ASTM D523-08
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss
Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Gloss is associated with the capacity of a surface to reflect more light in directions close to the specular than in others. Measurements by this test method correlate with visual observations of surface shininess made at roughly the corresponding angles.
Measured gloss ratings by this test method are obtained by comparing the specular reflectance from the specimen to that from a black glass standard. Since specular reflectance depends also on the surface refractive index of the specimen, the measured gloss ratings change as the surface refractive index changes. In obtaining the visual gloss ratings, however, it is customary to compare the specular reflectances of two specimens having similar surface refractive indices.
Other visual aspects of surface appearance, such as distinctness of reflected images, reflection haze, and texture, are frequently involved in the assessment of gloss (1), (6), (7). Test Method E 430 includes techniques for the measurement of both distinctness-of-image gloss and reflection haze. Test Method D 4039 provides an alternative procedure for measuring reflection haze.
Little information about the relation of numerical-to-perceptual intervals of specular gloss has been published. However, in many applications the gloss scales of this test method have provided instrumental scaling of coated specimens that have agreed well with visual scaling (10).
When specimens differing widely in perceived gloss or color, or both, are compared, nonlinearity may be encountered in the relationship between visual gloss difference ratings and instrumental gloss reading differences.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the specular gloss of nonmetallic specimens for glossmeter geometries of 60, 20, and 85° (1-7).
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D523 − 08
StandardTest Method for
1
Specular Gloss
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D523; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthemeasurementofthespecular 3.1 Definitions:
gloss of nonmetallic specimens for glossmeter geometries of 3.1.1 relative luminous reflectance factor, n—the ratio of the
2
60, 20, and 85° (1-7).
luminous flux reflected from a specimen to the luminous flux
reflected from a standard surface under the same geometric
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
conditions. For the purpose of measuring specular gloss, the
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
standard surface is polished glass.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard. 3.1.2 specular gloss, n—the relative luminous reflectance
factor of a specimen in the mirror direction.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Measurements are made with 60, 20, or 85° geometry
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(8, 9). The geometry of angles and apertures is chosen so that
these procedures may be used as follows:
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.1 The 60° geometry is used for intercomparing most
3
2.1 ASTM Standards: specimens and for determining when the 20° geometry may be
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness more applicable.
of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels 4.1.2 The 20° geometry is advantageous for comparing
D3964 Practice for Selection of Coating Specimens for
specimens having 60° gloss values higher than 70.
Appearance Measurements
4.1.3 The 85° geometry is used for comparing specimens
D3980 Practice for Interlaboratory Testing of Paint and
for sheen or near-grazing shininess. It is most frequently
4
Related Materials (Withdrawn 1998)
applied when specimens have 60° gloss values lower than 10.
D4039 Test Method for Reflection Haze of High-Gloss
Surfaces
5. Significance and Use
E97 Method of Test for Directional Reflectance Factor,
5.1 Gloss is associated with the capacity of a surface to
45-Deg 0-Deg, of Opaque Specimens by Broad-Band
reflect more light in directions close to the specular than in
4
Filter Reflectometry (Withdrawn 1991)
others. Measurements by this test method correlate with visual
E430 TestMethodsforMeasurementofGlossofHigh-Gloss
observations of surface shininess made at roughly the corre-
Surfaces by Abridged Goniophotometry
sponding angles.
5.1.1 Measured gloss ratings by this test method are ob-
1 tained by comparing the specular reflectance from the speci-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E12 on Color
and Appearance and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E12.03 on
men to that from a black glass standard. Since specular
Geometry.
reflectance depends also on the surface refractive index of the
Current edition approved June 1, 2008. Published June 2008. Originally
specimen, the measured gloss ratings change as the surface
approved in 1939. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D523 – 89 (2008).
refractive index changes. In obtaining the visual gloss ratings,
DOI: 10.1520/D0523-08.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
however, it is customary to compare the specular reflectances
this test method.
of two specimens having similar surface refractive indices.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.2 Other visual aspects of surface appearance, such as
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
distinctness of reflected images, reflection haze, and texture,
the ASTM website.
4
are frequently involved in the assessment of gloss (1), (6), (7).
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. Test Method E430 includes techniques for the measurement of
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D523 − 08
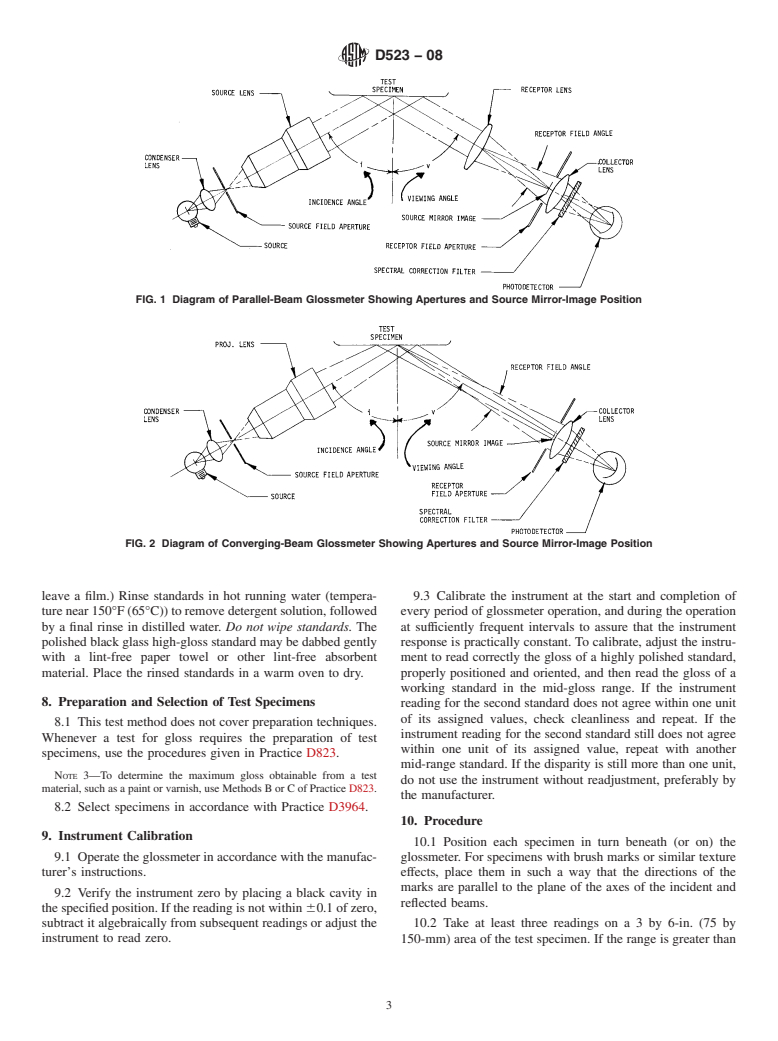
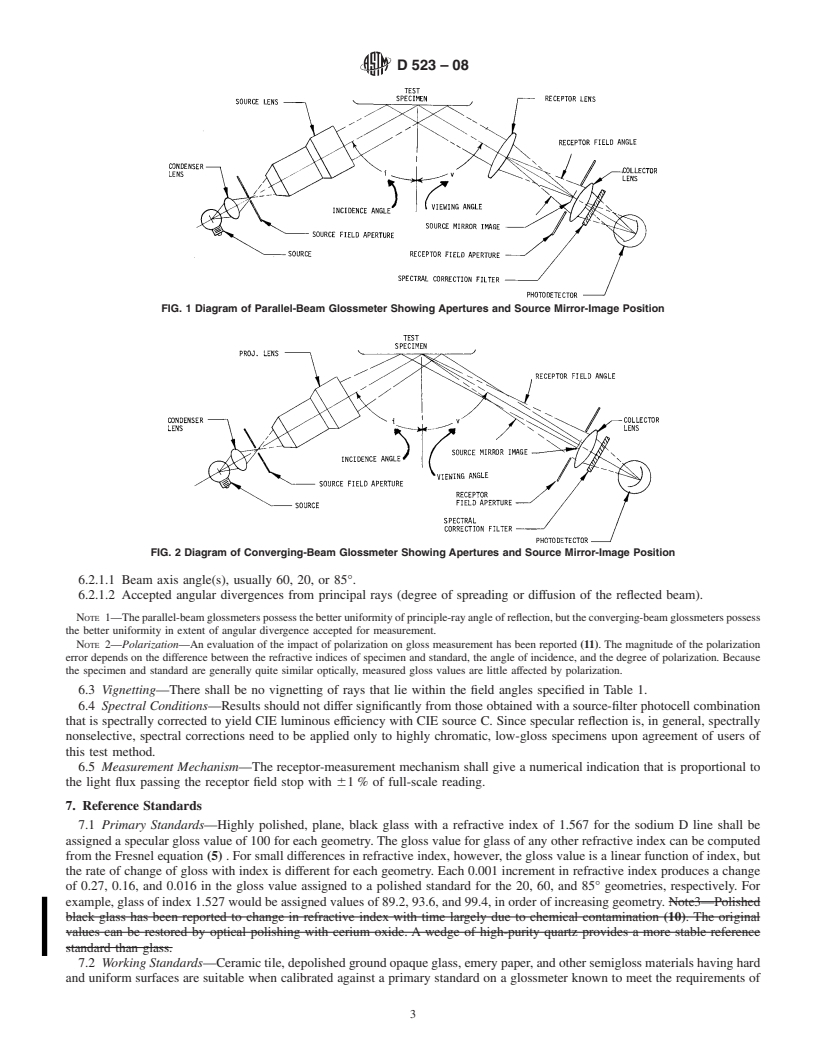
both distinctness-of-image gloss and reflection haze. Test 6.2.1 The important geometric dimensio
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D523–89(Reapproved2008) Designation:D523–08
Standard Test Method for
1
Specular Gloss
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 523; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the specular gloss of nonmetallic specimens for glossmeter geometries of 60,
2
20, and 85° (1-7).
1.2The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
D 3964 Practice for Selection of Coating Specimens for Appearance Measurements
4
D 3980 Practice for Interlaboratory Testing of Paint and Related Materials
D 4039 Test Method for Reflection Haze of High-Gloss Surfaces
E 97 Test Method for Directional Reflectance Factor, 45-Deg 0-Deg, of Opaque Specimens by Broad-Band Filter
0
Reflectometry
E 430 Test Methods for Measurement of Gloss of High-Gloss Surfaces by Abridged Goniophotometry
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 relative luminous reflectance factorrelative luminous reflectance factor, n—the ratio of the luminous flux reflected from
a specimen to the luminous flux reflected from a standard surface under the same geometric conditions. For the purpose of
measuring specular gloss, the standard surface is polished glass.
3.1.2 specular glossspecular gloss, n—the relative luminous reflectance factor of a specimen in the mirror direction.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Measurements are made with 60, 20, or 85° geometry (8, 9). The geometry of angles and apertures is chosen so that these
procedures may be used as follows:
4.1.1 The 60° geometry is used for intercomparing most specimens and for determining when the 20° geometry may be more
applicable.
4.1.2 The 20° geometry is advantageous for comparing specimens having 60° gloss values higher than 70.
4.1.3 The85°geometryisusedforcomparingspecimensforsheenornear-grazingshininess.Itismostfrequentlyappliedwhen
specimens have 60° gloss values lower than 10.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E12 on Color and Appearance and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E12.03 on Geometry.
Current edition approved Feb.June 1, 2008. Published AprilJune 2008. Originally approved in 1939. Last previous edition approved in 19992008 as D 523 – 89(1999).
89 (2008).
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of this test method.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Withdrawn.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D523–08
5. Significance and Use
5.1Gloss is associated with the capacity of a surface to reflect more light in some directions than in others. The directions
associated with mirror (or specular) reflection normally have the highest reflectances. Measurements by this test method correlate
with visual observations of surface shininess made at roughly the corresponding angles.
5.1.1Measured gloss ratings by this test method are obtained by comparing the specular reflectance from the specimen to that
from a black glass standard. Since specular reflectance depends also on the surface refractive index of the specimen, the measured
gloss ratings change as the surface refractive index changes. In obtaining the visual gloss ratings, howe
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.