ASTM G205-10
(Guide)Standard Guide for Determining Corrosivity of Crude Oils
Standard Guide for Determining Corrosivity of Crude Oils
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
In the absence of water, the crude oil is noncorrosive. The presence of sediment and water makes crude oil corrosive. Test Methods , , , and provide methods for the determination of the water and sediment content of crude oil.
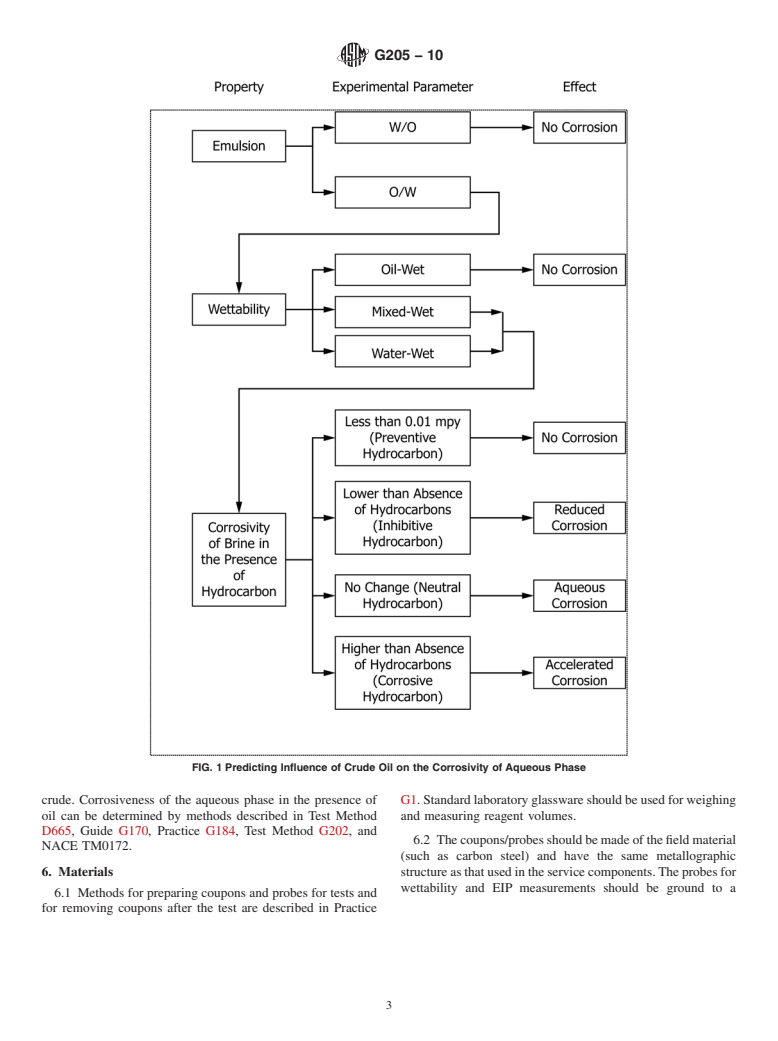
The corrosivity of crude oil containing water can be determined by a combination of three properties (Fig. 1) (1) : the type of emulsion formed between oil and water, the wettability of the steel surface, and the corrosivity of water phase in the presence of oil.
Water and oil are immiscible but, under certain conditions, they can form emulsion. There are two kinds of emulsion: O/W and W/O. W/O emulsion (in which oil is the continuous phase) has low conductivity and is thus less corrosive; whereas O/W (in which water is the continuous phase) has high conductivity and, hence, is corrosive (see ISO 6614) (2). The conductivities of various liquids are provided in Table 1(3). The percentage of water at which W/O converts to O/W is known as the emulsion inversion point (EIP). EIP can be determined by measuring the conductivity of the emulsion. At and above the EIP, a continuous phase of water or free water is present. Therefore, there is a potential for corrosion.
Whether water phase can cause corrosion in the presence of oil depends on whether the surface is oil wet (hydrophobic) or water wet (hydrophilic) (4-8). Because of higher resistance, an oil-wet surface is not susceptible to corrosion, but a water-wet surface is. Wettability can be characterized by measuring the contact angle or the conductivity (spreading method).
In the contact angle method, the tendency of water to displace hydrocarbon from steel is measured directly by observing the behavior of the three phase system. The contact angle is determined by the surface tensions (surface free energies) of the three phases. A hydrocarbon-steel interface will be replaced by a water-steel interface if this action will result in an energy decrease of the system. To determine whether the ...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide presents some generally accepted laboratory methodologies that are used for determining the corrosivity of crude oil.
1.2 This guide does not cover detailed calculations and methods, but rather a range of approaches that have found application in evaluating the corrosivity of crude oil.
1.3 Only those methodologies that have found wide acceptance in crude oil corrosivity evaluation are considered in this guide.
1.4 This guide does not address the change in oil/water ratio caused by accumulation of water at low points in a pipeline system.
1.5 This guide is intended to assist in the selection of methodologies that can be used for determining the corrosivity of crude oil under conditions in which water is present in the liquid state (typically up to 100°C). These conditions normally occur during oil and gas production, storage, and transportation in the pipelines.
1.6 This guide does not cover the evaluation of corrosivity of crude oil at higher temperatures (typically above 300°C) that occur during refining crude oil in refineries.
1.7 This guide involves the use of electrical currents in the presence of flammable liquids. Awareness of fire safety is critical for the safe use of this guide.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G205 − 10
Standard Guide for
Determining Corrosivity of Crude Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G205; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This guide presents some generally accepted laboratory
methodologies that are used for determining the corrosivity of
2. Referenced Documents
crude oil.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2 This guide does not cover detailed calculations and
D96 Test Method for Water and Sediment in Crude Oil by
methods, but rather a range of approaches that have found 3
Centrifuge Method (Field Procedure) (Withdrawn 2000)
application in evaluating the corrosivity of crude oil.
D473 Test Method for Sediment in Crude Oils and Fuel Oils
1.3 Only those methodologies that have found wide accep- by the Extraction Method
tance in crude oil corrosivity evaluation are considered in this D665 Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of
guide. Inhibited Mineral Oil in the Presence of Water
D724 Test Method for Surface Wettability of Paper (Angle-
1.4 Thisguidedoesnotaddressthechangeinoil/waterratio
of-Contact Method) (Withdrawn 2009)
caused by accumulation of water at low points in a pipeline
D1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Resis-
system.
tivity of Water
1.5 This guide is intended to assist in the selection of
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
methodologies that can be used for determining the corrosivity
D1141 Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean
of crude oil under conditions in which water is present in the
Water
liquid state (typically up to 100°C). These conditions normally
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
occurduringoilandgasproduction,storage,andtransportation
D4006 Test Method for Water in Crude Oil by Distillation
in the pipelines.
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
1.6 This guide does not cover the evaluation of corrosivity
ofcrudeoilathighertemperatures(typicallyabove300°C)that D4377 Test Method forWater in Crude Oils by Potentiomet-
ric Karl Fischer Titration
occur during refining crude oil in refineries.
G1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corro-
1.7 This guide involves the use of electrical currents in the
sion Test Specimens
presence of flammable liquids. Awareness of fire safety is
G31 Guide for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of
critical for the safe use of this guide.
Metals
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
G111 Guide for Corrosion Tests in High Temperature or
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
High Pressure Environment, or Both
standard.
G170 Guide for Evaluating and Qualifying Oilfield and
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors in the Laboratory
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the G184 Practice for Evaluating and Qualifying Oil Field and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- Refinery Corrosion Inhibitors Using Rotating Cage
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee G01 on Corrosion of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Metals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.05 on Laboratory Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Corrosion Tests. the ASTM website.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2010. Published October 2010. DOI: 10.1520/ The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
G0205–10. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
G205 − 10
G193 Terminology and Acronyms Relating to Corrosion 4.4 The corrosiveness of water phase in the presence of
G202 Test Method for UsingAtmospheric Pressure Rotating crude oil can be determined using several methods.
Cage
5. Significance and Use
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 6614 Petroleum products—Determination of Water
5.1 In the absence of water, the crude oil is noncorrosive.
Separability of Petroleum Oils and Synthetic Fluids
The presence of sediment and water makes crude oil corrosive.
2.3 NACE Standard:
Test Methods D96, D473, D4006, and D4377 provide methods
TM0172 Standard Test Method Determining Corrosive
for the determination of the water and sediment content of
Properties of Cargoes in Petroleum Product Pipelines
crude oil.
5.2 The corrosivity of crude oil containing water can be
3. Terminology
determined by a combination of three properties (Fig. 1)(1) :
3.1 Definitions—The terminology used herein, if not spe-
the type of emulsion formed between oil and water, the
cifically defined otherwise, shall be in accordance with Guide
wettability of the steel surface, and the corrosivity of water
G170, Terminology and Acronyms G193, and Terminology
phase in the presence of oil.
D1129. Definitions provided herein and not given in Guide
5.3 Water and oil are immiscible but, under certain
G170, Terminology and Acronyms G193, and Terminology
conditions, they can form emulsion. There are two kinds of
D1129 are limited only to this guide.
emulsion: O/W and W/O. W/O emulsion (in which oil is the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
continuous phase) has low conductivity and is thus less
3.2.1 emulsion, n—two-phase immiscible liquid system in
corrosive; whereas O/W (in which water is the continuous
which one phase is dispersed as droplets in the other phase.
phase) has high conductivity and, hence, is corrosive (see ISO
3.2.2 emulsion-inversion point, n—percentage of water at
6614) (2).The conductivities of various liquids are provided in
which a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion converts into an oil-in-
Table 1(3). The percentage of water at which W/O converts to
water (O/W) emulsion.
O/W is known as the emulsion inversion point (EIP). EIP can
be determined by measuring the conductivity of the emulsion.
3.2.3 wettability,n—tendencyofaliquidtowetoradhereon
AtandabovetheEIP,acontinuousphaseofwaterorfreewater
to a solid surface.
is present. Therefore, there is a potential for corrosion.
3.3 Acronyms:
5.4 Whether water phase can cause corrosion in the pres-
CO = Carbon dioxide
ence of oil depends on whether the surface is oil wet (hydro-
EIP = Emulsion inversion point
phobic) or water wet (hydrophilic) (4-8). Because of higher
H S = Hydrogen sulfide
resistance, an oil-wet surface is not susceptible to corrosion,
KOH = Potassium hydroxide
but a water-wet surface is. Wettability can be characterized by
NaCl = Sodium chloride
measuring the contact angle or the conductivity (spreading
Na CO = Sodium carbonate
2 3
method).
NaHCO = Sodium bicarbonate
5.4.1 In the contact angle method, the tendency of water to
NaOH = Sodium hydroxide
displace hydrocarbon from steel is measured directly by
Na S = Sodium sulfide
observing the behavior of the three phase system. The contact
O/W = Oil-in-water
angle is determined by the surface tensions (surface free
W/O = Water-in-oil
energies) of the three phases. A hydrocarbon-steel interface
4. Summary of Guide
will be replaced by a water-steel interface if this action will
result in an energy decrease of the system. To determine
4.1 This guide describes methods for determining the cor-
whether the surface is oil wet, mixed wet, or water wet, the
rosivity of crude oils by a combination of three properties: (1)
angle at the oil-water-solid intersection is observed and mea-
theemulsionoftheoilandwater, (2)thewettabilityofthesteel
sured.
surface, and (3) the corrosivity of water phase in the presence
5.4.2 In the spreading method of determining wettability,
of oil.
the resistance between steel pins is measured. If a conducting
4.2 Conductivity of emulsion can be used to determine the
phase (for example, water) covers (wets) the distance between
typeofemulsion:oilinwater(O/W)orwaterinoil(W/O).The
the pins, conductivity between them will be high. On the other
conductivity of the O/W emulsion (in which water is the
hand,ifanonconductingphase(forexample,oil)covers(wets)
continuous phase) is high. The conductivity of the W/O
the distance between the pins, the conductivity between them
emulsion (in which oil is the continuous phase) is low.
will be low.
4.3 The wettability of a steel surface is determined using
5.5 Dissolution of ingredients from crude oils may alter the
two methods: (1) contact angle method and (2) spreading
corrosiveness of the aqueous phase. Based on how the corro-
method.
sivity of the aqueous phase changes in its presence, a crude oil
can be classified as corrosive, neutral, inhibitory, or preventive
Available from theAmerican National Standards Institute, 25W. 43rd St., New
York, NY 10036.
5 6
AvailablefromtheNationalAssociationofCorrosionEngineers,1440S.Creek The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
Dr., Houston, TX 77084-4906. this standard.
G205 − 10
FIG. 1 Predicting Influence of Crude Oil on the Corrosivity of Aqueous Phase
crude. Corrosiveness of the aqueous phase in the presence of G1.Standardlaboratoryglasswareshouldbeusedforweighing
oil can be determined by methods described in Test Method and measuring reagent volumes.
D665, Guide G170, Practice G184, Test Method G202, and
6.2 Thecoupons/probesshouldbemadeofthefieldmaterial
NACE TM0172.
(such as carbon steel) and have the same metallographic
6. Materials structureasthatusedintheservicecomponents.Theprobesfor
wettability and EIP measurements should be ground to a
6.1 Methods for preparing coupons and probes for tests and
for removing coupons after the test are described in Practice
G205 − 10
TABLE 1 Conductivities of Selected Hydrocarbons and Aqueous
quired to be saturated with acid gases such as hydrogen sulfide
Phases (3)
(H S) and carbon dioxide (CO ). H S and CO are corrosive
2 2 2 2
A
Liquid Temperature, °C Conductivity
gases. H S is poisonous and shall not be released to the
-9
Acetic acid 0 5 × 10
atmosphere. The appropriate composition of gas can be ob-
-8
Aniline 25 2.4 × 10
tained by mixing H S, CO , and methane streams from the
-8
2 2
Benzene . 7.6 × 10
-5
standard laboratory gas supply. Nitrogen or any other inert gas
Formic acid 25 6.4 × 10
-8
Glycerol 25 6.4 × 10
can be used as a diluent to obtain the required partial pressures
-7
Glycol 25 3 ×10
-13 of the corrosive gases. Alternatively, gas mixtures of the
Heptane . <1 ×10
-18
appropriate compositions can be purchased from suppliers of
Hexane 18 <1 × 10
-8
Kerosene 25 <1.7 × 10
industrial gases. The composition of gas depends on the field
-10
Pentane 19.5 <2 × 10
gas composition. The oxygen concentration in solution de-
-12
Sulfur 115 1 × 10
-8
Sulfur dioxide 35 1.5 × 10 ) pends on the quality of gases used to purge the solution. The
-2
Sulfuric acid 25 1 × 10
oxygen content of nitrogen or the inert gas should be less then
-8
Sulfuryl chloride, S0 C1 25 3×10
2 2
-8 10ppmbyvolume.Leaksthroughthevessel,tubing,andjoints
Water 18 4×10
B
KOH 18 234 should be avoided.
B
NaCl 18 106.5
B 7.4 The test vessels should be heated slowly to avoid
NaOH 18 208
B
1/2Na S 18 104.3 (N= 1.0)
2 overheating. The thermostat in the heater or thermostatic bath
B
NaHC0 25 93.5
should be set not more than 20°C above the solution tempera-
B
1/2Na C0 18 112
2 3
ture until the test temperature is reached. The pressure in the
A
Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of the ac resistance in ohms measured
vessel should be monitored during heating to make sure it does
between opposite faces of a 1-cm cube of an aqueous solution at a specified
temperature (in accordance with Test Methods D1125). The unit of electrical not exceed the relief pressure. If necessary, some of the gas in
conductivity is Siemens per centimetre (S/cm). The previously used units of
the vessel may be bled off to reduce the pressure. The test
mhos/cm are numerically equivalent to S/cm. At low concentrations to obtain the
temperature should be maintained within +2°C of the specified
conductivity of electrolyte the conductivity of pure solvent should be subtracted
from that of the solution. temperature. Once the test temperature is reached, the test
B -1 2 -1
Equivalent conductivity of an electrolyte, Λ (Ω ·cm · equiv ) – the sum of
pressure should be adjusted to the predetermined value. The
contributions of the individual ions; Λ = κ/C, where C is concentration in
pressure should be maintained within +10 % of the specified
equivalents per litre. The volume of the solution in cubic centimetres per equivalent
is equal to 1000/C, andΛ = 1000κ/C. The values are taken at 0.001 concentration
value for the duration of the test.
(N), except where specified otherwise.
7.5 Ageneralproceduretocarryoutexperimentsatelevated
pressure and elevated temperature is described in Guide G111.
For elevated temperature and elevated pressure experiments
surface finish of 600 grit. Preparation of coupons for corrosion
using individual gases, first the autoclave is pressurized with
measurements is described in Guide G170, Practice G184, and
H S to the required partial pressure and left for 10 min. If there
Test Method G202.
is a decrease of pressure, the autoclave is repressurized. This
process is repeated until no further pressure drop occurs.Then,
7. Preparation of Test Solutions
the autoclave is pressurized with CO by opening the CO gas
2 2
7.1 Oil should be obtained from the field that is being
cylinder at a pressure equal to the CO +H S partial pressure
2 2
evaluated. Practice D4057 provides guidelines for collecting
and left for 10 min. If there is a decrease in pressure, the
crude oil. It is important that live fluids do not contain
autoclave is repressurized with CO gas. This process is
externally added contaminants, for example, corrosion
repeated until no further pressure drop is observed. Finally, the
inhibitors, biocides, and surfactants. A water sample should
autoclave is pressurized with an inert gas (for example,
also be obtained from the field. A synthetic aqueous solution
methane) by opening the appropriate cylinder at the total gas
could be used; the composition of which, however, should be
pressure at which the experiments are intended to be carried
based on field water analysis.Alternatively, standard 3 % brine
out.
or synthetic brine (of a com
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.