IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005
(Amendment)Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium
Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium
Amendement 1 - Accumulateurs alcalins et autres accumulateurs à électrolyte non acide - Accumulateurs individuels portables étanches - Partie 1: Nickel-cadmium
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 22-Nov-2005
- Technical Committee
- SC 21A - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes
- Drafting Committee
- WG 2 - TC 21/SC 21A/WG 2
- Current Stage
- DELPUB - Deleted Publication
- Start Date
- 15-Oct-2013
- Completion Date
- 13-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
Overview
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 is an important amendment to the international standard governing secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes. Specifically, it addresses portable sealed rechargeable single cells, Part 1: Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) cells. This amendment, developed by IEC Technical Committee 21, Subcommittee 21A, focuses on refining requirements for nickel-cadmium cylindrical cells used in rechargeable battery applications.
A key enhancement introduced by this amendment is the differentiation of cells designed for elevated operating temperatures-distinguishing cells suitable for continuous use at up to 40 °C from those rated for operations up to 50 °C. This distinction ensures improved reliability and safety standards for Ni-Cd cells used in varied environmental conditions.
Key Topics
Temperature Classification for Ni-Cd Cells
- Cells intended for permanent charge at elevated temperatures up to 40 °C carry a “T” designation after their size code letters (L, M, H, or X).
- Cells designed for operation up to 50 °C use a “U” designation following those letters.
Permanent Charge Endurance Testing
The amendment specifies rigorous endurance tests simulating long-term operation under elevated temperature conditions, including aging protocols:- For cells rated at 40 °C:
- Charge acceptance test at +40 °C
- Six months aging at +70 °C (simulating 4 years service at 40 °C)
- Final charge acceptance to verify aging effects
- For cells rated at 50 °C:
- Charge acceptance test at +50 °C
- Twelve months aging at +70 °C (simulating 4 years at 50 °C)
- Final charge acceptance test post-aging
- For cells rated at 40 °C:
Updated Discharge Performance Data
New tables provide standardized minimum discharge durations at both 20 °C and –18 °C for various cylindrical cell codes (L/LT/LU, M/MT/MU, H/HT/HU, and X), ensuring reliable performance metrics under typical and low temperature conditions.Test Procedures and Conditions
Detailed test cycle conditions include controlled charge and discharge rates, ambient temperature control, and post-test rest periods, enhancing consistency and reproducibility of battery qualification tests.
Applications
This amendment to IEC 61951-1 is critical for industries and applications where portable sealed rechargeable Ni-Cd cells are used in environments with elevated temperatures or where long-lasting reliability is essential. Key application areas include:
- Portable electronic devices operating in hot climates
- Power tools requiring robust battery cells with reliable charge endurance
- Emergency communication systems where battery dependability under thermal stress is mandatory
- Medical devices and instrumentation needing sealed rechargeable cells that meet strict standards for safety and performance
- Renewable energy storage solutions where battery cells must endure temperature variations
Manufacturers and testing laboratories use this standard amendment to certify Ni-Cd cells meet enhanced thermal performance and longevity requirements, optimizing battery safety and lifecycle management.
Related Standards
- IEC 61951-1 (Base Standard): Covers general requirements for portable sealed rechargeable nickel-cadmium cells.
- IEC 61951 (Series): Encompasses secondary cells and batteries with alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes, including various cell sizes and chemistries.
- IEC 62133: Standard for safety requirements of rechargeable batteries used in portable applications, complementing performance standards with safety and environmental aspects.
- ISO/IEC Battery Testing Standards: Provide additional guidelines on testing procedures for secondary batteries in industrial and consumer electronics.
Summary
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 Amendment 1 enhances the standardization of portable sealed rechargeable Ni-Cd cells by refining classifications for elevated temperature performance and introducing stringent endurance testing protocols. These advancements support the development, testing, and deployment of Ni-Cd batteries with improved reliability and safety for diverse industrial and consumer applications, ensuring compliance with internationally recognized benchmarks. This amendment is essential for manufacturers, testing bodies, and end-users prioritizing durability and functionality of nickel-cadmium rechargeable cells under challenging thermal conditions.
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 - Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium Released:11/23/2005 Isbn:2831883563
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Intertek Testing Services NA Inc.
Intertek certification services in North America.

UL Solutions
Global safety science company with testing, inspection and certification.

ANCE
Mexican certification and testing association.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 is a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its full title is "Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium". This standard covers: Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium
Amendment 1 - Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes - Portable sealed rechargeable single cells - Part 1: Nickel-cadmium
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 29.220.30 - Alkaline secondary cells and batteries. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to IEC 61951-1:2003, IEC 61951-1:2013. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
IEC 61951-1:2003/AMD1:2005 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
NORME CEI
INTERNATIONALE
IEC
61951-1
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
AMENDEMENT 1
AMENDMENT 1
2005-11
Amendement 1
Accumulateurs alcalins et autres accumulateurs
à électrolyte non acide –
Accumulateurs individuels portables étanches –
Partie 1:
Nickel-cadmium
Amendment 1
Secondary cells and batteries containing
alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes –
Portable sealed rechargeable single cells –
Part 1:
Nickel-cadmium
IEC 2005 Droits de reproduction réservés Copyright - all rights reserved
International Electrotechnical Commission, 3, rue de Varembé, PO Box 131, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland
Telephone: +41 22 919 02 11 Telefax: +41 22 919 03 00 E-mail: inmail@iec.ch Web: www.iec.ch
CODE PRIX
G
Commission Electrotechnique Internationale
PRICE CODE
International Electrotechnical Commission
МеждународнаяЭлектротехническаяКомиссия
Pour prix, voir catalogue en vigueur
For price, see current catalogue
– 2 – 61951-1 Amend. 1 CEI:2005
AVANT-PROPOS
Le présent amendement a été établi par le sous-comité 21A: Accumulateurs alcalins et autres
accumulateurs à électrolyte non acide, du comité d'études 21 de la CEI: Accumulateurs.
Ce premier amendement permet de différencier les éléments pouvant fonctionner à des
températures allant jusqu’à 40 °C, de ceux pouvant fonctionner à des températures allant
jusqu’à 50 °C.
Le texte de cet amendement est issu des documents suivants:
FDIS Rapport de vote
21A/421/FDIS 21A/422/RVD
Le rapport de vote indiqué dans le tableau ci-dessus donne toute information sur le vote ayant
abouti à l'approbation de cet amendement.
Le comité a décidé que le contenu de cet amendement et de la publication de base ne sera
pas modifié avant la date de maintenance indiquée sur le site web de la CEI sous
"http://webstore.iec.ch" dans les données relatives à la publication recherchée. A cette date,
la publication sera
• reconduite,
• supprimée,
• remplacée par une édition révisée, ou
• amendée.
_____________
Page 2
SOMMAIRE
Remplacer le titre existant du paragraphe 7.6.3 par ce qui suit:
7.6.3 Eléments cylindriques LT/LU, MT/MU ou HT/HU
Ajouter à la liste des tableaux, page 4, le titre du nouveau Tableau 26 ci-dessous:
Tableau 26 – Endurance en charge permanente éléments cylindriques LU, MU ou HU
Page 14
5.1.2 Eléments cylindriques
Remplacer le paragraphe qui suit la note par ce qui suit:
Lorsqu’un élément est destiné à la charge permanente à des températures élevées,
normalement jusqu’à 40 °C, la lettre “T” est placée après la lettre L, M, H ou X.
Lorsqu’un élément est destiné à la charge permanente à des températures élevées,
normalement jusqu’à 50 °C, la lettre “U” est placée après la lettre L, M, H ou X.
61951-1 Amend. 1 IEC:2005 – 3 –
FOREWORD
This amendment has been prepared by subcommittee 21A: Secondary cells and batteries
containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes, of IEC technical committee 21: Secondary
cells and batteries.
This first amendment allows differentiating cells for operation at temperatures of up to 40 °C
and cells for operation at temperatures of up to 50 °C.
The text of this amendment is based on the following documents:
FDIS Report on voting
21A/421/FDIS 21A/422/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this amendment can be found in the report
on voting indicated in the above table.
The committee has decided that the contents of this amendment and the base publication will
remain unchanged until the maintenance result date indicated on the IEC web site under
"http://webstore.iec.ch" in the data related to the specific publication. At this date, the
publication will be
• reconfirmed,
• withdrawn,
• replaced by a revised edition, or
• amended.
_____________
Page 3
CONTENTS
Replace the existing title of 7.6.3 by the following:
7.6.3 LT/LU, MT/MU or HT/HU cylindrical cells
Add, on page 5, to the list of tables, the title of new Table 26 as follows:
Table 26 – Permanent charge endurance for LU, MU or HU cylindrical cells
Page 15
5.1.2 Cylindrical cells
Replace the paragraph after the note by the following:
When a cell is intended for permanent charge at elevated temperatures, typically up to 40 °C,
a letter "T" is placed after the letter L, M, H or X.
When a cell is intended for permanent charge at elevated temperatures, typically up to 50 °C,
a letter "U" is placed after the letter L, M, H or X.
– 4 – 61951-1 Amend. 1 CEI:2005
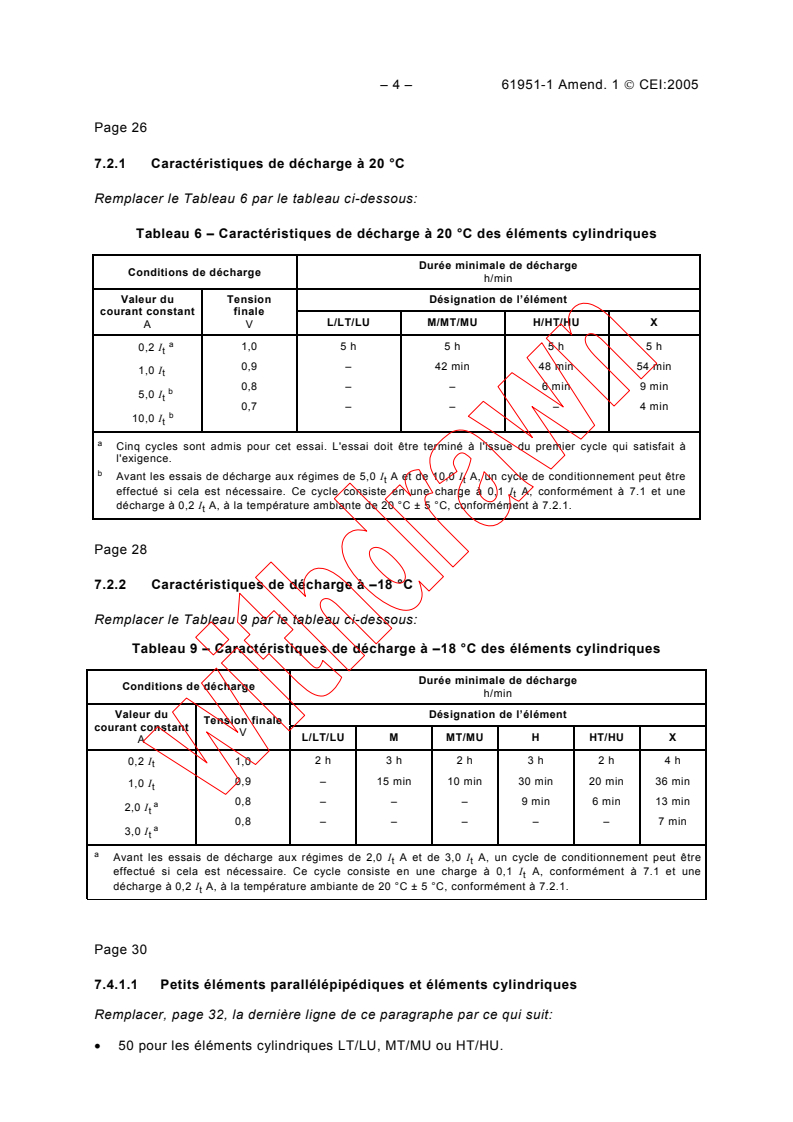
Page 26
7.2.1 Caractéristiques de décharge à 20 °C
Remplacer le Tableau 6 par le tableau ci-dessous:
Tableau 6 – Caractéristiques de décharge à 20 °C des éléments cylindriques
Durée minimale de décharge
Conditions de décharge
h/min
Valeur du Tension Désignation de l’élément
courant constant finale
L/LT/LU M/MT/MU H/HT/HU X
A V
a
1,0 5 h 5 h 5 h 5 h
0,2 I
t
0,9 – 42 min 48 min 54 min
1,0 I
t
0,8 – – 6 min 9 min
b
5,0 I
t
0,7 – – – 4 min
b
10,0 I
t
a
Cinq cycles sont admis pour cet essai. L'essai doit être terminé à l'issue du premier cycle qui satisfait à
l'exigence.
b
Avant les essais de décharge aux régimes de 5,0 I A et de 10,0 I A, un cycle de conditionnement peut être
t t
effectué si cela est nécessaire. Ce cycle consiste en une charge à 0,1 I A, conformément à 7.1 et une
t
décharge à 0,2 I A, à la température ambiante de 20 °C ± 5 °C, conformément à 7.2.1.
t
Page 28
7.2.2 Caractéristiques de décharge à –18 °C
Remplacer le Tableau 9 par le tableau ci-dessous:
Tableau 9 – Caractéristiques de décharge à –18 °C des éléments cylindriques
Durée minimale de décharge
Conditions de décharge
h/min
Valeur du Désignation de l’élément
Tension finale
courant constant
V
L/LT/LU M MT/MU H HT/HU X
A
0,2 I 1,0 2 h 3 h 2 h 3 h 2 h 4 h
t
0,9 – 15 min 10 min 30 min 20 min 36 min
1,0 I
t
0,8 – – – 9 min 6 min 13 min
a
2,0 I
t
0,8 – – – – – 7 min
a
3,0 I
t
a
Avant les essais de décharge aux régimes de 2,0 I A et de 3,0 I A, un cycle de conditionnement peut être
t t
effectué si cela est nécessaire. Ce cycle consiste en une charge à 0,1 I A, conformément à 7.1 et une
t
décharge à 0,2 I A, à la température ambiante de 20 °C ± 5 °C, conformément à 7.2.1.
t
Page 30
7.4.1.1 Petits éléments parallélépipédiques et éléments cylindriques
Remplacer, page 32, la dernière ligne de ce paragraphe par ce qui suit:
• 50 pour les éléments cylindriques LT/LU, MT/MU ou HT/HU.
61951-1 Amend. 1 IEC:2005 – 5 –
Page 27
7.2.1 Discharge performance at 20 °C
Replace the existing Table 6 by the following:
Table 6 – Discharge performance at 20 °C for cylindrical cells
Minimum discharge duration
Discharge conditions
h/min
Rate of Final Cell designation
constant current voltage
L/LT/LU M/MT/MU H/HT/HU X
A V
a
0,2 I 1,0 5 h 5 h 5 h 5 h
t
1,0 I 0,9 – 42 min 48 min 54 min
t
b
5,0 I 0,8 – – 6 min 9 min
t
b
10,0 I 0,7 – – – 4 min
t
a
Five cycles are permitted for this test. The test shall be terminated at the end of the first cycle which meets the
requirement.
b
Prior to the 5,0 I A and 10,0 I A tests, a conditioning cycle may be included if necessary. This cycle shall
t t
consist of charging at 0,1 I A in accordance with 7.1 and discharging at 0,2 I A, at an ambient temperature of
t t
20 °C ± 5 °C, according to 7.2.1.
Page 29
7.2.2 Discharge performance at –18 °C
Replace the existing Table 9 by the following:
Table 9 – Discharge performance at –18 °C for cylindrical cells
Minimum discharge duration
Discharge conditions
h/min
Rate of Final voltage Cell designation
constant current
L/LT/LU M MT/MU H HT/HU X
A V
0,2 I 1,0 2 h 3 h 2 h 3 h 2 h 4 h
t
1,0 I 20 min 36 min
0,9 – 15 min 10 min 30 min
t
a
2,0 I 0,8 – – – 9 min 6 min 13 min
t
a
3,0 I 0,8 – – – – – 7 min
t
a
Prior to the 2,0 I A and 3,0 I A tests, a conditioning cycle may be included if necessary. This cycle consists of
t t
charging at 0,1 I A in accordance with 7.1 and discharging at 0,2 I A at an ambient temperature of 20 °C ± 5 °C,
t t
according to 7.2.1.
Page 31
7.4.1.1 Small prismatic and cylindrical cells
Replace, on page 33, the last line of this subclause by the following
• 50 for cylindrical cells LT/LU, MT/MU or HT/HU
– 6 – 61951-1 Amend. 1 CEI:2005
Page 38
7.4.2.3 Eléments cylindriques LT, MT ou HT
Remplacer le texte existant de ce paragraphe par le nouveau texte suivant:
L’essai d’endurance en charge permanente doit être réalisé en trois étapes dans les
conditions spécifiées au Tableau 18.
Il consiste en:
• un essai d'aptitude à la charge à +40 °C;
• une période de vieillissement de six mois à +70 °C;
• un essai final d'aptitude à la charge pour vérifier les caractéristiques de l’élément après
vieillissement.
NOTE La période de vieillissement de 6 mois et la température de +70 °C ont été choisies pour simuler quatre
ans de fonctionnement en charge permanente à +40 °C.
Avant l’essai, l’élément doit être déchargé à 0,2 I A à 20 °C ± 5 °C jusqu’à une tension finale
t
de 1,0 V et mis au repos, à une température ambiante de +40 °C ± 2 °C, pendant au moins
16 h et au plus 24 h.
L’élément doit ensuite être chargé et déchargé à courant constant dans les conditions
spécifiées au Tableau 18, tout en maintenant, selon les cas, la température ambiante soit à
+40 °C ± 2 °C, soit à +70 °C ± 2 °C.
Il est possible de choisir le mode de décharge A ou B en fonction des exigences des
utilisateurs. La décharge est réalisée immédiatement après la fin de charge.
Après la réalisation du premier essai d'aptitude à la charge à +40 °C, l’élément est mis au
repos, à une température ambiante de +70 °C ± 2 °C, pendant au moins 16 h et au plus 24 h.
Pendant la période de vieillissement de six mois à +70 °C, pour éviter que la température du
boîtier de l’élément ne dépasse +75 °C, il convient de prendre, si nécessaire, des précautions
telles que la mise en œuvre d'air pulsé.
NOTE La température réelle du boîtier de l’élément, et non pas la température ambiante, détermine la
performance de l'élément.
La durée de la décharge des trois cycles à +70 °C doit être notée. Aucune fuite d’électrolyte
ne doit être observée pendant l’essai.
A la fin de la période de vieillissement, les éléments doivent être mis au repos, à la
température ambiante de +40 °C ± 2 °C, pendant au moins 16 h et au plus 24 h. Les trois
cycles à +40 °C de l’essai initial d'aptitude à la charge sont effectués à nouveau dans les
conditions spécifiées au Tableau 18. La durée de décharge ne doit pas être inférieure aux
valeurs spécifiées au Tableau 18.
Page 40
Ajouter le nouveau paragraphe 7.4.2.4, ainsi que le nouveau Tableau 26, ci-dessous:
7.4.2.4 Eléments cylindriques LU, MU ou HU
L’essai d’endurance en charge permanente doit être réalisé en trois étapes dans les
conditions spécifiées au Tableau 26.
61951-1 Amend. 1 IEC:2005 – 7 –
Page 39
7.4.2.3 LT, MT or HT cylindrical cells
Replace the existing text of this subclause by the following:
The permanent charge endurance test shall be performed in three steps according to the
conditions specified in Table 18.
It consists of:
• a charge acceptance test at +40 °C;
• an ageing period of six months at +70 °C;
• a final charge acceptance test to check the cell’s performance after ageing.
NOTE The six months ageing period and the temperature of +70 °C have been selected to simulate four years of
permanent charge operation at +40 °C.
Prior to this test, the cell shall be discharged at 0,2 I A at 20 °C ± 5 °C to a final voltage o
...



Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...