ASTM D5769-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene, Toluene, and Total Aromatics in Finished Gasolines by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene, Toluene, and Total Aromatics in Finished Gasolines by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene, toluene, and total aromatics in finished motor gasoline, including reformulated gasoline (RFG) containing oxygenated blending components, by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS).
1.2 This test method is applicable to the following concentration ranges, in liquid volume %, for the following aromatics: benzene, 0.1 to 3%; toluene, 1 to 15%; and total (C6-C12) aromatics, 10 to 40%. The test method has not been tested by ASTM for gasoline samples containing a concentration of uncalibrated C10-C12 aromatic compounds greater than approximately 3 volume %. Also, the test method has not been tested by ASTM for individual hydrocarbon process streams in a refinery, such as reformates, fluid catalytic cracked naphthas, etc., used in blending of gasolines.
1.3 Results are reported to the nearest 0.01% for benzene and 0.1% for the other aromatics by either mass or liquid volume.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation:D5769–98
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Benzene, Toluene, and Total Aromatics in
Finished Gasolines by Gas Chromatography/Mass
Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5769; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene, 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
toluene, other specified individual aromatic compounds, and 3.1.1 aromatic—any hydrocarbon compound containing a
total aromatics in finished motor gasoline, including gasolines benzene or naphthalene ring.
containing oxygenated blending components, by gas 3.1.2 split ratio— in capillary gas chromatography, the
chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). ratio of the total flow of carrier gas to the sample inlet versus
1.2 This test method has been tested for the following theflowofthecarriergastothecapillarycolumn,expressedby
concentration ranges, in liquid volume %, for the following
split ratio 5 ~S1C!/C (1)
aromatics: benzene, 0.1 to 4 %; toluene, 1 to 13 %; and total
(C6 to C12) aromatics, 10 to 42 %. The round-robin study did where:
S = flow rate at the splitter vent, and
not test the method for individual hydrocarbon process streams
C = flow rate at the column outlet.
in a refinery, such as reformates, fluid catalytic cracked
3.1.3 wall coated open tubular (WCOT)—a type of capil-
naphthas, and so forth, used in the blending of gasolines.
lary column prepared by coating or bonding the inside wall of
1.3 Results are reported to the nearest 0.01 % for benzene
the capillary with a thin film of stationary phase.
and 0.1 % for the other aromatics by liquid volume.
3.1.4 cool on-column injector—in gas chromatography,a
1.4 SIunitsofmeasurementarepreferredandusedthrough-
direct sample introduction system that is set at a temperature at
out this standard.
orbelowtheboilingpointofsolutesorsolventoninjectionand
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
then heated at a rate equal to or greater than the column.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Normally used to eliminate boiling point discrimination on
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
injection or to reduce adsorption on glass liners within injec-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tors, or both. The sample is injected directly into the head of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
the capillary column tubing.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.5 open split interface—GC/MS interface used to main-
tain atmospheric pressure at capillary column outlet and to
2.1 ASTM Standards:
eliminate mass spectrometer vacuum effects on the capillary
D 1298 Practice for Density, Relative Density (Specific
column. Can be used to dilute the sample entering the mass
Gravity),oraAPIGravityofCrudePetroleumProductsby
spectrometer to maintain response linearity.
Hydrometer Method
3.1.6 retention gap—in gas chromatography, refers to a
D 4052 Test Method for Density and Relative Density of
deactivated precolumn which acts as a zone of low retention
Liquids by Digital Density Meter
power for reconcentrating bands in space. The polarity of the
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
precolumn must be similar to that of the analytical column.
Petroleum Product
3.1.7 total ion chromatogram (TIC)—mass spectrometer
D 4307 PracticeforPreparationofLiquidBlendsforUseas
computer output representing either the summed intensities of
Analytical Standards
all scanned ion currents or a sample of the current in the ion
beam for each spectrum scan plotted against the corresponding
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
spectrum number. Generally, it can be correlated with a flame
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
ionization detector chromatogram.
D.02.04 on Hydrocarbon Analysis.
Current edition approved July 10, 1998. Published October 1998. Last previous 3.1.8 reconstructed ion chromatogram (RIC)—a limited
edition D 5769 – 95.
mass chromatogram representing the intensities of ion mass
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01
spectrometric currents for only those ions having particular
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D5769–98
mass to charge ratios. Used in this test method to selectively a thicker film of stationary phase, such as 4–5 µm, is recom-
extract or identify aromatic components in the presence of a mended to prevent column sample overload.
complex hydrocarbon matrix, such as gasoline.
Resolution R between 1,3,5-
2~t2– t1!
R 5
trimethylbenzene and 1-methyl-2-
1.699~y2 1 y1!
3.1.9 calibrated aromatic component—the individual aro-
ethylbenzene at the 3 mass % level
matic components that have a specific calibration.
each must be equal to or greater than
t2 = retention time of 1,3,5-
3.1.10 uncalibrated aromatic component—individual aro- 2.0
trimethylbenzene
t1 = retention time of 1-methyl-2-
matics for which a calibration is not available. These compo-
ethylbenzene
nents are estimated from the calibration of several calibrated
y2 = peak width at half height of 1,3,5-
aromatic components.
trimethylbenzene
y1 = peak width at half height 1-methyl-
2-ethyl benzene
4. Summary of Test Method
6.2 Mass Spectrometry:
4.1 A gas chromatograph equipped with a dimethylpolysi-
6.2.1 Mass spectrometer capable of producing electron
loxane WCOT column is interfaced to a fast scanning mass
impactspectraat70,orhigher,electronvoltsorequivalent,and
spectrometer that is suitable for capillary column GC/MS
capable of scanning the range of the specified quantitation
analyses. The sample is injected either through a capillary
masses or m/e. The mass scan range shall cover the masses of
splitter port or a cool-on-column injector capable of introduc-
interest for quantitation and should yield at least 5 scans across
ing a small sample size without overloading the column. The
the peak width at half peak width fora1to3 mass % toluene
capillarycolumnisinterfaceddirectlytothemassspectrometer
and cover the masses of interest for quantitation.Ascan range
orbywayofanopensplitinterfaceorotherappropriatedevice.
of 41 to 200 daltons is adequate.
4.2 Calibrationisperformedonamassbasis,usingmixtures
6.2.2 The mass spectrometer must be capable of being
of specified pure aromatic hydrocarbons. Volume % data is
interfaced to a gas chromatograph and WCOT columns. The
calculated from the densities of the individual components and
interface must be at a high enough temperature to prevent
thedensityofthesample.Amultipointcalibrationconsistingof
condensationofcomponentsboilingupto220°C,usually20°C
at least five levels and bracketing the expected concentrations
above the final column temperature is adequate. Direct column
of the specified individual aromatics is required. Specified
interface to the mass spectrometer can be used. An open split
deuterated hydrocarbons are used as the internal standards, for
interfacewithcomputercontrolledprogrammableflowcontrol-
example, d6-benzene for quantitating benzene. Unidentified
ler(s) can also be used, particularly with cool on-column
aromatic hydrocarbons present that have not been specifically
injections, to maintain all aromatic components within the
calibrated for are quantitated using the calibration of an
linearity of the mass spectrometer and at the same time
adjacent calibrated compound and summed with the other
maintain detectability of lower concentration aromatic compo-
aromatic components to obtain a total aromatic concentration
nents. For example, a higher open-split-interface make-up gas
of the sample.
flow can be used for the high concentration components, such
4.3 Specified quality control mixture(s), such as synthetic
as toluene and xylenes, and a lower make-up gas flow rate may
quality control mixtures must be analyzed to monitor the
be used during the elution of the lower concentration benzene
performance of the calibrated GC/MS system. Analysis of a
and C9+ components. Other interfaces may be used provided
gasoline as a reference material is strongly recommended.
the criteria specified in Sections 9 and 10 are met.
6.2.3 A computer system shall be interfaced to the mass
5. Significance and Use
spectrometer to allow acquisition of continuous mass scans or
5.1 Test methods to determine benzene and the aromatic
total ion chromatogram (TIC) for the duration of the chromato-
content of gasoline are necessary to assess product quality and
graphic program and be able to analyze repeatedly 0.01 mass
to meet fuel regulations.
% 1,4-diethylbenzene with the specified signal/noise ratio of 5.
5.2 This test method can be used for gasolines that contain
Software must be available to allow searching any GC/MS run
oxygenates (alcohols and ethers) as additives. It has been
for specific ions or reconstructed ions and plotting the intensity
determined that the common oxygenates found in finished
of the ions with respect to time or scan number. The ability to
gasolinedonotinterferewiththeanalysisofbenzeneandother
integrate the area under a specific ion plot peak is essential for
aromatics by this test method.
quantitation. The quantitation software must allow linear least
squares or quadratic nonlinear regression and quantitation with
6. Apparatus
multiple internal standards. It is also recommended that soft-
6.1 Gas Chromatography:
ware be available to automatically perform the identification of
6.1.1 System equipped with temperature-programmable gas
aromatic components as specified in 13.1.1.
chromatographsuitableforsplitinjectionswithWCOTcolumn
7. Reagents and Materials
or cool-on-column injector that allows the injection of small
(for example, 0.1 µL) samples at the head of the WCOT 7.1 Carrier Gas—Helium and hydrogen have been used
columnoraretentiongap.Anautosamplerismandatoryforthe successfully. The recommended minimum purity of the carrier
on-column injections. gas used is 99.999 mol %. Additional purification using
6.1.2 WCOT column containing dimethylpolysiloxane commercially available scrubbing reagents may be necessary
bonded stationary phase, meeting the specification in the to remove trace oxygen, which may deteriorate the perfor-
followingtable.Foron-columninjections,acolumncontaining mance of the GC WCOT.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D5769–98
NOTE 1—Warning: Helium and hydrogen are supplied under high
spectral match (see 13.1.1). Naphthalene is hygroscopic and
pressure. Hydrogen can be explosive and requires special handling.
should be stored away from high humidity.
Hydrogen monitors that automatically shut off supply to the GC in case of
serious leaks are available from GC supply manufacturers.
8. Sampling
7.2 Dilution Solvents—Reagent grade 2,2,4-
8.1 Every effort should be made to ensure that the sample is
trimethylpentane (iso-octane), n-heptane, n-nonane, cyclo- representative of the fuel source from which it is taken. Follow
hexane, or toluene, or a combination thereof, used as a solvent the recommendations of Practice D 4057D 4057, or its equiva-
in the preparation of the calibration mixtures.
lent, when obtaining samples from bulk storage or pipelines.
Sampling to meet certain regulatory specifications may require
NOTE 2—Toluene should be used as a solvent only for the preparation
the use of specific sampling procedures. Consult appropriate
of C9+ components and shall be free from interfering aromatics.
regulations.
NOTE 3—Warning: The gasoline samples and solvents used as re-
8.2 Appropriate steps should be taken to minimize the loss
agents such as iso-octane, cyclohexane, n-heptane, n-octane, and toluene,
are flammable and may be harmful or fatal if ingested or inhaled. Benzene oflighthydrocarbonsfromthegasolinesamplewhilesampling
is a known carcinogen. Use with proper ventilation. Safety glasses and
and during analyses. Upon receipt in the laboratory, chill the
gloves are required while preparing samples and standards. Samples
sample in its original container to between 0 to 5°C (32 to
should be kept in well ventilated laboratory areas.
40°F)beforeandafterasamplealiquotisremovedforanalysis.
7.3 Internal Standards—Deuterated analogs of benzene,
8.3 After the sample is prepared for analysis with internal
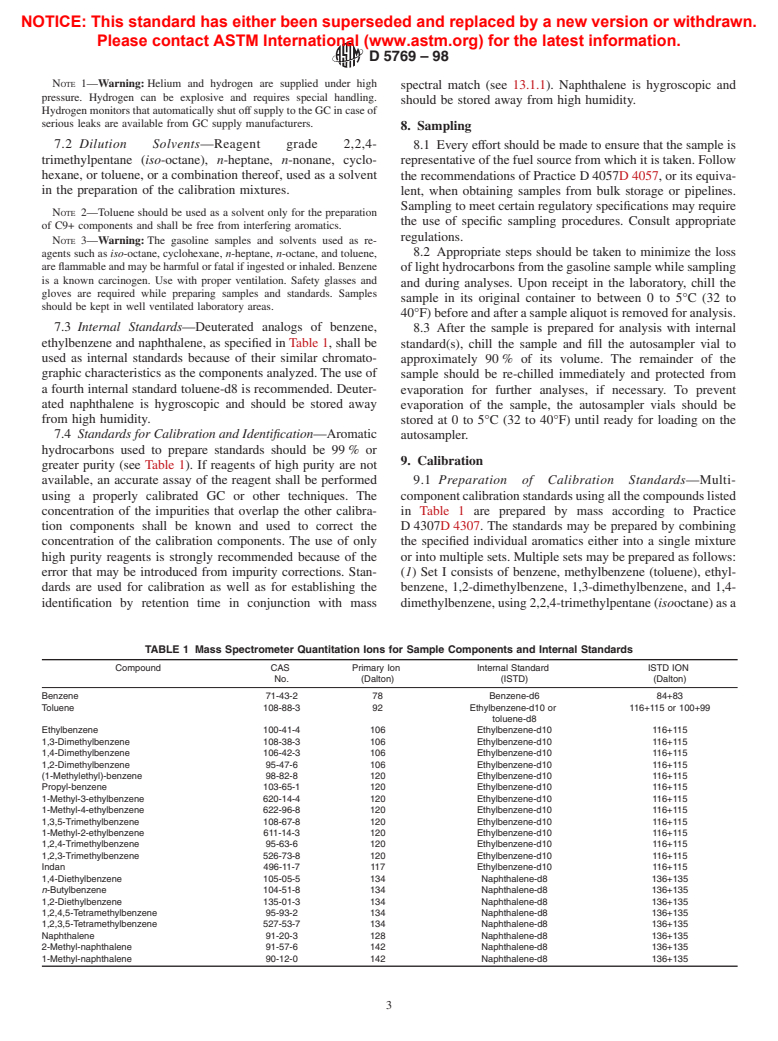
ethylbenzene and naphthalene, as specified in Table 1, shall be
standard(s), chill the sample and fill the autosampler vial to
used as internal standards because of their similar chromato-
approximately 90 % of its volume. The remainder of the
graphic characteristics as the components analyzed. The use of
sample should be re-chilled immediately and protected from
a fourth internal standard toluene-d8 is recommended. Deuter-
evaporation for further analyses, if necessary. To prevent
ated naphthalene is hygroscopic and should be stored away
evaporation of the sample, the autosampler vials should be
from high humidity.
stored at 0 to 5°C (32 to 40°F) until ready for loading on the
7.4 Standards for Calibration and Identification—Aromatic
autosampler.
hydrocarbons used to prepare standards should be 99 % or
9. Calibration
greater purity (see Table 1). If reagents of high purity are not
available, an accurate assay of the reagent shall be performed 9.1 Preparation of Calibration Standards—Multi-
using a properly calibrated GC or other techniques. The componentcalibrationstandardsusingallthecompoundslisted
concentration of the impurities that overlap the other calibra- in Table 1 are prepared by mass according to Practice
tion components shall be known and used to correct the D 4307D 4307. The standards may be prepared by combining
concentration of the calibration components. The use of only the specified individual aromatics either into a single mixture
high purity reagents is strongly recommended because of the or into multiple sets. Multiple sets may be prepared as follows:
error that may be introduced from impurity corrections. Stan- (1) Set I consists of benzene, methylbenzene (toluene), ethyl-
dards are used for calibration as well a
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.