ASTM D7039-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Jet Fuel, Kerosine, Biodiesel, Biodiesel Blends, and Gasoline-Ethanol Blends by Monochromatic Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Jet Fuel, Kerosine, Biodiesel, Biodiesel Blends, and Gasoline-Ethanol Blends by Monochromatic Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method provides for the precise measurement of the total sulfur content of samples within the scope of this test method with minimal sample preparation and analyst involvement. The typical time for each analysis is five minutes.
4.2 Knowledge of the sulfur content of diesel fuels, gasolines, and refinery process streams used to blend gasolines is important for process control as well as the prediction and control of operational problems such as unit corrosion and catalyst poisoning, and in the blending of products to commodity specifications.
4.3 Various federal, state, and local agencies regulate the sulfur content of some petroleum products, including gasoline and diesel fuel. Unbiased and precise determination of sulfur in these products is critical to compliance with regulatory standards.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur by monochromatic wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence (MWDXRF) spectrometry in single-phase gasoline, diesel fuel, refinery process streams used to blend gasoline and diesel, jet fuel, kerosine, biodiesel, biodiesel blends, and gasoline-ethanol blends.
Note 1: Volatile samples such as high-vapor-pressure gasolines or light hydrocarbons might not meet the stated precision because of the evaporation of light components during the analysis.
1.2 The range of this test method is between the pooled limit of quantitation (PLOQ) value (calculated by procedures consistent with Practice D6259) of 3.2 mg/kg total sulfur and the highest level sample in the round robin, 2822 mg/kg total sulfur.
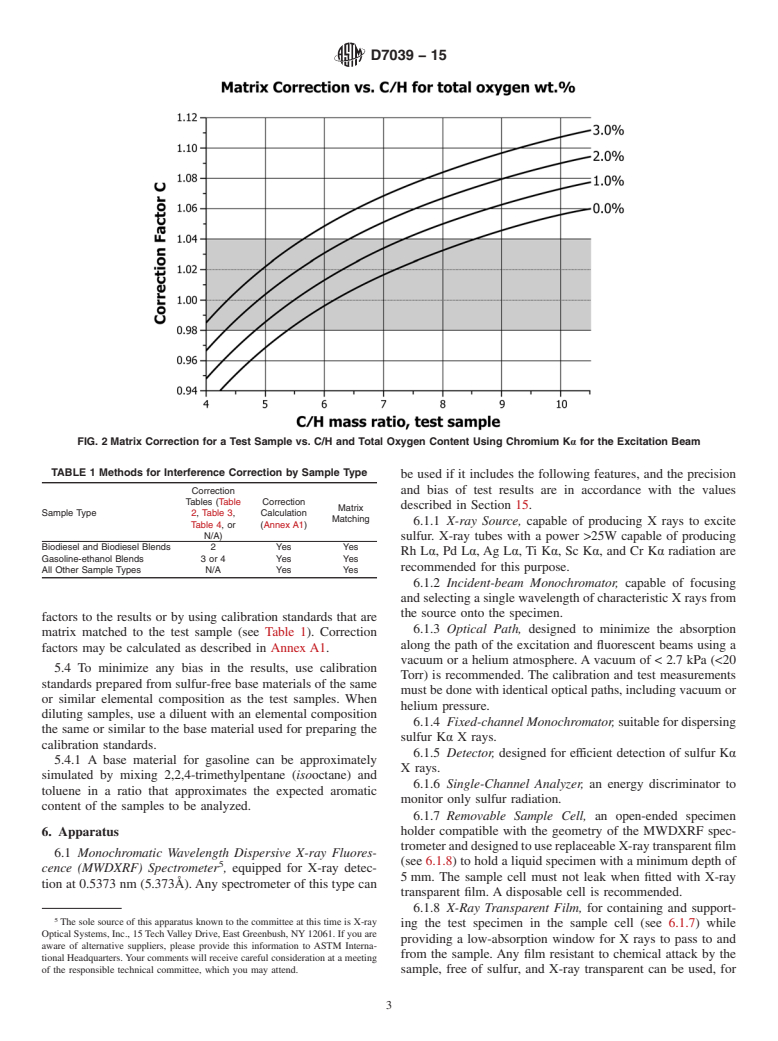
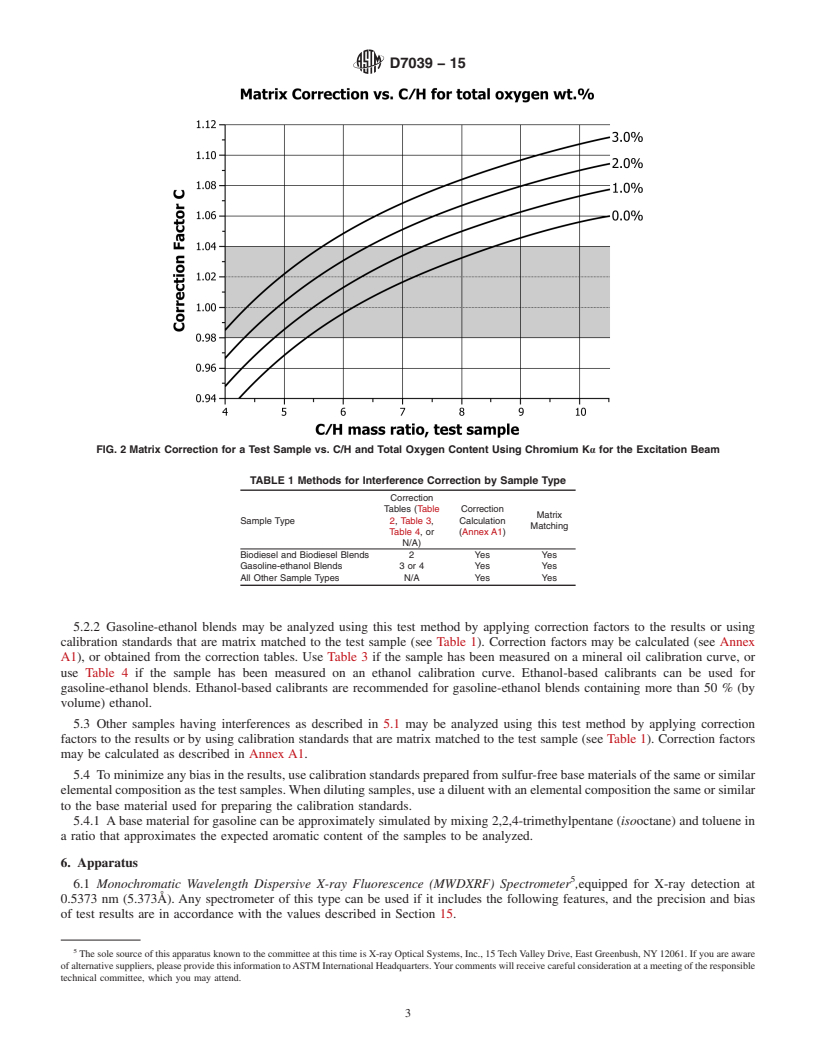
1.3 Samples containing oxygenates can be analyzed with this test method provided the matrix of the calibration standards is either matched to the sample matrices or the matrix correction described in Section 5 or Annex A1 is applied to the results. The conditions for matrix matching and matrix correction are provided in the Interferences section (Section 5).
1.4 Samples with sulfur content above 2822 mg/kg can be analyzed after dilution with appropriate solvent (see 5.4). The precision and bias of sulfur determinations on diluted samples has not been determined and may not be the same as shown for neat samples (Section 15).
1.5 When the elemental composition of the samples differ significantly from the calibration standards used to prepare the calibration curve, the cautions and recommendation in Section 5 should be carefully observed.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard information, see 3.1.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7039 − 15
StandardTest Method for
Sulfur in Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Jet Fuel, Kerosine,
Biodiesel, Biodiesel Blends, and Gasoline-Ethanol Blends
by Monochromatic Wavelength Dispersive X-ray
1
Fluorescence Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7039; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur
only.
by monochromatic wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(MWDXRF)spectrometryinsingle-phasegasoline,dieselfuel,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
refinery process streams used to blend gasoline and diesel, jet
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
fuel,kerosine,biodiesel,biodieselblends,andgasoline-ethanol
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
blends.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
NOTE 1—Volatile samples such as high-vapor-pressure gasolines or
information, see 3.1.
light hydrocarbons might not meet the stated precision because of the
evaporation of light components during the analysis.
2. Referenced Documents
2
1.2 Therangeofthistestmethodisbetweenthepooledlimit
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of quantitation (PLOQ) value (calculated by procedures con-
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
sistent with Practice D6259) of 3.2 mg⁄kg total sulfur and the
Petroleum Products
highest level sample in the round robin, 2822 mg⁄kg total
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
sulfur.
Petroleum Products
D6259 Practice for Determination of a Pooled Limit of
1.3 Samples containing oxygenates can be analyzed with
Quantitation
this test method provided the matrix of the calibration stan-
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
dards is either matched to the sample matrices or the matrix
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
correction described in Section 5 or AnnexA1 is applied to the
Measurement System Performance
results. The conditions for matrix matching and matrix correc-
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias
tion are provided in the Interferences section (Section 5).
Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
1.4 Samples with sulfur content above 2822 mg⁄kg can be Lubricants
3
analyzed after dilution with appropriate solvent (see 5.4). The
2.2 EPA Documents:
precision and bias of sulfur determinations on diluted samples
40 CFR 80.584 Code of Federal Regulations; Title 40; Part
has not been determined and may not be the same as shown for
80; U.S. Environmental Agency, July 1, 2005
neat samples (Section 15).
3. Summary of Test Method
1.5 When the elemental composition of the samples differ
3.1 A monochromatic X-ray beam with a wavelength suit-
significantly from the calibration standards used to prepare the
able to excite the K-shell electrons of sulfur is focused onto a
calibration curve, the cautions and recommendation in Section
test specimen contained in a sample cell (see Fig. 1). The
5 should be carefully observed.
fluorescent Kα radiation at 0.5373 nm (5.373 Å) emitted by
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2015. Published May 2015. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D7039 – 13. DOI: Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, 732 N. Capitol Street, NW,
10.1520/D7039-15. Washington, DC 20401.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7039 − 15
FIG. 1 Schematic of the MWDXRF Analyzer
sulfur is collected by a fixed monochromator (analyzer). The method, elements contributing to bias resulting from differ-
intensity (counts per second) of the sulfur X rays is measured ences in the matrices of calibrants and test samples are
using a suitable detector and converted
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7039 − 13 D7039 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Sulfur in Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Jet Fuel, Kerosine,
Biodiesel, Biodiesel Blends, and Gasoline-Ethanol Blends
by Monochromatic Wavelength Dispersive X-ray
1
Fluorescence Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7039; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total sulfur by monochromatic wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence
(MWDXRF) spectrometry in single-phase gasoline, diesel fuel, refinery process streams used to blend gasoline and diesel, jet fuel,
kerosine, biodiesel, biodiesel blends, and gasoline-ethanol blends.
NOTE 1—Volatile samples such as high-vapor-pressure gasolines or light hydrocarbons might not meet the stated precision because of the evaporation
of light components during the analysis.
1.2 The range of this test method is between the pooled limit of quantitation (PLOQ) value (calculated by procedures consistent
with Practice D6259) of 3.23.2 mg ⁄ mg/kg kg total sulfur and the highest level sample in the round robin, 28222822 mg ⁄ mg/kg
kg total sulfur.
1.3 Samples containing oxygenates can be analyzed with this test method provided the matrix of the calibration standards is
either matched to the sample matrices or the matrix correction described in Section 5 or Annex A1 is applied to the results. The
conditions for matrix matching and matrix correction are provided in the Interferences section (Section 5).
1.4 Samples with sulfur content above 28222822 mg ⁄ mg/kg kg can be analyzed after dilution with appropriate solvent (see
5.4). The precision and bias of sulfur determinations on diluted samples has not been determined and may not be the same as shown
for neat samples (Section 15).
1.5 When the elemental composition of the samples differ significantly from the calibration standards used to prepare the
calibration curve, the cautions and recommendation in Section 5 should be carefully observed.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard information, see 3.1.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D6259 Practice for Determination of a Pooled Limit of Quantitation
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
3
2.2 EPA Documents:
40 CFR 80.584 Code of Federal Regulations; Title 40; Part 80; U.S. Environmental Agency, July 1, 2005
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2013April 1, 2015. Published October 2013May 2015. Originally approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 20072013 as
D7039 – 07.D7039 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/D7039-13.10.1520/D7039-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, 732 N. Capitol Street, NW, Washington, DC 20401.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7039 − 15
FIG. 1 Schematic of the MWDXRF Analyzer
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A monochromatic X-ray beam with a wavelength suitable to excite the K-shell electrons of sulfur is focused onto a
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.