ASTM D1016-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freezing Points
Standard Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freezing Points
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the sampling and determination of purity of essentially pure compounds for which the freezing points for zero impurity and cryoscopic constants are given. The compounds to which the test method is applicable are: ( Warning-Extremely flammable liquids and liquefied gases.)n-butane1,3-butadieneisobutaneisoprene(2-methyl-1,3-butadiene)n-pentanebenzeneisopentanetoluene (methylbenzene)n-hexaneethylbenzenen-heptaneo-xylene (1,2-dimethylbenzene)n-octanem-xylene (1,3-dimethylbenzene)2,2,4-trimethylpentanep-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene)methylcyclohexanestyrene (ethenylbenzene)isobutene
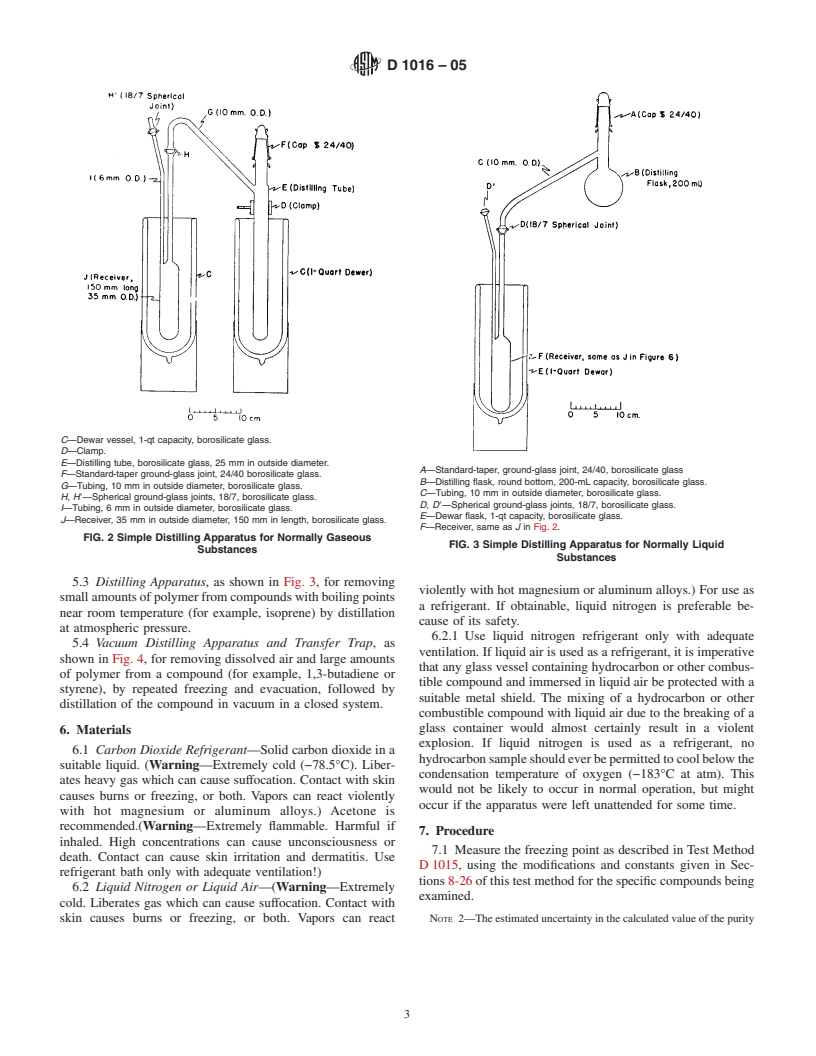
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections , , , and .Note 1
This test method covers systems in which the impurities form with the major component a substantially ideal or sufficiently dilute solution, and also systems which deviate from the ideal laws, provided that, in the latter case, the lowering of the freezing point as a function of the concentration is known for each most probable impurity in the given substance.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D1016–05
Standard Test Method for
1
Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freezing Points
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1016; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D1015 Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity
Hydrocarbons
1.1 This test method covers the sampling and determination
of purity of essentially pure compounds for which the freezing
3. Summary of Test Method
2
points for zero impurity and cryoscopic constants are given.
3.1 After measurement of the freezing point of the actual
The compounds to which the test method is applicable are:
sample, purity can be calculated from the value of the
(Warning—Extremelyflammableliquidsandliquefiedgases.)
determinedfreezingpointandthevaluesgivenforthefreezing
n-butane 1,3-butadiene
point for zero impurity and for the applicable cryoscopic
isobutane isoprene(2-methyl-1,3-butadiene)
4
n-pentane benzene
constant or constants.
isopentane toluene (methylbenzene)
3.2 For the equilibrium between an infinitesimal amount of
n-hexane ethylbenzene
thecrystallinephaseofthemajorcomponentandaliquidphase
n-heptane o-xylene (1,2-dimethylbenzene)
n-octane m-xylene (1,3-dimethylbenzene)
ofthemajorcomponentandoneormoreothercomponents,the
2,2,4-trimethylpentane p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene)
thermodynamic relation between the temperature of equilib-
methylcyclohexane styrene (ethenylbenzene)
rium and the composition of the liquid phase is expressed by
isobutene
5
the equation:
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
21nN 521n ~1 2N ! 5A~t 2t !@1 1B~t 2t ! 1.] (1)
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only. 1 2 f0 f f0 f
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
where:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
N = mole fraction of the major component,
1
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
N =(1−N )=sum of the mole fractions of all the other
2 1
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
components,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
t = freezing point, in degrees Celsius, of the given
f
statements, see Sections 1, 6, 8, and 10-26.
substance (in which the mole fraction of the major
component is N ), defined as the temperature at
NOTE 1—Thistestmethodcoverssystemsinwhichtheimpuritiesform
1
with the major component a substantially ideal or sufficiently dilute which an infinitesimal amount of crystals of the
solution, and also systems which deviate from the ideal laws, provided
major component is in thermodynamic equilibrium
that, in the latter case, the lowering of the freezing point as a function of
with the liquid phase (see Note 3 of Test Method
the concentration is known for each most probable impurity in the given
D1015),
substance.
t = freezing point for zero impurity, in degrees Celsius,
f0
for the major component when pure, that is, when
2. Referenced Documents
N =1or N =0,
3
1 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A = first or main cryoscopic constant, in mole fraction
per degree, and
B = secondary cryoscopic constant, in mole fraction per
1
degree.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04 on Hydrocarbon Analysis.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2005. Published November 2005. Originally
e1
approved in 1949. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D1016–99(2004) .
2 4
Numerical constants in this test method were taken from the most recently For a more complete discussion of this test method, see Glasgow, A. R., Jr.,
published data appearing in “Tables of Physical and Thermodynamic Properties of Streiff, A. J., and Rossini, F. D., “Determination of the Purity of Hydrocarbons by
Hydrocarbons and Related Compounds,” or ASTM DS 4A, Physical Constants of Measurement of Freezing Points,” Journal of Research, JRNBA, National Institute
Hydrocarbons C to C , or both, prepared by the American Petroleum Institute, of Standards and Technology, Vol 35, No. 6, 1945, p. 355.
1 10
5
Research Project 44. For details, see Taylor, W. J., and Rossini, F. D., “Theoretical Analysis of
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Time-Temperature Freezing and Melting Curves as Applied to Hydrocarbons,”
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Journal of Research, JRNBA, Nat. Bureau Standards, Vol 32, No. 5, 1944, p. 197;
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on also Lewi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.