ASTM B312-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Green Strength of Specimens Compacted from Metal Powders
Standard Test Method for Green Strength of Specimens Compacted from Metal Powders
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The green strength value determined under the conditions specified by this test method is influenced by the characteristics of the powder, how it compacts under the specified conditions (that is, the particle to particle bonding that exists following compacting), and the lubrication system used.
5.2 Knowledge of the green strength value is useful to the production, characterization, and utilization of metal powders in the manufacture of PM structural parts and bearings.
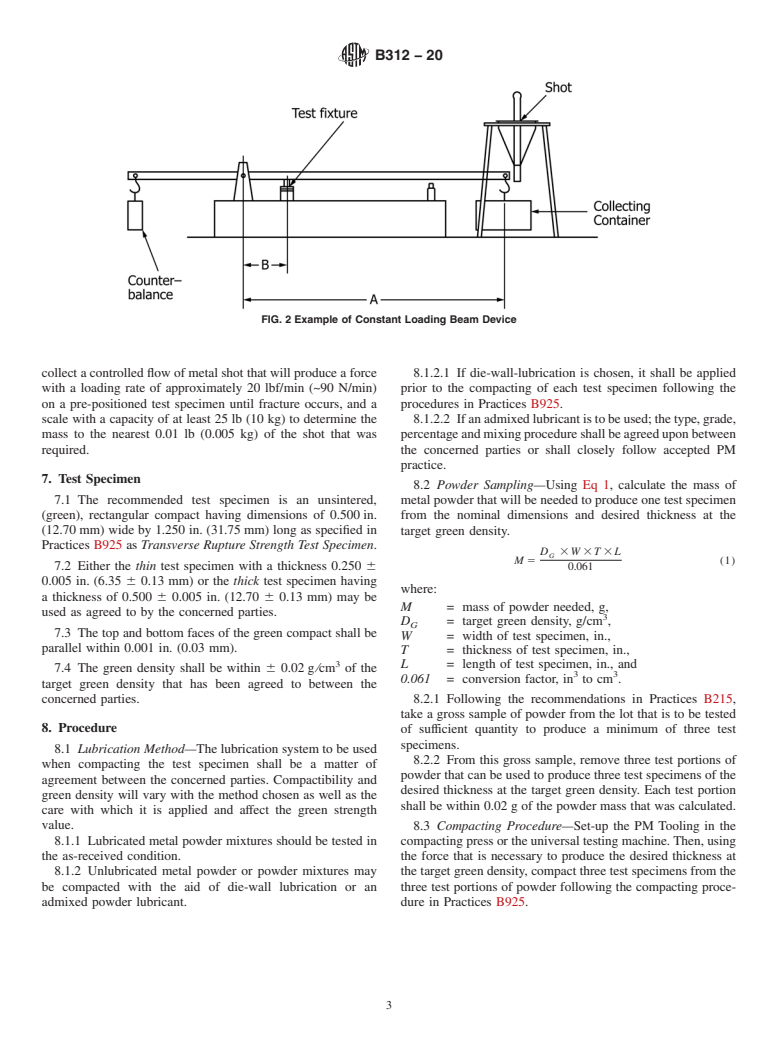
5.3 The test for green strength of a compacted metal powder can be used to:
5.3.1 Relate the resistance of a pressed compact to breakage or damage due to handling.
5.3.2 Compare the quality of a metal powder or powder mixture from lot to lot.
5.3.3 Determine the effect of the addition of a lubricant or other powders to a base powder.
5.3.4 Evaluate powder mixing or blending variables.
5.4 Factors that are known to influence the green strength of a metal powder are particle shape, particle size distribution, and compressibility of the metal powder.
5.5 The amount and type of lubricant or other additives and the mixing procedures have a strong effect on the green strength of specimens produced from metal powder mixtures.
SCOPE
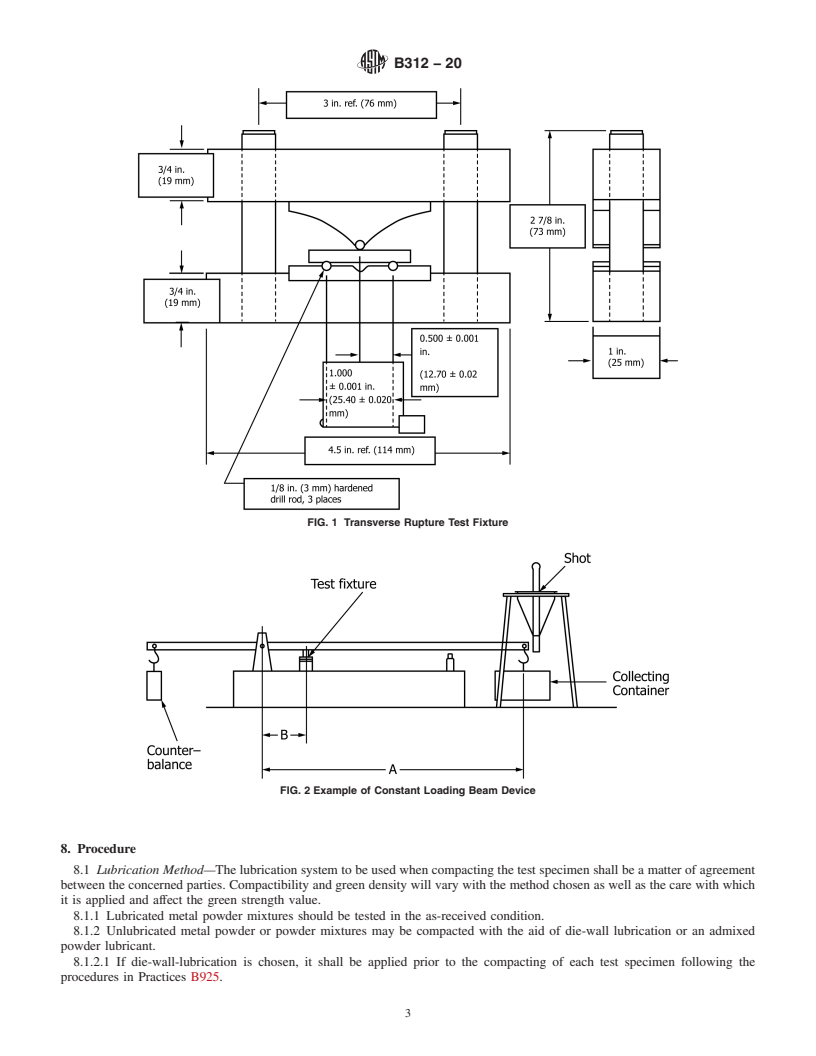
1.1 This standard covers a test method that may be used to measure the transverse rupture strength of a compacted but unsintered (green) test specimen produced from lubricated or unlubricated metal powders or powder mixtures.
1.2 Green strength is measured by a quantitative laboratory procedure in which the fracture strength is calculated from the force required to break an unsintered test specimen supported as a simple beam while subjected to a uniformly increasing three-point transverse load under controlled conditions.
1.3 This test method is a companion standard to Test Method B528 that covers the measurement of the transverse rupture strength of sintered PM test specimens.
1.4 Units—With the exception of the values for density and the mass used to determine density, for which the use of the gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) and gram (g) units is the longstanding industry practice, the values in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B312 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Green Strength of Specimens Compacted from Metal
1
Powders
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B312; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This standard covers a test method that may be used to 2.1 ASTM Standards:
measure the transverse rupture strength of a compacted but B215 Practices for Sampling Metal Powders
unsintered (green) test specimen produced from lubricated or B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
unlubricated metal powders or powder mixtures. B528 Test Method for Transverse Rupture Strength of Pow-
der Metallurgy (PM) Specimens
1.2 Green strength is measured by a quantitative laboratory
B925 Practices for Production and Preparation of Powder
procedure in which the fracture strength is calculated from the
Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
force required to break an unsintered test specimen supported
B962 Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered
as a simple beam while subjected to a uniformly increasing
Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’
three-point transverse load under controlled conditions.
Principle
1.3 This test method is a companion standard to Test
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Method B528 that covers the measurement of the transverse
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
rupture strength of sintered PM test specimens.
3. Terminology
1.4 Units—With the exception of the values for density and
the mass used to determine density, for which the use of the 3.1 Definitions—The definitions of powder metallurgy (PM)
3
gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm ) and gram (g) units is the terms used in this test method can be found in Terminology
longstanding industry practice, the values in inch-pound units B243. Additional descriptive PM information is available in
are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses the Related Material section of Vol 02.05 of the Annual Book
are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
of ASTM Standards.
information only and are not considered standard.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Three rectangular test specimens are compacted to a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
predetermined green density or at a specified compacting
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
pressure from test portions of the metal powder or powder
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mixture that is to be tested.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.2 Each unsintered bar is placed, in turn, in a test fixture
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
and subjected to a uniformly increasing transverse load under
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
controlled conditions until fracture occurs.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.3 The green strength or maximum flexural stress of each
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
specimenisdeterminedbycalculationusingthestressequation
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
for a simply supported beam with a concentrated mid-point
load.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal
Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
2
mittee B09.02 on Base Metal Powders. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published April 2020. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1956. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as B312 – 14. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/B0312-20. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B312 − 20
4.4 The green strength of the material being tested is 5.5 The amount and type of lubricant or other additives and
reported as the arithmetic mean of the results of three indi- the mixing procedures have a strong effect on the green
vidual tests at
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B312 − 14 B312 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Green Strength of Specimens Compacted from Metal
1
Powders
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B312; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This standard covers a test method that may be used to measure the transverse rupture strength of a compacted but
unsintered (green) test specimen produced from lubricated or unlubricated metal powders or powder mixtures.
1.2 Green strength is measured by a quantitative laboratory procedure in which the fracture strength is calculated from the force
required to break an unsintered test specimen supported as a simple beam while subjected to a uniformly increasing three-point
transverse load under controlled conditions.
1.3 This test method is a companion standard to Test Method B528 that covers the measurement of the transverse rupture
strength of sintered PM test specimens.
1.4 Units—With the exception of the values for density and the mass used to determine density, for which the use of the gram
3
per cubic centimeter (g/cm ) and gram (g) units is the longstanding industry practice, the values in inch-pound units are to be
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information
only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B215 Practices for Sampling Metal Powders
B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
B528 Test Method for Transverse Rupture Strength of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Specimens
B925 Practices for Production and Preparation of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
B962 Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—theThe definitions of powder metallurgy (PM) terms used in this test method can be found in Terminology
B243. Additional descriptive PM information is available in the Related Material section of Vol 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM
Standards.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Three rectangular test specimens are compacted to a predetermined green density or at a specified compacting pressure from
test portions of the metal powder or powder mixture that is to be tested.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B09.02
on Base Metal Powders.
Current edition approved June 1, 2014April 1, 2020. Published July 2014April 2020. Originally approved in 1956. Last previous edition approved in 20092014 as
B312 – 09.B312 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/B0312-14.10.1520/B0312-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B312 − 20
4.2 Each unsintered bar is placed, in turn, in a test fixture and subjected to a uniformly increasing transverse load under
controlled conditions until fracture occurs.
4.3 The green strength or maximum flexural stress of each specimen is determined by calculation using the stress equation for
a simply supported beam with a concentrated mid-point load.
4.4 The green strength of the material being tested is
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.