ASTM D5132-93(1994)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Flexible Cellular and Rubber Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Flexible Cellular and Rubber Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended for use as a small-scale laboratory screening procedure for comparing the relative horizontal burning rates of flexible cellular and rubber materials used in the occupant compartments of motor vehicles.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard should be used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire-hazard or fire-risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, the results of this test may be used as elements of a fire-hazard assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: D 5132 – 93 (Reapproved 1994)
Standard Test Method for
Horizontal Burning Rate of Flexible Cellular and Rubber
Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of Motor
Vehicles
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5132; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Section 14, Keywords, was revised editorially in December 1994.
1. Scope Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Industries
E 176 Terminology Relating to Fire Standards
1.1 This test method is intended for use as a small-scale
2.2 Federal Safety Standard:
laboratory screening procedure for comparing the relative
DOTMVSS 302 Flammability of Interior Materials—
horizontal burning rates of flexible cellular and rubber materi-
2 Passenger Cars, Multipurpose Passenger Vehicles, Trucks
als used in the occupant compartments of motor vehicles.
and Buses
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3. Terminology
only.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of fire-related terms used in
1.3 This standard should be used to measure and describe
this test method refer to Terminology E 176.
the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and
flame under controlled conditions and should not be used to
4. Summary of Test Method
describe or appraise the fire-hazard or fire-risk of materials,
4.1 This test method for measuring the burning rate of
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However,
materials employs a standard test specimen 100 by 360 by 13
the results of this test may be used as elements of a fire-hazard
mm (4.0 by 14.0 by 0.5 in.) mounted in a U-shaped metal
assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes into account
frame. The specimen is ignited by means of a 38-mm (1.5-in.)
all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the
high flame from an appropriate burner.
fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
4.2 The rate of burning is reported for each set of specimens
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
as determined by measurements of the horizontal distance
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
burned in relation to the time of burning.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
5.1 This test method provides a standard laboratory proce-
statements are given in Section 7.
dure for measuring and comparing the burning rates of flexible
cellular materials and rubber under specified controlled condi-
2. Referenced Documents
tions.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.2 The rate of burning is affected by such factors as density,
D 1349 Practice for Rubber—Standard Temperatures for
3 direction of rise, and type and amount of surface treatments.
Testing
The thickness of the finished specimens must also be taken into
D 3767 Practice for Rubber—Measurement of Dimensions
account. These factors must be considered in order to compare
D 4483 Practice for Determining Precision for Test Method
materials on the same basis.
5.3 This test method is not intended to be a criterion for fire
This test method is under the jurisdication of ASTM Committee D-20 on
hazard. Fire hazard evaluation more properly includes other
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal
factors, such as flame spread, ease of ignition, fuel contribu-
Properties.
tion, heat evolution, products of combustion, and others.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 1993. Published December 1993. Originally
published as D 5132 – 90. Last previous edition D 5132 – 90.
The source document used for the preparation of this test method was United
States Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 302. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, United States Code of Federal Regulations, 49 CFR 571.302, 36 FR 28991,
Washington, DC 20402. available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01. Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 5132
6. Apparatus 7. Hazards
7.1 During the course of combustion, gases or vapors, or
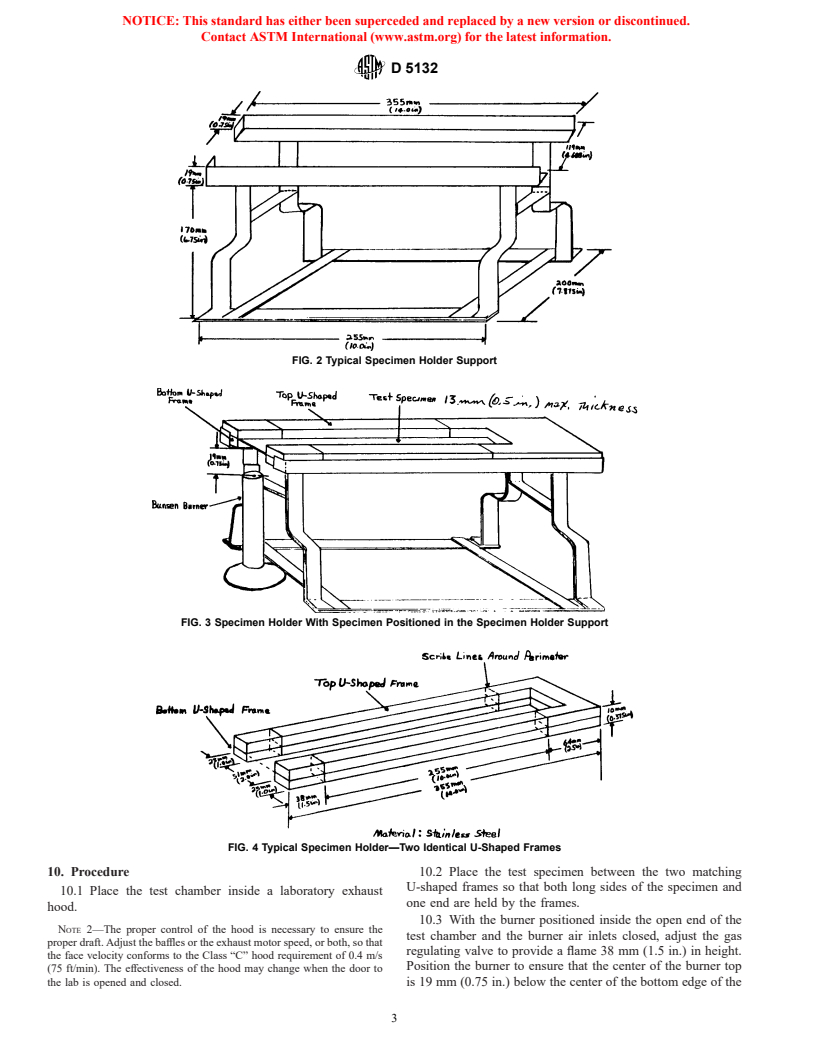
6.1 The apparatus shall be as shown in Figs. 1-6 and shall
include the following: both, are evolved that may be hazardous. Adequate precautions
should be taken to protect the operator. See 1.4.
6.1.1 Test Chamber—A chamber approximately 380 by 355
by 200 mm (15 by 14 by 8 in.) constructed of 1.27-mm
8. Test Specimens
(0.050-in.) steel sheet and fabricated in accordance with Fig. 1.
6.1.2 Burner—A standard 9.5-mm (0.375-in.) barrel Bunsen 8.1 A minimum of five specimens 100 by 355 by a maxi-
mum of 13 mm (4.0 by 14.0 by 0.5 in.) are needed. If the
or Tirrill burner.
sample has a coating or covering that is considered directional
NOTE 1—The burner may be mounted on the door, as shown in Fig. 6,
in nature, then five specimens should be burned in each
to ensure proper alignment.
direction.
6.1.3 Fuel Supply—Methane or natural gas having a heating
8.2 Cut cellular specimens from uniform density samples.
3 3
value of 33 to 41 MJ/m (900 to 1100 Btu/ft ) regulated to
Cut materials supplied in thicknesses greater than 13 mm (0.5
approximately 17 kPa (2.5 psi).
in.) to this thickness. Test materials supplied at less than 13 mm
6.1.4 Specimen Holder Support—A device capable of main-
(0.5 in.) at the supplied thickness and record this information as
taining the specimen holder horizontally in place so that the top
part of the test results.
of the burner tube is positioned 19 mm (0.75 in.) below the top
8.3 Where it is not possible to obtain a flat specimen
surface of the bottom U-shaped frame when placed in the
because of the component configuration, cut the specimen to
specimen holder support, as shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. The
not more than 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) thickness at any point, from
base of the support shall not obstruct the ventilation holes in
the area with the least curvature, and in such a manner as to
the base of the cabinet.
include the face side. Use the maximum available length or
6.1.5 Specimen Holder—Two matching U-shaped frames of
width of a specimen where either dimension is less than the
noncorro
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.