ASTM E2205/E2205M-22
(Guide)Standard Guide for Risk-Based Corrective Action for Protection of Ecological Resources
Standard Guide for Risk-Based Corrective Action for Protection of Ecological Resources
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The Eco-RBCA process presented in this guide is a streamlined decision-making process for implementing corrective action protective of ecological resources at chemical release sites in a consistent manner. Eco-RBCA provides a framework for sites not covered under regulatory programs, for sites under regulatory programs that lack guidance, or for sites under programs with guidance that lack detail. Eco-RBCA may also provide a useful framework to help merge an approach when multiple regulatory programs apply.
4.2 Ecological risk assessment is a science-based process that can be used to provide insight for risk management decision-making. Numerous federal and state programs have guidance for conducting ERA. Available regulatory approaches to ERA were reviewed in preparation for the development of this Eco-RBCA guide. Eco-RBCA was designed to be adaptable to the use of a variety of methods for considering risks to relevant ecological receptors and habitats. Some attributes of the standard are:
4.2.1 Use of a tiered approach, including process flow charts to identify critical steps and facilitate the development of an overview of the entire process;
4.2.2 Identification, development, and use of TPDs from Step 1 and throughout the entire Eco-RBCA process;
4.2.3 Indications of the value and timing of stakeholder involvement, recognizing that some regulations require coordination with federal, state, tribal, and natural-resource trustees, and other stakeholders;
4.2.4 Identification of situations under which an ERA may or may not be necessary; and
4.2.5 Identification of decision points where ERA results are used for risk management decision making.
4.3 Activities described in this guide should involve persons with the appropriate skills and expertise. The user may rely on individuals expert in remediation science and technology, ecology/biology, ecotoxicology, ERA practices, and site characterization techniques.
4.4 This guide and supporting app...
SCOPE
1.1 This is a guide to risk-based corrective action for the protection of ecological resources and supplements the RBCA process (Guide E2081). The primary objective of the Eco-RBCA process is to provide a flexible framework for a tiered approach to ERA and risk management decision making at chemical release sites. To this end, available guidance documents from various federal and state agencies were reviewed and their common attributes incorporated into this guide, where possible. The Eco-RBCA process complements existing technical and regulatory ecological risk guidance (see 4.2). In particular, it is intended to be compatible with the USEPA programmatic guidelines for ERA (1)2, guidance for the Superfund program (2), and other USEPA (3) risk assessment and corrective-action programs. Eco-RBCA might also be used in conjunction with corrective action strategies that include human health issues (for example, Guide E2081).
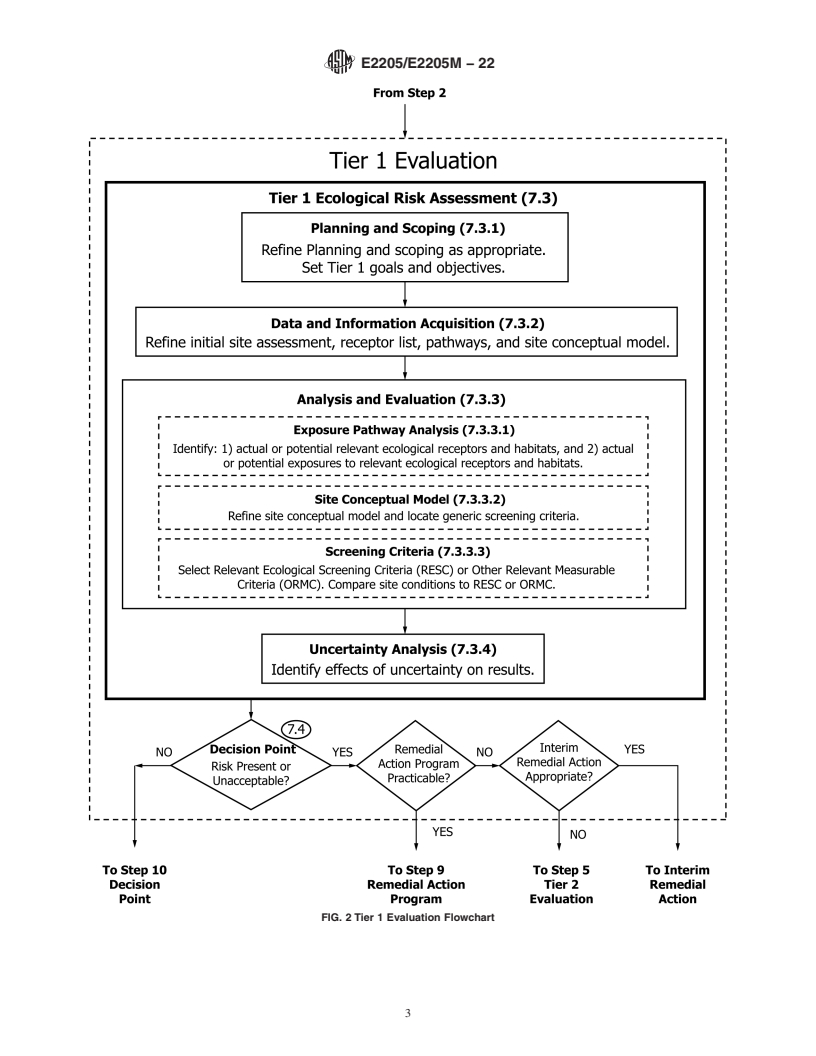
1.2 Chemical release sites vary greatly in terms of complexity, physical and chemical characteristics, and the risk that they might pose to ecological resources. The Eco-RBCA process, as described in Guide E2081, recognizes this variability and incorporates a tiered approach that integrates site assessment, response actions, and remedial actions with ERA. The process begins with relatively simple analyses in Tier 1 and, if necessary, proceeds to more detailed evaluations in Tier 2 or Tier 3. The process of gathering and evaluating data is conducted in such a manner that only those data that are necessary for a given tier's decision making are collected at each tier. Hence, this can facilitate effective use of resources and reduce initial data requirements.
1.3 Eco-RBCA is intended to provide a framework for sites not covered under regulatory programs and for sites under regulatory programs that lack specific guidance. Eco-RBCA may also provide a useful framework to help merge several possible appr...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2205/E2205M − 22
Standard Guide for
Risk-Based Corrective Action for Protection of Ecological
1
Resources
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2205/E2205M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This guide for risk-based corrective action for the protection of ecological resources (Eco-RBCA)
provides a flexible framework for a tiered approach to ecological risk assessment (ERA) and risk
management decision-making at chemical release sites. The framework of the Eco-RBCA guide
parallels the framework in Guide E2081 with respect to the tiered approach for data gathering,
evaluation and decision-making, and should, when possible, be conducted concurrent with the broader
RBCA process activities. The Eco-RBCA guide directs the user to Guide E2081 for development and
implementation of a corrective action program. This guide supplements Guide E2081 and was
developed after careful consideration of the peer-reviewed published literature and existing federal,
regional, and state ecological risk–assessment guidance. The user of this guide, as defined in 3.1.45,
needs to be familiar with Guide E2081 and the overall RBCA process. The RBCA process provides
a flexible, technically defensible framework for corrective action that has applicability to a wide range
of sites and chemicals of concern.
ASTM guides are not federal or state regulations; rather, they are consensus standards that can be
followed voluntarily. It is not within the scope of this standard to provide the details of specific
regulatory requirements. Collectively, the Eco-RBCA and RBCA guides provide an integrated
framework to corrective action. Eco-RBCA is intended to complement rather than replace the
decision-making structures of regulatory programs. In addition, Eco-RBCA is intended to provide a
framework for sites not covered under regulatory programs, for sites under regulatory programs that
lack guidance, or for sites under programs with guidance that lack detail. Eco-RBCA may also provide
a useful framework to help merge an approach when multiple regulatory programs apply. Even when
a site is not currently governed by a regulatory program, consultation with the appropriate regulatory
agency(ies) will ensure regulatory compliance and provide technical guidance.
The Eco-RBCA process is intended to accommodate a diversity of sites and conditions by providing
a framework that can address site-specific needs. The appendixes provide useful technical details and
case study examples, although the application of this guide does not require their use. Eco-RBCA is
a process for evaluating ecological risk and decision making. To facilitate the implementation of
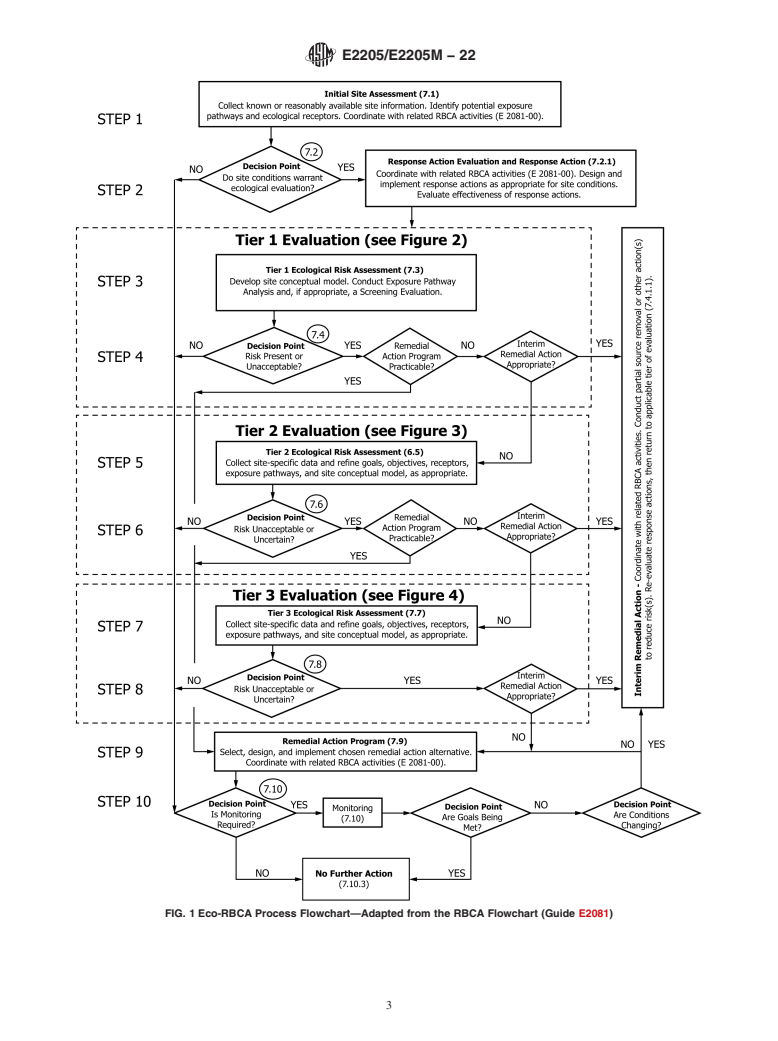
Eco-RBCA, the framework is organized into ten steps and three risk assessment tiers that begin with
relatively simple analyses and progress to more complex assessments as site conditions warrant (see
Fig. 1). Although organized into steps and tiers, the user should recognize that Eco-RBCA progresses
conceptually in a linear manner, but may not be implemented in a linear manner. The objective should
be to conduct the evaluation in the manner that most appropriately meets the needs and goals of the
assessment. Each tier includes five types of activities that increase in complexity and level of effort
as the evaluation progresses through the RBCA process. These activities are (1) planning and scoping,
(2) data and information acquisition, (3) analysis and evaluation, (4) decision making, and (5)
remedial actions. The details of the activities and how they are implemented can vary, depending on
the nature and complexity of the site and the tier level. Early in the Eco-RBCA process, assumptions
are biased toward being overly protective (that is, “conservative”) because of uncertainties inherent in
non–site-specific data. Typically, as the site progresses through the tiered evaluation, more site-specific
information is collected and uncertainty decreases; therefore, less-conservative assumptions can be
used in the evaluation.
NOTE 1—This is a consequence of the screening process since the primary purpose is to quickly refine the lists of
chemicals of concern to understand which ones are the primary risk drivers. Commensurate with this reduced
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2205/E2205M − 02 (Reapproved 2014) E2205/E2205M − 22
Standard Guide for
Risk-Based Corrective Action for Protection of Ecological
1
Resources
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2205/E2205M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This guide for risk-based corrective action for the protection of ecological resources (Eco-RBCA)
provides a flexible framework for a tiered approach to ecological risk assessment (ERA) and risk
management decision-making at chemical release sites. The framework of the Eco-RBCA guide
parallels the framework in Guide E2081 with respect to the tiered approach for data gathering,
evaluation and decision-making, and should, when possible, be conducted concurrent with the broader
RBCA process activities. The Eco-RBCA guide directs the user to Guide E2081 for development and
implementation of a corrective action program. This guide supplements Guide E2081 and was
developed after careful consideration of the peer-reviewed published literature and existing federal,
regional, and state ecological risk–assessment guidance. The user of this guide, as defined in 3.1.45,
needs to be familiar with Guide E2081 and the overall RBCA process. The RBCA process provides
a flexible, technically defensible framework for corrective action that has applicability to a wide range
of sites and chemicals of concern.
ASTM guides are not federal or state regulations; rather, they are consensus standards that can be
followed voluntarily. It is not within the scope of this standard to provide the details of specific
regulatory requirements. Collectively, the Eco-RBCA and RBCA guides provide an integrated
framework to corrective action. Eco-RBCA is intended to complement rather than replace the
decision-making structures of regulatory programs. In addition, Eco-RBCA is intended to provide a
framework for sites not covered under regulatory programs, for sites under regulatory programs that
lack guidance, or for sites under programs with guidance that lack detail. Eco-RBCA may also provide
a useful framework to help merge an approach when multiple regulatory programs apply. Even when
a site is not currently governed by a regulatory program, consultation with the appropriate regulatory
agency(ies) will ensure regulatory compliance and provide technical guidance.
The Eco-RBCA process is intended to accommodate a diversity of sites and conditions by providing
a framework that can address site-specific needs. The appendixes provide useful technical details and
case study examples, although the application of this guide does not require their use. Eco-RBCA is
a process for evaluating ecological risk and decision making. To facilitate the implementation of
Eco-RBCA, the framework is organized into ten steps and three risk assessment tiers that begin with
relatively simple analyses and progress to more complex assessments as site conditions warrant (see
Fig. 1). Although organized into steps and tiers, the user should recognize that Eco-RBCA progresses
conceptually in a linear manner, but may not be implemented in a linear manner. The objective should
be to conduct the evaluation in the manner that most appropriately meets the needs and goals of the
assessment. Each tier includes five types of activities that increase in complexity and level of effort
as the evaluation progresses through the RBCA process. These activities are (1) planning and scoping,
(2) data and information acquisition, (3) analysis and evaluation, (4) decision making, and (5)
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E50 on Environmental Assessment, Risk Management and Corrective Action and is the direct responsibility
of Subcommittee E50.04 on Corrective Action.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014Oct. 1, 2022. Published May 2015February 2023. Originally approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 20092014 as
ε1
E2205 – 02(2009)(2014). . DOI: 10.1520/E2205_E2205M-02R14.10.1520/E2205_E2205M-22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2205/E2205M − 22
FIG. 1 Eco-RBCA Process Flowchart—Adapted from the RBCA Flowchart (Guide E2081)
2
---------------------- Page: 2 --
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.