ASTM D1049-98
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Covers
Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Covers
SCOPE
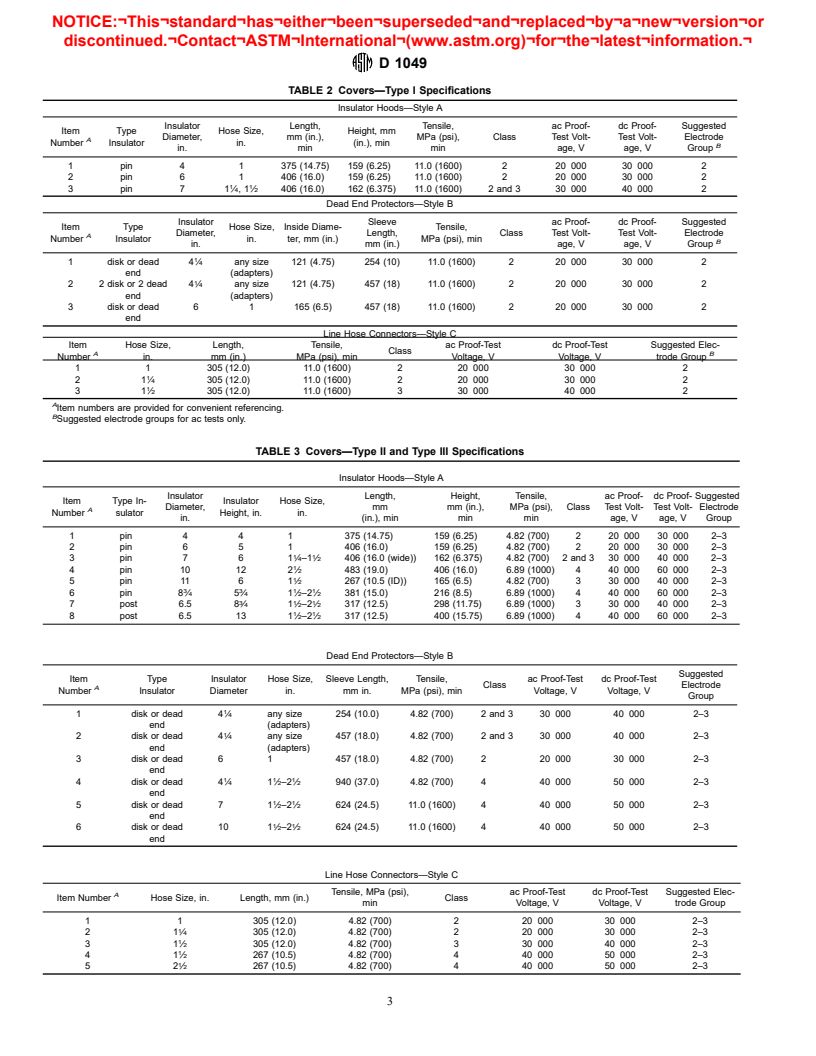
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber insulating covers for use as portable protective devices for protection of workers from accidental contact with live electrical conductors, apparatus, or circuits. It includes insulator hoods, dead-end protectors, line hose connectors, cable end covers, and miscellaneous covers. The electrical, physical, and chemical requirements of this specification shall apply also to any new or modified styles of covers that may be developed for specific purposes.
1.2 Two types of covers, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided, and are designated as Type I and Type II covers.
1.3 Five classes of covers, differing in electrical characteristics, are provided, and are designated as Class 0, Class 1, Class 2, Class 3, and Class 4.
1.4 Five styles of covers, differing in design characteristics, are provided, and are designated as Style A, Style B, Style C, Style D, and Style E. Note 1-Because of the use requirements some covers are semi-rigid and others flexible. The flexible devices should remain suitably flexible for application and removal through normal temperatures of -29 to 54.5°C (-20 to 130°F).
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 18.2.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 1049 – 98
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
1
Rubber Insulating Covers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1049; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D 573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
2
Oven
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber
insulating covers for use as portable protective devices for
3. Terminology
protection of workers from accidental contact with live elec-
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
trical conductors, apparatus, or circuits. It includes insulator
3.1.1 breakdown—the electrical discharge or arc occurring
hoods, dead-end protectors, line hose connectors, cable end
between the electrodes and through the equipment being tested.
covers, and miscellaneous covers. The electrical, physical, and
3.1.2 flashover—the electrical discharge or arc occurring
chemical requirements of this specification shall apply also to
between electrodes and over or around, but not through, the
any new or modified styles of covers that may be developed for
equipment being tested.
specific purposes.
3.1.3 ozone—a very active form of oxygen that may be
1.2 Three types of covers, differing in chemical and physical
produced by corona, arcing, or ultraviolet rays.
characteristics, are provided, and are designated as Type I,
3.1.4 ozone cutting and checking—the cutting action pro-
non-resistant to ozone, and Type II and Type III, resistant to
duced by ozone on rubber under mechanical stress into a series
ozone.
of interlacing cracks.
1.3 Five classes of covers, differing in electrical character-
3.1.5 rubber—a generic term that includes elastomers and
istics, are provided, and are designated as Class 0, Class 1,
elastomeric compounds, regardless of origin.
Class 2, Class 3, and Class 4.
3.1.6 user —as used in 4.3.1, the entity employing the
1.4 Five styles of covers, differing in design characteristics,
actual worker(s) using the equipment; if no separate employer,
are provided, and are designated as Style A, Style B, Style C,
then the individual.
Style D, and Style E.
3.1.7 voltage, maximum use—the ac voltage (rms) rating of
NOTE 1—Because of the use requirements some covers are semi-rigid
the protective equipment that designates the maximum nominal
and others flexible. The flexible devices should remain suitably flexible for
design voltage of the energized system that may be safely
application and removal through normal temperatures of − 29 to 54.5°C
worked. The nominal design voltage is equal to the phase to
(−20 to 130°F).
phase voltage on multiphase circuits.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.7.1 Discussion—If there is no multiphase exposure in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
system area and the voltage exposure is limited to phase
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(polarity on dc systems) to ground potential, the phase (polarity
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
on dc systems) to ground potential shall be considered to be the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 18.2.
nominal design voltage. If electrical equipment and devices are
insulated, or isolated, or both, such that the multiphase expo-
2. Referenced Documents
sure on a grounded wye circuit is removed, then the nominal
2.1 ASTM Standards:
design voltage may be considered as the phase-to-ground
D 297 Test Methods for Rubber Products—Chemical
voltage on that circuit.
2
Analysis
3.1.8 voltage, nominal design—a nominal value consistent
D 412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermo-
with the latest revision on ANSI C84.1, assigned to the circuit
2
plastic Rubbers and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension
or system for the purpose of conveniently designating its
voltage class.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-18 on
Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of 4. Significance and Use
Subcommittee F18.25 on Insulating Cover-Up Equipment. This standard replaces
4.1 This specification covers the minimum electrical,
ANSI Standard J6.2, which is no longer available.
chemical, and physical properties guaranteed by the manufac-
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1998. Published February 1999. Originally
published as D 1049 – 49 T. Last previous editi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.