1 A weighed amount of sample is charged to the top of a
Current edition approved March 1, 2023. Published March 2023. Originally
glass chromatographic column packed with activated bauxite
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D2549 – 02 (2017).
DOI: 10.1520/D2549-23.
and silica gel. n-Pentane is added to the column to elute the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
nonaromatics. When all of the nonaromatics are eluted, the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
aromatics fraction is eluted by additions of diethyl ether,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. chloroform, and ethyl alcohol.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Con
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2549 − 02 (Reapproved 2017) D2549 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Separation of Representative Aromatics and Nonaromatics
1
Fractions of High-Boiling Oils by Elution Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2549; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the separation and determination of representative aromatics and nonaromatics fractions from
hydrocarbon mixtures that boil between 232 °C and 538 °C (450 °F and 1000 °F). Alternative procedures are provided for the
separation of 2 g or 10 g of hydrocarbon mixture.
NOTE 1—Some components may not be eluted from the chromatographic column for some types of samples under the conditions used in this method.
NOTE 2—Test Method D2007 is an alternative method of separating high-boiling oils into polar compounds, aromatics, and saturates fractions.
1.2 An alternative procedure is provided to handle samples boiling below 232 °C (450 °F), but whose 5 % point is above 178 °C
(350 °F) as determined by Test Method D2887. This procedure is given in Appendix X1.
1.3 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
information purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2007 Test Method for Characteristic Groups in Rubber Extender and Processing Oils and Other Petroleum-Derived Oils by the
Clay-Gel Absorption Chromatographic Method
D2425 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Middle Distillates by Mass Spectrometry
D2786 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types Analysis of Gas-Oil Saturates Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass
Spectrometry
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Petroleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0C on Liquid Chromatography.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017March 1, 2023. Published December 2017March 2023. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 20122017
as D2549 – 02 (2012).(2017). DOI: 10.1520/D2549-02R17.10.1520/D2549-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2549 − 23
D3239 Test Method for Aromatic Types Analysis of Gas-Oil Aromatic Fractions by High Ionizing Voltage Mass Spectrometry
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 aromatics fraction—fraction, n—the portion of the sample desorbed with the polar eluants. The aromatics fraction may
contain aromatics, condensed naphthenic-aromatics, aromatic olefins, and compounds containing sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen
atoms.
3.2.2 nonaromatics fraction—fraction, n—the portion of the sample eluted with n-pentane. The nonaromatics fraction is a mixture
of paraffinic and naphthenic hydrocarbons if the sample is a straight-run material. If the sample is a cracked stock, the nonaromatics
fraction will also contain aliphatic and cyclic olefins.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A weighed
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.