ISO 11784:1996
(Main)Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure
Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure
Contains the structure of the radio-frequency identification code for animals. Does not specify the characteristics of the transmission protocols between transponder and transceiver. Replaces the first edition.
Identification des animaux par radiofréquence — Structure du code
La présente Norme internationale prescrit la structure du code d'identification des animaux par radiofréquence (RF). L'identification des animaux par radiofréquence (RFID) nécessite que les bits transmis par un transpondeur puissent être interprétés par un émetteur-récepteur. Habituellement, le train de bits contient des bits d'information qui définissent le code d'identification ainsi qu'un certain nombre de bits destinés à garantir la réception correcte des bits d'information. La présente Norme internationale prescrit la structure du code d'identification. La présente Norme internationale ne prescrit pas les caractéristiques des protocoles de transmission entre transpondeurs et émetteurs-récepteurs. Ces caractéristiques font l'objet de l'ISO 11785. NOTE -- Une procédure d'attribution du code du fabricant est à l'étude.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 14-Aug-1996
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 23/SC 19 - Agricultural electronics
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 23/SC 19/WG 3 - Identification
- Current Stage
- 9599 - Withdrawal of International Standard
- Start Date
- 10-Dec-2024
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
- Directive
- Not Harmonized2014-01-3644 - Pravilnik o označevanju in registraciji hišnih živali
Relations
- Amended By
ISO 11784:1996/Amd 1:2004 - Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure — Amendment 1 - Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Parent
ISO 11784:1996/Amd 1:2004 - Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure — Amendment 1 - Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 11784:1996 is an internationally recognized standard that defines the code structure for radio-frequency identification (RFID) of animals. Established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), this standard specifies the formatting of the unique identification codes transmitted by RFID transponders implanted or attached to animals. Importantly, ISO 11784 focuses on the structure of the identification code itself and does not define transmission protocols between transponders and transceivers, which are covered in ISO 11785.
The standard ensures a globally consistent code format, facilitating animal identification, traceability, and management across multiple countries and industries such as agriculture, livestock breeding, veterinary medicine, and wildlife monitoring.
Key Topics
Animal Identification Code Structure
The RFID code consists of a series of binary bits arranged into specific fields:- Flag Bit (bit 1): Indicates if the tag is for animal identification (set to 1) or not.
- Reserved Bits (bits 2-15): Reserved for future use, allowing future enhancements without altering the fundamental code structure.
- Data Block Flag (bit 16): Signals whether additional data blocks are included beyond the basic identification code.
- Country Code (bits 17-26): Encoded using ISO 3166 numeric-3 country codes to identify the country where the transponder was issued.
- National Identification Code (bits 27-64): A unique number assigned within the country ensuring worldwide uniqueness when combined with the country code.
Unique Global Identification
The combination of the ISO country code and the national identification code provides a unique worldwide animal ID. This prevents duplication of codes internationally and supports centralized tracking.Manufacturer and Data Block Options
Although not defined in ISO 11784, additional bits and data blocks allow flexibility for manufacturers to encode extended data, such as physiological measurements or specific animal information.Responsibility and Compliance
Ensuring uniqueness of national codes is a national responsibility, recommended to be managed via centralized databases. The standard requires RFID transponders used in animals to conform to this structured coding format for interoperability.
Applications
Livestock Management
Farmers and agricultural organizations use RFID tags conforming to ISO 11784 to uniquely identify cattle, sheep, pigs, and other domestic animals for health monitoring, breeding control, and inventory management.Veterinary Practices
Veterinarians utilize ISO 11784-based RFID systems for individual animal identification to track medical histories, vaccinations, and treatments.Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife researchers and conservationists employ standardized animal RFID tags to monitor endangered species, track migration patterns, and manage protected populations.Regulatory Compliance and Food Safety
Governments and regulatory bodies require standardized animal identification for disease control, food traceability, and compliance with international trade standards.Animal Breeding and Genetic Tracking
Breeders use the unique code system to maintain pedigree records and support genetic evaluation across datasets at national and international levels.
Related Standards
ISO 11785: Radio-frequency identification of animals - Transmission protocols
Defines the communication protocols between transponders and transceivers to complement the code structure specified in ISO 11784.ISO 3166: Codes for the representation of names of countries
Provides the numeric country codes referenced in ISO 11784 for assigning country identifiers within the RFID code.Standards for Agricultural Electronics (ISO/TC 23/SC 19)
ISO 11784 is developed under this technical committee focused on interrelated agricultural and livestock equipment standards.
Summary
ISO 11784:1996 lays the foundation for standardized, globally unique RFID animal identification codes essential for modern animal traceability systems. By specifying a clear, standardized code structure, it enables interoperability across different countries and industries, supporting animal health, food safety, regulatory compliance, and wildlife preservation. This standard plays a crucial role in agricultural electronics and RFID-based livestock management solutions worldwide.
Buy Documents
ISO 11784:1996 - Radio frequency identification of animals -- Code structure
ISO 11784:1996 - Identification des animaux par radiofréquence -- Structure du code
ISO 11784:1996 - Identification des animaux par radiofréquence -- Structure du code
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Control Union Certifications
Global certification for agriculture and sustainability.

ECOCERT
Organic and sustainability certification.

Rainforest Alliance Certification
Sustainable agriculture and forestry certification.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 11784:1996 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure". This standard covers: Contains the structure of the radio-frequency identification code for animals. Does not specify the characteristics of the transmission protocols between transponder and transceiver. Replaces the first edition.
Contains the structure of the radio-frequency identification code for animals. Does not specify the characteristics of the transmission protocols between transponder and transceiver. Replaces the first edition.
ISO 11784:1996 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 65.040.99 - Other standards related to farm buildings and installations. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 11784:1996 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 11784:1996/Amd 1:2004, ISO 11784:1996/Amd 2:2010, ISO 11784:2024, ISO 11784:1994; is excused to ISO 11784:1996/Amd 2:2010, ISO 11784:1996/Amd 1:2004. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 11784:1996 is associated with the following European legislation: EU Directives/Regulations: 2014-01-3644. When a standard is cited in the Official Journal of the European Union, products manufactured in conformity with it benefit from a presumption of conformity with the essential requirements of the corresponding EU directive or regulation.
ISO 11784:1996 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL
IS0
STANDARD
Second edition
1996-08-I 5
Radio-frequency identification of
animals - Code structure
Identification des animaux par radiofrbquence - Structure du code
Reference number
IS0 -l 1784: 1996(E)
IS0 11784:1996(E)
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide fed-
eration of national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of
preparing International Standards is normally carried out through IS0
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be
represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. IS0
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard IS0 11784 was prepared by Technical Committee
lSO/TC 23, Tractors and machinery for agriculture and forestry, subcom-
mittee SC 19, Agricultural electronics.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition
(IS0 11784:1994), which has been technically revised.
0 IS0 1996
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be
reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-1211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
IS0 11784:1996(E)
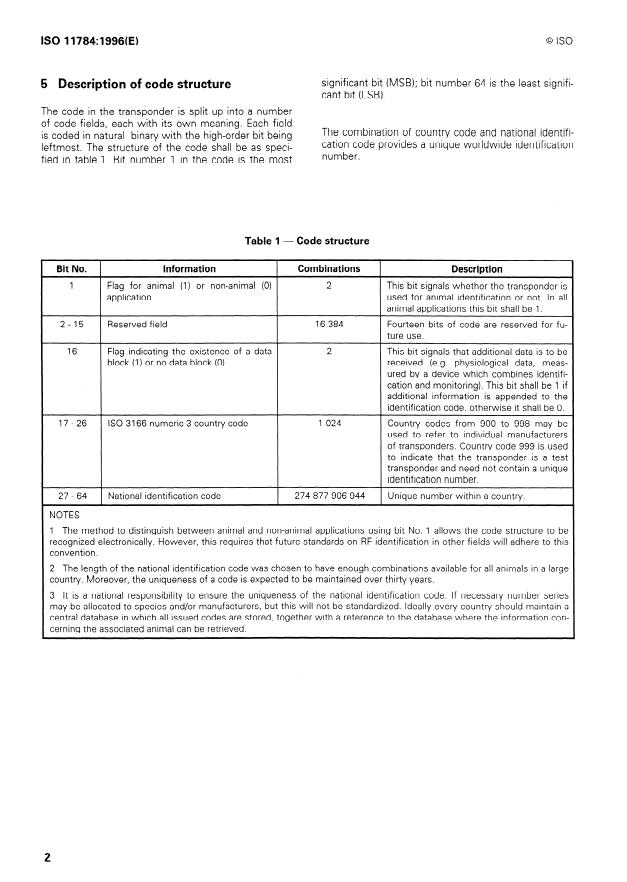
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD @ IS0
Radio-frequency identification of animals - Code structure
4 Definitions
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies the structure of For the purposes of this International Standard, the
following definitions apply.
the radio-frequency (RF) identification code for ani-
mals.
4.1 animal code: Bit pattern to identify an animal.
RF identification of animals requires that the bits
transmitted by a transponder are interpretable by a
transceiver. Usually the bit stream contains data bits,
4.2 bit pattern: Sequence of binary digits or bits
defining the identification code and a number of bits
LO, II.
to ensure correct reception of the data bits. This In-
ternational Standard specifies the structure of the
43 code field: Group of bits in the identification
identification code.
code with a specific meaning.
This International Standard does not specify the
characteristics of the transmission protocols between
44 . country code: Bit pattern to define the country
transponder and transceiver. These characteristics are
where the transponder was issued.
the subject of IS0 11785.
NOTE - A procedure for the allocation of the manufactu-
4.5 data block: Additional group of bits with a
rer ’s code is under study.
specific meaning.
2 Conformance
4.6 flag: Single bit with a specific meaning.
The unique individual identification codes transmitted
by a transponder are in conformance with this Inter-
4.7 identification code: Part of the code that is
national Standard provided they meet the require-
used for identification (control codes such as header,
ments of clause 5. trailer and checksum are excluded).
3 Normative reference
4.8 manufacturer ’s code: Bit pattern identifying the
manufacturer of the transponder.
The following standard contains provisions which,
through reference in this text, constitute provisions of
this International Standard. At the time of publication,
4.9 national id
...
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1996-08-l 5
Identification des animaux par
radiofréquence -
Structure du code
Radio-frequency iden tifica tien of animais - Code structure
Numéro de référence
ISO 11784:-l 996(F)
Avant-propos
LYS0 (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 11784 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 23, Tracteurs et matériels agricoles et forestiers, sous-comité
SC 19, Électronique en agriculture.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 11784:1994), dont elle constitue une révision technique.
0 ISO 1996
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56.CH-1211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
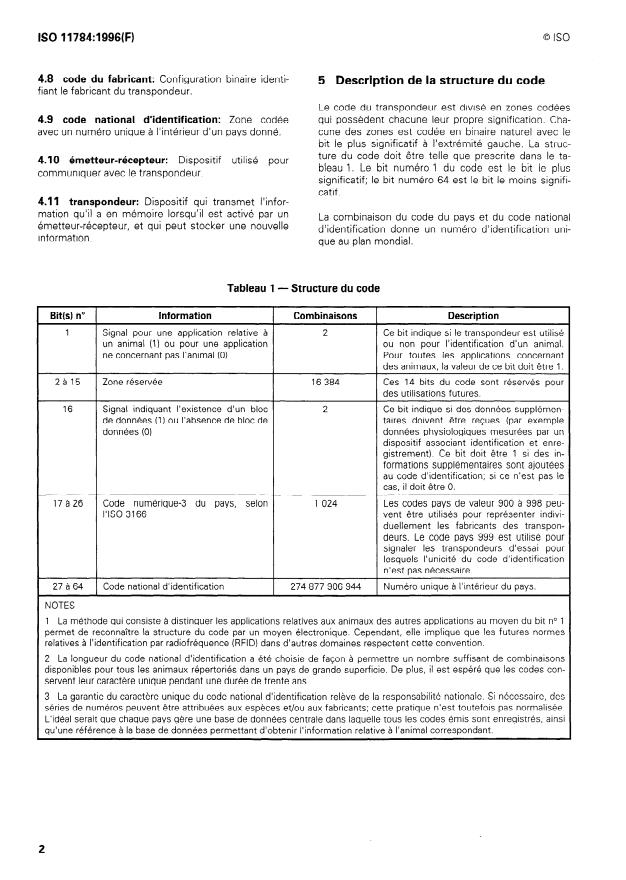
NORME INTERNATIONALE @ ISO ISO 11784:1996(F)
Identification des animaux par radiofréquence -
Structure du code
rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition la plus ré-
1 Domaine d’application
cente de la norme indiquée ci-après. Les membres de
la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des Normes
La présente Norme internationale prescrit la structure
internationales en vigueur à un moment donné.
du code d’identification des animaux par radiofré-
quence (RF).
ISO 3 166: 1993, Codes pour la représentation des
noms de pays.
L’identification des animaux par radiofréquence (RFID)
nécessite que les bits transmis par un transpondeur
puissent être interprétés par un émetteur-récepteur.
Habituellement, le train de bits contient des bits d’in-
4 Définitions
formation qui définissent le code d’identification ainsi
qu’un certain nombre de bits destinés à garantir la ré-
ception correcte des bits d’information. La présente
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale,
Norme internationale prescrit la structure du code
les définitions suivantes s’appliquent.
d’identification.
La présente Norme internationale ne prescrit pas les
4.1 code de l’animal: Configuration binaire identi-
caractéristiques des protocoles de transmission entre
fiant un animal.
transpondeurs et émetteurs-récepteurs. Ces caracté-
ristiques font l’objet de I’ISO 11785.
4.2 configuration binaire: Série de chiffres binaires
NOTE - Une procédure d’attribution du code du fabricant ou bits [0, Il.
est à l’étude.
4.3 zone codée: Groupe de bits dans le code
d’identification, ayant une signification particulière.
2 Conformité
Pour être conforme à la présente Norme inter-
4.4 code du pays: Configuration binaire définissant
nationale, le code d’identification unique transmis par
le pays dans lequel le transpondeur a été émis.
un transpondeur doit répondre aux exigences de
l’article 5.
4.5 bloc de données: Groupe supplémentaire de
bits ayant une signification particulière.
3 Référence normative
4.6 signai: Bit unique ayant une signification parti-
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par
culière.
suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente Norme interna-
4.7 code d’identification: Partie du code utilisée
tionale. Au moment de la publication, l’édition indi-
pour l’identification (en sont
...
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1996-08-l 5
Identification des animaux par
radiofréquence -
Structure du code
Radio-frequency iden tifica tien of animais - Code structure
Numéro de référence
ISO 11784:-l 996(F)
Avant-propos
LYS0 (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 11784 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 23, Tracteurs et matériels agricoles et forestiers, sous-comité
SC 19, Électronique en agriculture.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 11784:1994), dont elle constitue une révision technique.
0 ISO 1996
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56.CH-1211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
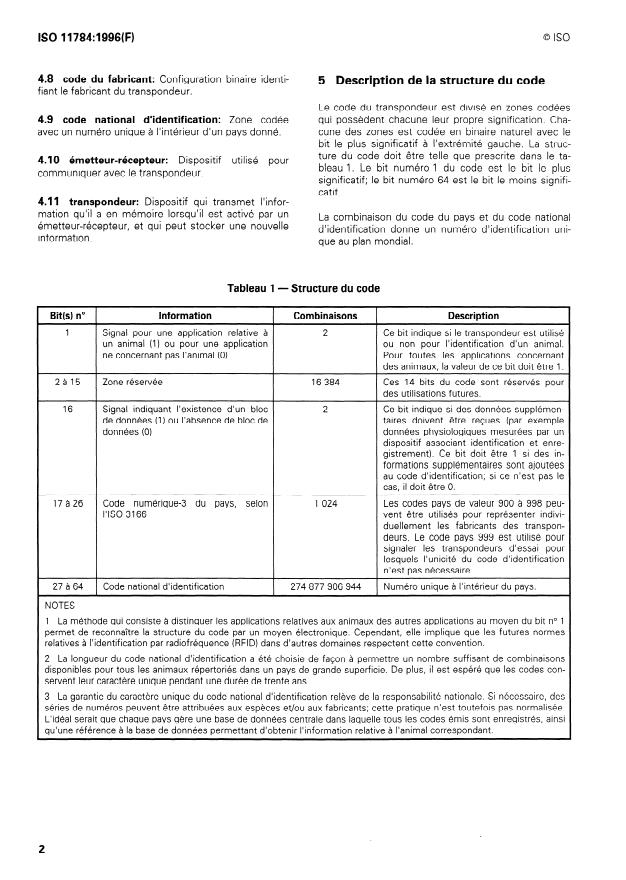
NORME INTERNATIONALE @ ISO ISO 11784:1996(F)
Identification des animaux par radiofréquence -
Structure du code
rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition la plus ré-
1 Domaine d’application
cente de la norme indiquée ci-après. Les membres de
la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des Normes
La présente Norme internationale prescrit la structure
internationales en vigueur à un moment donné.
du code d’identification des animaux par radiofré-
quence (RF).
ISO 3 166: 1993, Codes pour la représentation des
noms de pays.
L’identification des animaux par radiofréquence (RFID)
nécessite que les bits transmis par un transpondeur
puissent être interprétés par un émetteur-récepteur.
Habituellement, le train de bits contient des bits d’in-
4 Définitions
formation qui définissent le code d’identification ainsi
qu’un certain nombre de bits destinés à garantir la ré-
ception correcte des bits d’information. La présente
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale,
Norme internationale prescrit la structure du code
les définitions suivantes s’appliquent.
d’identification.
La présente Norme internationale ne prescrit pas les
4.1 code de l’animal: Configuration binaire identi-
caractéristiques des protocoles de transmission entre
fiant un animal.
transpondeurs et émetteurs-récepteurs. Ces caracté-
ristiques font l’objet de I’ISO 11785.
4.2 configuration binaire: Série de chiffres binaires
NOTE - Une procédure d’attribution du code du fabricant ou bits [0, Il.
est à l’étude.
4.3 zone codée: Groupe de bits dans le code
d’identification, ayant une signification particulière.
2 Conformité
Pour être conforme à la présente Norme inter-
4.4 code du pays: Configuration binaire définissant
nationale, le code d’identification unique transmis par
le pays dans lequel le transpondeur a été émis.
un transpondeur doit répondre aux exigences de
l’article 5.
4.5 bloc de données: Groupe supplémentaire de
bits ayant une signification particulière.
3 Référence normative
4.6 signai: Bit unique ayant une signification parti-
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par
culière.
suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente Norme interna-
4.7 code d’identification: Partie du code utilisée
tionale. Au moment de la publication, l’édition indi-
pour l’identification (en sont
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...