ASTM F3153-22
(Specification)Standard Specification for Verification of Aircraft Systems and Equipment
Standard Specification for Verification of Aircraft Systems and Equipment
ABSTRACT
This specification describes a process for verifying the intended function and compliance with safety objectives of avionics systems by means of system-level testing. This verification process includes functional verification planning, testing, resolution of test failures, and regression analysis and testing. It also covers organizational requirements and the process of product definition (function identification, classification, and specification) as well as the requirements for producing a statement of verification.
SCOPE
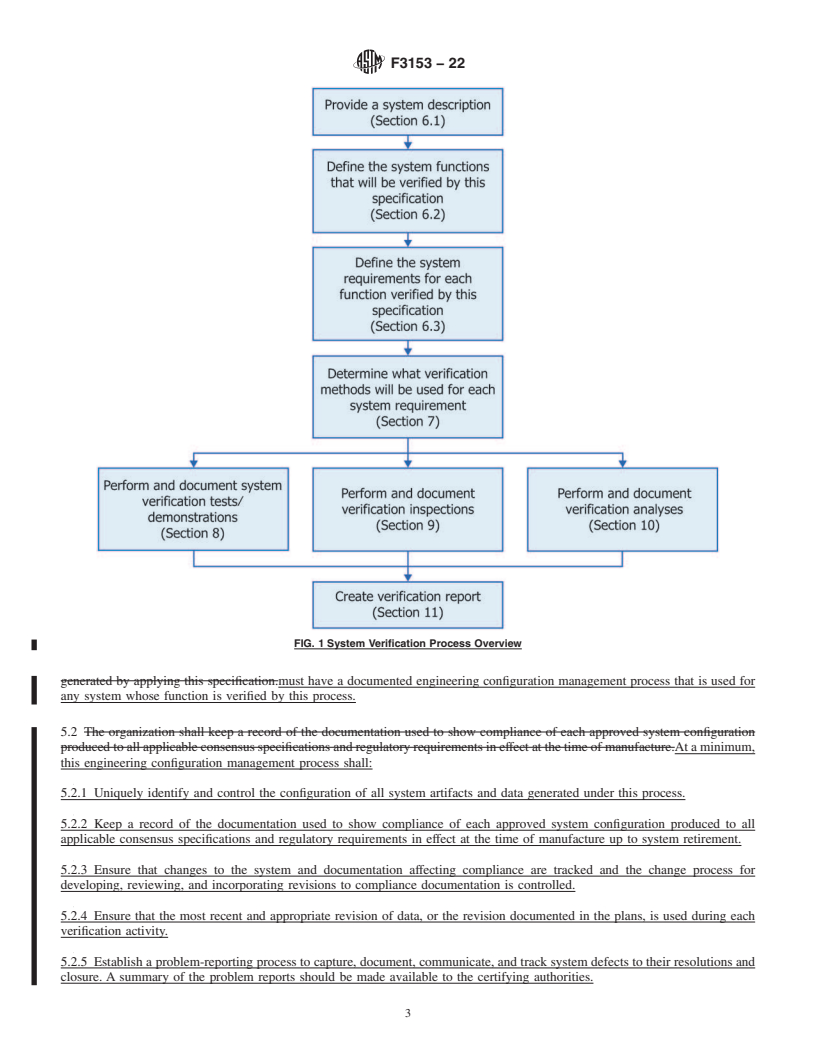
1.1 This specification provides a process for performing system level verification of aircraft systems and equipment. It provides a means of compliance that can be used for systems and equipment with software and Airborne Electronic Hardware (AEH) that have not been addressed by traditional development assurance methods.
1.2 This process can be used to show compliance to regulations that require a demonstration that functionality was implemented as intended, including safety mitigations that address failure conditions for software and AEH aspects for aircraft systems and equipment.
1.3 While this specification was developed with systems and equipment installed on aircraft certification level 1 and 2 (or class I and II in accordance with Advisory Circular (AC) 23.1309-1) normal category aeroplanes in mind, the content may be more broadly applicable. It is the responsibility of the Applicant to substantiate broader applicability as a specific means of compliance and obtain concurrence for its use from the applicable Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
1.4 When using this specification, regulations that govern system safety requirements applicable to the aircraft still apply. In complying with those regulations, additional architectural mitigations such as redundancy, independence, separation, system monitors, etc., may be required in addition to the verification process specified in this specification.
1.5 The system level verification activities expected by this specification increase as the severity of the failure conditions applicable to or affected by the function increase. Those functions, which have hazardous and catastrophic failure conditions, receive additional activities through this process to provide detailed scrutiny. For normal category aircraft, refer to Practice F3309, Practice F3230, or AC 23.1309-1 for more information on the identification and classification of system failure conditions. Involvement of the applicable CAA personnel or their designees in this system verification process should be discussed early in the project.
1.6 This verification process specifically addresses definition, identification, and verification of system functions. Processes conducted under this specification may not satisfy all applicable external requirements; additional review on the part of the system developer, integrator, or installer may be required to meet specific requirements or the specified mission of the aircraft, or both.
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F3153 −22
Standard Specification for
1
Verification of Aircraft Systems and Equipment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3153; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope nel or their designees in this system verification process should
be discussed early in the project.
1.1 This specification provides a process for performing
1.6 This verification process specifically addresses
system level verification of aircraft systems and equipment. It
definition, identification, and verification of system functions.
provides a means of compliance that can be used for systems
Processesconductedunderthisspecificationmaynotsatisfyall
and equipment with software and Airborne Electronic Hard-
applicable external requirements; additional review on the part
ware (AEH) that have not been addressed by traditional
development assurance methods. ofthesystemdeveloper,integrator,orinstallermayberequired
to meet specific requirements or the specified mission of the
1.2 This process can be used to show compliance to
aircraft, or both.
regulations that require a demonstration that functionality was
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
implemented as intended, including safety mitigations that
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
address failure conditions for software and AEH aspects for
standard.
aircraft systems and equipment.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.3 While this specification was developed with systems
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and equipment installed on aircraft certification level 1 and 2
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(or class I and II in accordance with Advisory Circular (AC)
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
23.1309-1) normal category aeroplanes in mind, the content
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
may be more broadly applicable. It is the responsibility of the
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
Applicant to substantiate broader applicability as a specific
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
means of compliance and obtain concurrence for its use from
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the applicable Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.4 When using this specification, regulations that govern
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
system safety requirements applicable to the aircraft still apply.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
In complying with those regulations, additional architectural
mitigations such as redundancy, independence, separation,
2. Referenced Documents
system monitors, etc., may be required in addition to the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
verification process specified in this specification.
F3060 Terminology for Aircraft
1.5 The system level verification activities expected by this F3061/F3061M Specification for Systems and Equipment in
specification increase as the severity of the failure conditions Aircraft
applicable to or affected by the function increase. Those F3230 Practice for Safety Assessment of Systems and
functions, which have hazardous and catastrophic failure Equipment in Small Aircraft
conditions, receive additional activities through this process to F3309 Practice for Simplified SafetyAssessment of Systems
provide detailed scrutiny. For normal category aircraft, refer to and Equipment in Small Aircraft
3
Practice F3309, Practice F3230, or AC 23.1309-1 for more
2.2 Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC) Standard:
information on the identification and classification of system
ARINC Mark 33 Digital Information Transfer System
failure conditions. Involvement of the applicable CAAperson-
(DITS), Specification 429, Parts 1–15, November 2012
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF39onAircraft contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F39.03 on Design of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Avionics Systems. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved April 1, 2022. Published April 2022. Originally Available from ARINC Industry Activities, SAE ITC, 16701 Melford
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F3153 − 15 F3153 − 22
Standard Specification for
1
Verification of AvionicsAircraft Systems and Equipment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3153; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification provides a process by which the intended function and compliance with safety objectives of avionics
systems may be verified by system-level testing.for performing system level verification of aircraft systems and equipment. It
provides a means of compliance that can be used for systems and equipment with software and Airborne Electronic Hardware
(AEH) that have not been addressed by traditional development assurance methods.
1.2 This process can be used to show compliance to regulations that require a demonstration that functionality was implemented
as intended, including safety mitigations that address failure conditions for software and AEH aspects for aircraft systems and
equipment.
1.3 While this specification was developed with systems and equipment installed on aircraft certification level 1 and 2 (or class
I and II in accordance with Advisory Circular (AC) 23.1309-1) normal category aeroplanes in mind, the content may be more
broadly applicable. It is the responsibility of the Applicant to substantiate broader applicability as a specific means of compliance
and obtain concurrence for its use from the applicable Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
1.4 Software and hardware development assurance are not in the scope of this specification and this specification should not be
used if a development assurance process is required.When using this specification, regulations that govern system safety
requirements applicable to the aircraft still apply. In complying with those regulations, additional architectural mitigations such as
redundancy, independence, separation, system monitors, etc., may be required in addition to the verification process specified in
this specification.
1.5 The specification intentionally does not attempt to define its own applicability with regard to the type, category, class of
aircraft, or criticality of function to which avionics systems verified by the specification may be applied as doing so could
ultimately place system level verification activities expected by this specification increase as the severity of the failure conditions
applicable to or affected by the function increase. Those functions, which have hazardous and catastrophic failure conditions,
receive additional activities through this process to provide detailed scrutiny. For normal category aircraft, refer to Practice F3309,
Practice F3230the language of the specification in conflict with external requirements and guidance. Aircraft applicability, intended
use, and limitations must ultimately be determined by the designer, installer, and recognizing body., or AC 23.1309-1 for more
information on the identification and classification of system failure conditions. Involvement of the applicable CAA personnel or
their designees in this system verification process should be discussed early in the project.
1.6 This verification process specifically addresses definition, identification, and verification of system functions. Processes
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F39 on Aircraft Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F39.03 on Design of Avionics
Systems.
Current edition approved July 15, 2015April 1, 2022. Published September 2015April 2022. Originally approved in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as
F3153–15. DOI: 10.1520/F3153-15.10.1520/F3153-22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F3153 − 22
conducted under this specification may not satisfy all applicable external requirements; additional review on the part of the system
developer, integrator, or installer may be required to meet specific requirements or the specified mission of the aircraft, or both.
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of t
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.