ASTM D7823-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Level, Regulated Phthalates in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Plastics by Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography/Mass Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Level, Regulated Phthalates in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Plastics by Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography/Mass Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Identification and quantification of phthalates: DBP, BBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP, and DIDP are required for regulated articles. Regulations include: EU-Directive 2005/84/EC, US-Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of 2008-section 108, Japan-Health, Labor and Welfare Ministry guideline No.336 (2010). This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify regulated phthalates in PVC.
5.2 Other techniques successfully used to separate and identify phthalates in PVC include GC/MS, HPLC/UV, HPLC/MS, FTIR, and GC/FID (flame ionization detector).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify six phthalates by thermal desorption (TD) gas chromatography (GC) mass spectrometry (MS). The phthalates are BBP, DBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP and DIDP.Note 1-The method can be extended to include other phthalates.
1.2 Within the context of this method, “low level” is defined as 1000 ppm.
1.3 The values in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4 This test method includes references, notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in the tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this method.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 2-There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
General Information
Relations
Frequently Asked Questions
ASTM D7823-13 is a standard published by ASTM International. Its full title is "Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Level, Regulated Phthalates in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Plastics by Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography/Mass Chromatography". This standard covers: SIGNIFICANCE AND USE 5.1 Identification and quantification of phthalates: DBP, BBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP, and DIDP are required for regulated articles. Regulations include: EU-Directive 2005/84/EC, US-Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of 2008-section 108, Japan-Health, Labor and Welfare Ministry guideline No.336 (2010). This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify regulated phthalates in PVC. 5.2 Other techniques successfully used to separate and identify phthalates in PVC include GC/MS, HPLC/UV, HPLC/MS, FTIR, and GC/FID (flame ionization detector). SCOPE 1.1 This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify six phthalates by thermal desorption (TD) gas chromatography (GC) mass spectrometry (MS). The phthalates are BBP, DBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP and DIDP.Note 1-The method can be extended to include other phthalates. 1.2 Within the context of this method, “low level” is defined as 1000 ppm. 1.3 The values in SI units are to be regarded as standard. 1.4 This test method includes references, notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in the tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this method. 1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 2-There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE 5.1 Identification and quantification of phthalates: DBP, BBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP, and DIDP are required for regulated articles. Regulations include: EU-Directive 2005/84/EC, US-Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of 2008-section 108, Japan-Health, Labor and Welfare Ministry guideline No.336 (2010). This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify regulated phthalates in PVC. 5.2 Other techniques successfully used to separate and identify phthalates in PVC include GC/MS, HPLC/UV, HPLC/MS, FTIR, and GC/FID (flame ionization detector). SCOPE 1.1 This test method provides a procedure to identify and quantify six phthalates by thermal desorption (TD) gas chromatography (GC) mass spectrometry (MS). The phthalates are BBP, DBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP and DIDP.Note 1-The method can be extended to include other phthalates. 1.2 Within the context of this method, “low level” is defined as 1000 ppm. 1.3 The values in SI units are to be regarded as standard. 1.4 This test method includes references, notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in the tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this method. 1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 2-There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
ASTM D7823-13 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 83.040.30 - Auxiliary materials and additives for plastics. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ASTM D7823-13 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ASTM D7823-14, ASTM D7993-15(2019), ASTM F2931-19a, ASTM D8133-23, ASTM D7083-16(2022). Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
You can purchase ASTM D7823-13 directly from iTeh Standards. The document is available in PDF format and is delivered instantly after payment. Add the standard to your cart and complete the secure checkout process. iTeh Standards is an authorized distributor of ASTM standards.
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7823 − 13
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Low Level, Regulated Phthalates in Poly
(Vinyl Chloride) Plastics by Thermal Desorption—Gas
Chromatography/Mass Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7823; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E355 Practice for Gas ChromatographyTerms and Relation-
ships
1.1 This test method provides a procedure to identify and
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
quantify six phthalates by thermal desorption (TD) gas chro-
in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
matography (GC) mass spectrometry (MS). The phthalates are
IEEE/ASTM SI{10 Practice for Use of the International
BBP, DBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP and DIDP.
System of Units (SI), the Modernized Metric System
NOTE 1—The method can be extended to include other phthalates.
1.2 Withinthecontextofthismethod,“lowlevel”isdefined 3. Terminology
as 1000 ppm.
3.1 Definitions—For definition of plastic terms used in this
1.3 The values in SI units are to be regarded as standard. test method, see Terminologies D883 and D1600.
1.4 This test method includes references, notes and foot-
3.2 For units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this test
notes that provide explanatory material. These notes and method refer to Practices E594, E355,or SI10.
footnotes (excluding those in the tables and figures) shall not
3.3 Compounds and Instrumentation:
be considered as requirements of this method.
3.3.1 (DOA) Hexanedioic acid, 1,6{bis(2{ethylhexyl) ester
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
CAS #103{23{1
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.3.2 (DINCH) 1,2{Cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid, dinonyl
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ester, branched and linear CAS #474919{59{0
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.3.3 (DBP) 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid, 1,2{di{n{butyl
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ester CAS #84{74{2
3.3.4 (BBP) Benzyl butyl phthalate CAS #85{68{7
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
3.3.5 (DEHP) Bis(2{Ethyhexyl) Phthalate CAS #117{81{7
3.3.6 (DNOP) Di(n{Dioctyl) phthalate CAS #117{84{0
2. Referenced Documents
3.3.7 (DINP) 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
di{C8{10{branched alkyl esters, C9{rich (Jayflex) CAS
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
#68515{48{0
D1600 TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
3.3.8 (DINP) 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid, 1,2{diisononyl
tics
(Palatinol) CAS #28553{12{0
D3465 Test Method for Purity of Monomeric Plasticizers by
3.3.9 (DIDP) 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid,
Gas Chromatography
di{C9{11{branched alkyl esters, C10{rich (Jayflex) CAS
D7083 Practice for Determination of Monomeric Plasticiz-
#68515{49{1
ers in Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) by Gas Chromatogra-
3.3.10 (DIDP) 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid, 1,2{diisodecyl
phy
CAS #26761{40{0
3.3.11 TD Thermal Desorption
3.3.12 GC Gas Chromatography
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
3.3.13 GC/MS Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
3.3.14 PVC Poly (Vinyl Chloride)
Current edition approved April 1, 2013. Published April 2013. DOI: 10.1520/
D7823-13.
3.3.15 THF GC grade or higher “Tetrahydrofuran”
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.3.16 DCM GC grade or higher "Methylene Chloride”
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3.3.17 EGA{MS Evolved Gas Analysis{mass spectrometry
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 3.3.18 FTIR Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7823 − 13
3.3.19 TIC Total ion chromatogram solvents used to prepare standards and sample solutions must
3.3.20 DQO Data quality objectives be free of contamination.
NOTE 3—DINP and DIDP, when used in various PVC formulations are
6.3 The presence or absence of each phthalateisbasedupon
technical mixtures. Take care, when preparing the phthalate calibration
three criteria: (1) the relative retention time of the peak (2) the
standard to use the technical grade. Here is specific information on DINP
presence or absence of the quant ion and the two confirming
and DIDP. For more information, please refer to Appendix X3.
Jayflex DIDP: 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid, di{C9{11{branched alkyl ions and (3) the ratio of the quant and the confirming ion one
esters, C10{rich: CAS# 68515{49{1.
must satisfy the established guideline (see Table 1).
Jayflex DINP: 1,2{Benzenedicarboxylicacid, di{C8{10{branched alkyl
esters, C9{rich: CAS# 68515{ 48{0.
6.4 Calculating the phthalate concentrations using the areas
of compound specific ions and standard addition significantly
4. Summary of Test Method
reduces interference from non{target compounds.
4.1 200 mg of the PVC sample are dissolved in 10 mL of
THF.10µLoftheTHFsolutionareanalyzedusingTDGC/MS.
7. Apparatus
Phthalates are identified by their retention times and their mass
7.1 Gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer capable of oper-
spectra. Quantification is based on the area of a designated
ating in the 75 to 350°C range.
quant ion (SIM or full scan)—see Table 1. Standard addition is
the calibration method.
NOTE 5—Optional but recommended: Vent{free GC/MS Adapter. This
facilitates the rapid conversion between detailed analysis and evolved gas
NOTE 4—Standard addition calibration will negate matrix interference.
analysis.
It also takes into account the overall performance of the instrumentation
at the time the samples are analyzed.
7.2 Thermal desorption unit capable of heating the sample
from 100 to 350°C at 20°C/min.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Identification and quantification of phthalates: DBP,
7.3 Inert, reusable or disposable sample containers or cups.
BBP, DEHP, DNOP, DINP, and DIDP are required for regu-
7.4 GC capillary column: UA{5 (5 % diphenyl{95 % poly
lated articles. Regulations include: EU—Directive 2005/84/
(dimethylsiloxane) stainless steel, 30 m by 0.25 mm ID with a
EC, US—Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of
0.25 µm film thickness, or equivalent.
2008—section 108, Japan—Health, Labor and Welfare Minis-
try guideline No.336 (2010). This test method provides a
7.5 Integrator or data handling system, capable of measur-
proceduretoidentifyandquantifyregulatedphthalatesinPVC.
ing peak areas and retention times to four significant figures.
5.2 Other techniques successfully used to separate and
7.6 Analyticalbalance,capableofweighingto 60.000001g
identify phthalates in PVC include GC/MS, HPLC/UV, HPLC/
(1 µg). If using a balance capable of weighing to 60.00001 g
MS, FTIR, and GC/FID (flame ionization detector).
(10 µg), weight used in the sample and standard preparation
must be scaled accordingly in order to ensure that the data is
6. Interferences
accurate to three significant figures.
6.1 Retention times for GC are dependent on several vari-
7.7 Pressure regulators, for all required gas cylinders.
ables and it is possible to have two or more components with
identical retention times. The analyst shall take the necessary
7.8 Flow meter, or other means of measuring gas flow rates
steps to insure that adequate separation of the plasticizer
60.1 mL/min.
components is achieved and or the ions used to monitor for a
target phthalate are free of interference. This includes, but is
8. Reagents and Materials
not limited to changing the selectivity of the chromatographic
column. Calibration by standard addition offers the advantage
8.1 Helium carrier gas, chromatographic grade.
of minimizing interferences.
8.2 Methylene chloride (DCM) or n{hexane for preparing
6.2 WhenusingaTD{GC/MSmethod,caremustbetakento
the phthalate standard solution (Solution #1, 10.2), spectral
ensure that the sample cups are inert and clean. Any and all
quality or chromatographic grade.
8.3 Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or a solvent suitable for prepar-
TABLE 1 Ions and Ion Ratios Used to Identify Each Phthalate ing the PVC sample (Solution #2, 10.3), spectral quality or
chromatographic grade.
DBP BBP DEHP DNOP DINP DIDP
Quant ion 223 206 279 279 293 307
Confirm 149 149 149 149 149 149 8.4 Standards of the appropriate phthalates for use when
ion 1
constructinganexternalcalibrationcurveorpreparingSolution
Area ratio <0.04 <0.23 <0.08 <0.06 <0.20 <0.12
#3 (10.4) used for standard addition. See Note 2.
(±10%)
(Quant/
Confirm
9. Safety and Precautions
1)
Confirm 167 167 167 167 167 167
9.1 Use THF and methylene chloride in a well{ventilated
ion 2
space.
D7823 − 13
NOTE 6—A critical step in the accurate determination of phthalates is
10. Preparation of the Analytical Samples (based upon
sample homogeneity. This is discussed in more detail in Appendix X2.
usinga1µg balance) Weights must be scaled up if
NOTE 7—The THF sample solution may contain inorganic material.
using a 10-µg balance.
Studies have shown that the presence of insoluble inorganic material will
10.1 Three solutions must be prepared: (1) a stock solution
not affect either the accuracy or precision of the phthalate determination.
of the target phthalate standards, (2) a solution of the sample
10.4 Solution #3—Place 10 µL of the sample solution (#2)
and (3) the sample solution spiked with the standard stock
into a clean sample cup. Add 10 µL of the phthalate standard
solution.
solution (#1). Evaporate the solvent.
10.2 Solution #1—Prepare a stock standard solution of the
phthalates by dissolving 0.30 mg of each phthalate in 10 mLof NOTE 8—To expedite the evaporation process, pass a steady stream of
a high purity inert gas using clean, (plasticizer- and additive-free) tubing
methylene chloride (0.30 mg/10 mL). N{hexane has also been
over the sample cup.
used with success. See Fig. 1 for a typical chromatogram.
10.3 Solution #2—Dissolve 200 mg of the sample in 10 mL
11. Procedure
THF (200 mg/10 mL). Shake (or sonicate) the solution for five
minutes—see Note 6. The solution may range from clear to 11.1 Establish that the analytical system is free of phthalate
contaminationbyanalyzing10µLofTHF.Acceptablelevelsof
slightly cloudy. Place 10 µL of the sample solution in a clean
sample cup. Evaporate the solvent; the sample is ready to background contamination will be determined by the project
analyze. See Figs. 2 and 3 for example chromatograms. specific Data Quality Objectives.
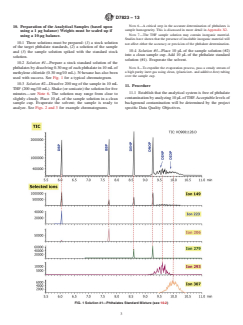
FIG. 1 Solution #1—Phthalates Standard Mixture (see 10.2)
D7823 − 13
FIG. 2 Solution #2—Chromatograms (TIC) of PVC with Three Different Plasticizers, TD-GC/MS Analysis (see 10.3 and 11.3)
D7823 − 13
FIG. 3 Solution #2—Reproducibility of PVC-DINCH (n=6) (see 10.3 and 11.3)
D7823 − 13
11.2 Establish the relative retention time and mass spectrum
Thermal Desorption (TD){GC/MS Analysis
TD temperature: 100 { 20°C/min { 320°C (5 min hold)
of each phthalate using Solution #1—10.2: The following
Py interface: 320°C (Auto mode),
conditions were used to obtain the example chromatograms
GC injector : 300°C
shown in Figs. 1-4:
FIG. 4 Solution #3—Standard Addition (see 11.7)
D7823 − 13
Fig. 4. Standard addition is very useful when it is difficult to
GC oven: 80 (1 min hold) to 200°C (at 50°C/
min) to 320°C (15°C/min, 2 min hold)
eliminate interferences from the sample matrix. This is often
Solvent delay: 6 min
the case when analyzing PVC where DINCH, Mesamoll or
Column: UA{5 (5 % Diphenyl{95 % dimethyl
polysiloxane) 30 m by 0.25 mm i.d, both are present.
0.25 µm film) or equivalent
11.8 Attention should be paid to the chromatographic peak
Column He flow: 1.2 mL/min, Split ratio: 1/20
Mass range: 29{60
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...