ASTM F945-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Stress-Corrosion of Titanium Alloys by Aircraft Engine Cleaning Materials
Standard Test Method for Stress-Corrosion of Titanium Alloys by Aircraft Engine Cleaning Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
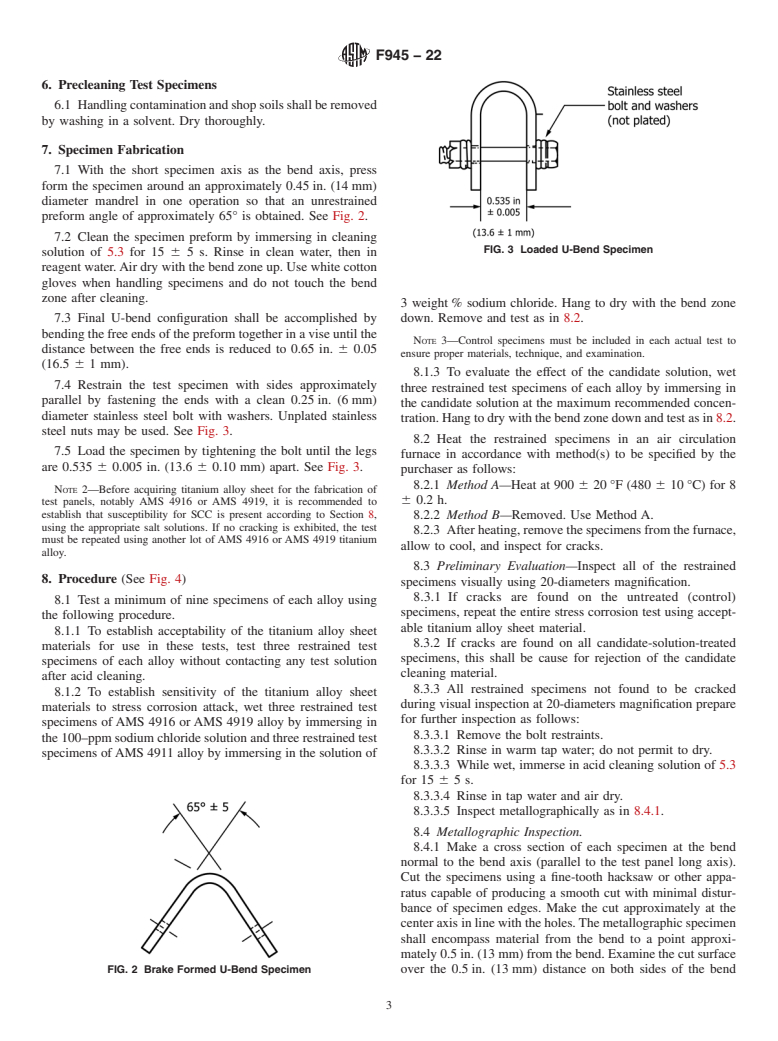
3.1 Because of the tendency of prestressed titanium alloy parts to crack if heated while in contact with certain chemical reagents, it is necessary to ensure that cleaning and maintenance materials will not initiate stress corrosion of titanium alloys under controlled conditions. For test specimens, two common titanium alloys are selected, one that is very susceptible (AMS 4916 or AMS 4919) and one that is not very susceptible (AMS 4911) to stress corrosion cracking.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method establishes a test procedure for determining the propensity of aircraft turbine engine cleaning and maintenance materials for causing stress corrosion cracking of titanium alloy parts.
1.2 The evaluation is conducted on representative titanium alloys by determining the effect of contact with cleaning and maintenance materials on tendency of prestressed titanium alloys to crack when subsequently heated to elevated temperatures.
1.3 Test conditions are based upon manufacturer's maximum recommended operating solution concentration.
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see 5.3 and 5.6.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F945 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Stress-Corrosion of Titanium Alloys by Aircraft Engine
1
Cleaning Materials
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF945;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
Chemical solutions and compounds used for preinspection cleaning or for preservation of titanium
alloy aircraft turbine engine parts shall be subject to qualification requirements of this test method.
1. Scope mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This test method establishes a test procedure for deter-
mining the propensity of aircraft turbine engine cleaning and
2. Referenced Documents
maintenance materials for causing stress corrosion cracking of
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
titanium alloy parts.
D740 Specification for Methyl Ethyl Ketone
1.2 The evaluation is conducted on representative titanium
D841 Specification for Nitration Grade Toluene
alloys by determining the effect of contact with cleaning and
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3
maintenance materials on tendency of prestressed titanium
2.2 SAE Aerospace Material Specifications:
alloys to crack when subsequently heated to elevated tempera-
AMS 4911 Sheet, Strip and Plate-6AL-4VAnnealed 0.050”
tures.
Thick
AMS 4916 Sheet, Strip, and Plate-8AL 1MO 1V, Duplex
1.3 Test conditions are based upon manufacturer’s maxi-
Annealed 0.050” Thick
mum recommended operating solution concentration.
AMS 4919 Sheet, Strip, and Plate-6AL 2 Sn, 4 Zr, 2 Mo,
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
Duplex Annealed 0.050” Thick
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
3. Significance and Use
information only and are not considered standard.
3.1 Because of the tendency of prestressed titanium alloy
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
parts to crack if heated while in contact with certain chemical
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
reagents, it is necessary to ensure that cleaning and mainte-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
nance materials will not initiate stress corrosion of titanium
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
alloys under controlled conditions. For test specimens, two
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
common titanium alloys are selected, one that is very suscep-
For specific precautionary statements, see 5.3 and 5.6.
tible (AMS 4916 or AMS 4919) and one that is not very
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
susceptible (AMS 4911) to stress corrosion cracking.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Apparatus
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 Measuring Devicecapableoflinearmeasurementwitha
60.01 in. (60.25 mm) tolerance.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.07 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Qualification Testing of Aircraft Cleaning Materials. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2022. Published September 2022. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approvedin1985.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2019asF945 – 12(2019).DOI: Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr.,
10.1520/F0945-22. Warrendale, PA 15096.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F945 − 22
4 5
4.2 Press Forming Apparatus with 0.56 in. (14 mm) diam- where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
eter mandrel capable of producing approximately 65° bends in used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
0.050 in. (1.25 mm) titanium alloy sheet specimens. sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
accuracy of analysis.
4.3 Beakers or Small Tanks for containment of cleaning,
rinsing, and test solutions, appropriately lined to prevent
5.2 Purity
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F945 − 12 (Reapproved 2019) F945 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Stress-Corrosion of Titanium Alloys by Aircraft Engine
1
Cleaning Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F945; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
Chemical solutions and compounds used for preinspection cleaning or for preservation of titanium
alloy aircraft turbine engine parts shall be subject to qualification requirements of this test method.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method establishes a test procedure for determining the propensity of aircraft turbine engine cleaning and
maintenance materials for causing stress corrosion cracking of titanium alloy parts.
1.2 The evaluation is conducted on representative titanium alloys by determining the effect of contact with cleaning and
maintenance materials on tendency of prestressed titanium alloys to crack when subsequently heated to elevated temperatures.
1.3 Test conditions are based upon manufacturer’s maximum recommended operating solution concentration.
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see 5.3 and 5.6.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D740 Specification for Methyl Ethyl Ketone
D841 Specification for Nitration Grade Toluene
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.07 on Qualification
Testing of Aircraft Cleaning Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2019Sept. 1, 2022. Published June 2019September 2022. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 20122019 as
F945 – 12.F945 – 12(2019). DOI: 10.1520/F0945-12R19.10.1520/F0945-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F945 − 22
3
2.2 SAE Aerospace Material Specifications:
AMS 4911 Sheet, Strip and Plate-6AL-4V Annealed 0.050” Thick
AMS 4916 Sheet, Strip, and Plate-8AL 1MO 1V, Duplex Annealed 0.050” Thick
AMS 4919 Sheet, Strip, and Plate-6AL 2 Sn, 4 Zr, 2 Mo, Duplex Annealed 0.050” Thick
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Because of the tendency of prestressed titanium alloy parts to crack if heated while in contact with certain chemical reagents,
it is necessary to ensure that cleaning and maintenance materials will not initiate stress corrosion of titanium alloys under
controlled conditions. For test specimens, two common titanium alloys are selected, one that is very susceptible (AMS 4916) 4916
or AMS 4919) and one that is not very susceptible (AMS 4911) to stress corrosion cracking.
4. Apparatus
4.1 Measuring Device capable of linear measurement with a 60.01-in. (60.25-mm)60.01 in. (60.25 mm) tolerance.
4
4.2 Press Forming Apparatus with 0.56-in. (14-mm)0.56 in. (14 mm) diameter mandrel capable of producing approximately 65°
bends in 0.050-in. (1.25-mm)0.050 in. (1.25 mm) titanium alloy sheet specimens.
4.3 Beakers or Small Tanks for containment of cleaning, rinsing, and test solutions, appropriately lined to prevent contamination
of the solutions
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.