ASTM D6519-00
(Practice)Standard Practice for Sampling of Soil Using the Hydraulically Operated Stationary Piston Sampler
Standard Practice for Sampling of Soil Using the Hydraulically Operated Stationary Piston Sampler
SCOPE
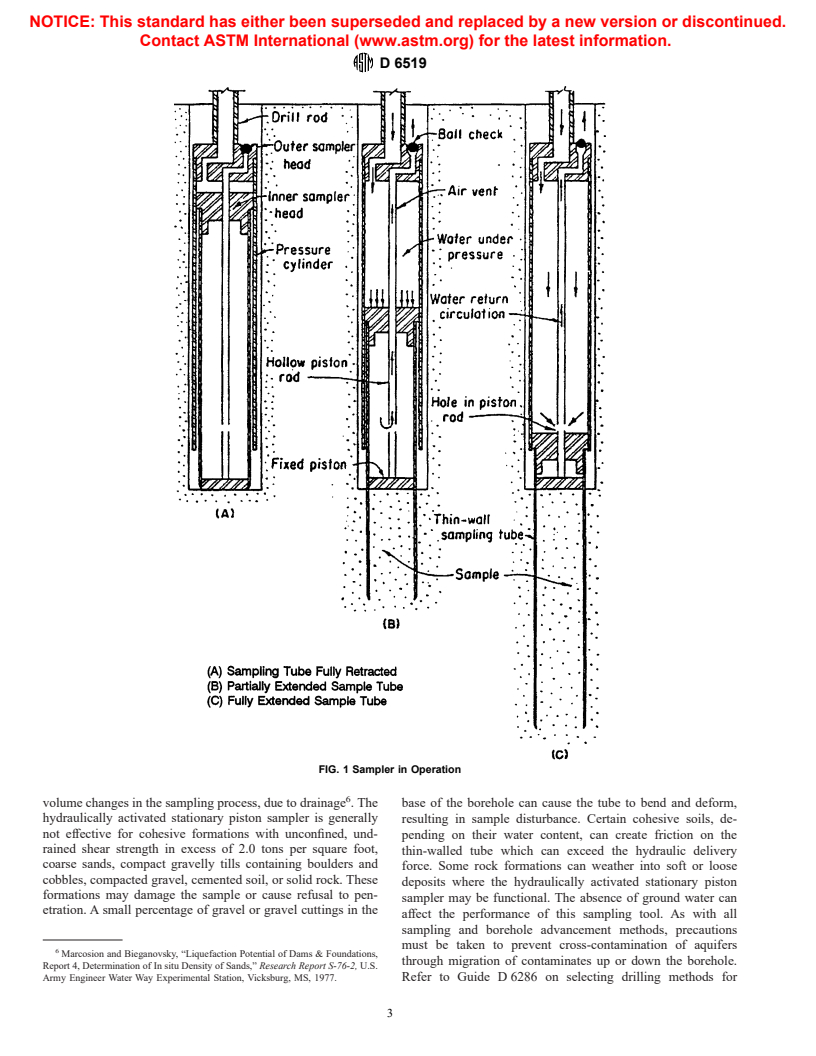
1.1 This practice covers a procedure for sampling of cohesive, organic, or fine-grained soils, or combination thereof, using a thin-walled metal tube that is inserted into the soil formation by means of a hydraulically operated piston. It is used to collect relatively undisturbed soil samples suitable for laboratory tests to determine structural and chemical properties for geotechnical and environmental site characterizations.
1.1.1 Guidance on preservation and transport of samples in accordance with Practice D 4220 may apply. Samples for classification may be preserved using procedures similar to Class A. In most cases, a thin-walled tube sample can be considered as Class B, C, or D. Refer to Guide D 6286 for use of the hydraulically operated stationary piston soil sampler for environmental site characterization. This sampling method is often used in conjunction with rotary drilling methods such as fluid rotary; Guide D 5783; and hollow stem augers, Practice D 6151. Sampling data should be reported in the substance log in accordance with Guide D 5434.
1.2 The hydraulically operated stationery piston sampler is limited to soils and unconsolidated materials that can be penetrated with the available hydraulic pressure that can be applied without exceeding the structural strength of the thin-walled tube.
This practice does not purport to address all the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use and may involve use of hazardous materials, equipment, and operations. It is the responsibility of the user to establish and adopt appropriate safety and health practices. Also, the user must comply with prevalent regulatory codes, such as OSHA (Occupational Health and Safety Administration) guidelines, while using this practice. For good safety practice, consult applicable OSHA regulations and other safety guides on drilling.
1.3 The values stated in SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
1.4 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgement. Not all aspects of this practice may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without consideration of a project's many unique aspects. The word "Standard" in the title means only that the document has been approved through the ASTM consensus process. This practice does not purport to comprehensively address all of the methods and the issues associated with sampling of soil. Users should seek qualified professionals for decisions as to the proper equipment and methods that would be most successful for their site investigation. Other methods may be available for drilling and sampling of soil, and qualified professionals should have flexibility to exercise judgment as to possible alternatives not covered in this practice. The practice is current at the time of issue, but new alternative methods may become available prior to revisions, therefore, users should consult with manufacturers or producers prior to specifying program requirements. ^REFERENCE: ASTM Standards-Soil Classification:D 653Termninology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained FluidsD 2488Practice for Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Method)D 5434Guide for Field Logging of Subsurface Explorations of Soil and RockASTM Standards-Drilling Methods: D 1452Practice for Soil Investigation and Sampling by Auger BoringsD 5782Guide for Use of Direct Air-Rotary Drilling for Geoenvironmental Exploration and the Installation of S...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 6519 – 00
Standard Practice for
Sampling of Soil Using the Hydraulically Operated
1
Stationary Piston Sampler
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6519; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
1.1 This practice covers a procedure for sampling of cohe-
standard.
sive, organic, or fine-grained soils, or combination thereof,
1.5 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing
using a thin-walled metal tube that is inserted into the soil
one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace
formation by means of a hydraulically operated piston. It is
education or experience and should be used in conjunction
used to collect relatively undisturbed soil samples suitable for
with professional judgement. Not all aspects of this practice
laboratory tests to determine structural and chemical properties
may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is
for geotechnical and environmental site characterizations.
not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by
1.1.1 Guidance on preservation and transport of samples in
which the adequacy of a given professional service must be
accordance with Practice D 4220 may apply. Samples for
judged, nor should this document be applied without consid-
classification may be preserved using procedures similar to
eration of a project’s many unique aspects. The word “Stan-
Class A. In most cases, a thin-walled tube sample can be
dard” in the title means only that the document has been
considered as Class B, C, or D. Refer to Guide D 6286 for use
approved through the ASTM consensus process. This practice
of the hydraulically operated stationary piston soil sampler for
does not purport to comprehensively address all of the methods
environmental site characterization. This sampling method is
and the issues associated with sampling of soil. Users should
often used in conjunction with rotary drilling methods such as
seek qualified professionals for decisions as to the proper
fluid rotary; Guide D 5783; and hollow stem augers, Practice
equipment and methods that would be most successful for their
D 6151. Sampling data should be reported in the substance log
site investigation. Other methods may be available for drilling
in accordance with Guide D 5434.
and sampling of soil, and qualified professionals should have
1.2 The hydraulically operated stationery piston sampler is
flexibility to exercise judgment as to possible alternatives not
limited to soils and unconsolidated materials that can be
covered in this practice. The practice is current at the time of
penetrated with the available hydraulic pressure that can be
issue, but new alternative methods may become available prior
applied without exceeding the structural strength of the thin-
to revisions, therefore, users should consult with manufacturers
walled tube.
or producers prior to specifying program requirements.
1.3 This practice does not purport to address all the safety
concerns, if any, associated with its use and may involve use of
2. Referenced Documents
hazardous materials, equipment, and operations. It is the
2.1 ASTM Standards-Soil Classification:
responsibility of the user to establish and adopt appropriate
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
safety and health practices. Also, the user must comply with
3
Fluids
prevalent regulatory codes, such as OSHA (Occupational
D 2488 Practice for Description and Identification of Soils
Health and Safety Administration) guidelines, while using this
3
(Visual-Manual Method)
practice. For good safety practice, consult applicable OSHA
2 D 5434 Guide for Field Logging of Subsurface Explorations
regulations and other safety guides on drilling.
3
of Soil and Rock
1.4 The values stated in SI units or inch-pound units are to
2.2 ASTM Standards-Drilling Methods:
be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
D 1452 Practice for Soil Investigation and Sampling by
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
3
Auger Borings
D 5782 Guide for Use of Direct Air-Rotary Drilling for
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-18 on Soil and
Geoenvironmental Exploration and the Installation of
4
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.02 on Sampling and
Subsurface Water-Quality Monitoring Devices
Related Field Testing for Soil Evaluation
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2000. Published April 2000.
2 3
Drilling S
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.