ASTM D3412-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Coefficient of Friction, Yarn to Yarn
Standard Test Method for Coefficient of Friction, Yarn to Yarn
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method for testing yarn-to-yarn friction is being used, but is not recommended, for acceptance testing of commercial shipments since between-laboratory precision is known to be poor.
5.1.1 In some cases, the purchaser and supplier may have to test a commercial shipment of one or more specific materials by the best available method even though the method has not been recommended for acceptance testing of commercial shipments. In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported test results when using Test Method D 3412 for acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias. As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are from a lot of material of the type in question. The test specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The average results from the two laboratories should be compared using Student’t-test for unpaired data and an acceptable probability level chosen by the two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consideration to the known bias.
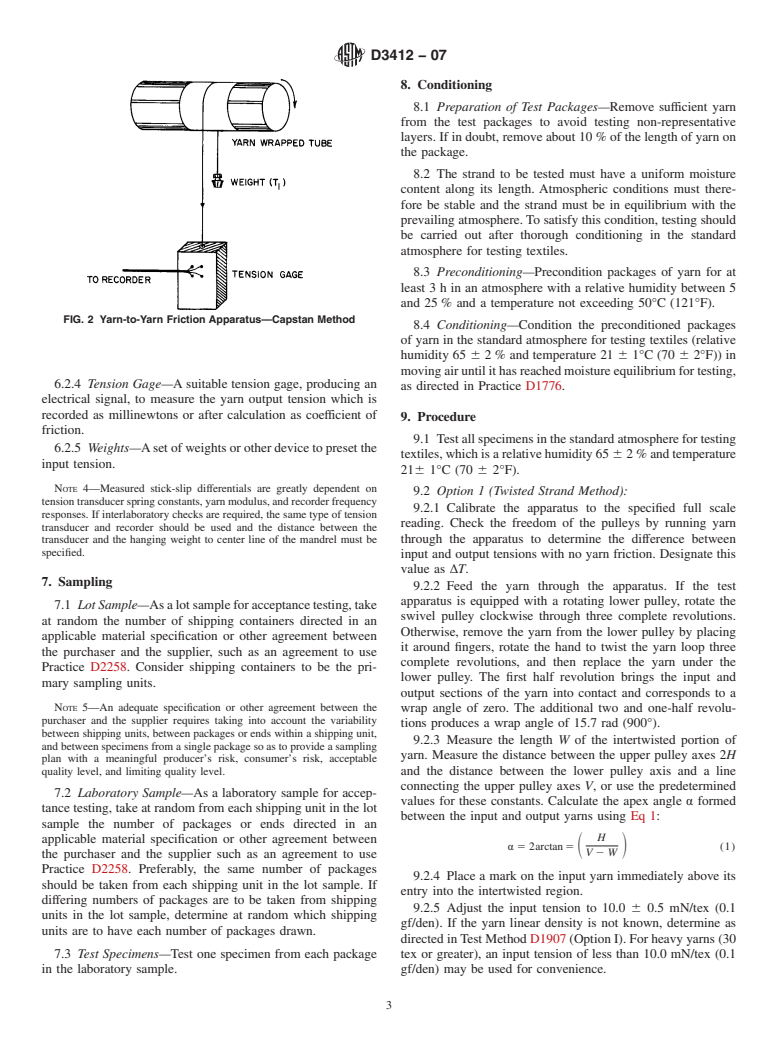
This test method is intended for the determination of yarn-to-yarn boundary friction coefficients measured over a specified length of yarn.
The test method is useful for quality control, research, and the characterization of yarn boundary lubricants.
Note 3—Because the geometry of the yarns is different, Options 1 and 2 should not be expected to give the same numerical values on the same yarns.
FIG. 1 Twisted Strand Yarn-to-Yarn Friction Apparatus—Twisted-Yarn Method
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of frictional properties for both continuous filament and spun-staple yarns under boundary friction conditions.
1.2 This test method has been used with yarns having linear densities ranging from 1.5 to 200 tex, but may be used with yarns outside these ranges (15 to 1800 denier). Note 1For coefficient of friction, yarn to metal, see Test Method D 3108.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3412 − 07
StandardTest Method for
1
Coefficient of Friction, Yarn to Yarn
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3412; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of frictional
4.1 A length of yarn is moved at a known speed in contact
properties for both continuous filament and spun-staple yarns
with itself or similar yarn at a specified wrap angle. The input
under boundary friction conditions.
and output tensions are measured and the coefficient of friction
calculated. Alternatively, apparatus may be used in which the
1.2 This test method has been used with yarns having linear
ratio of input to output tension is measured allowing the
densities ranging from 1.5 to 200 tex, but may be used with
coefficient of friction to be indicated directly.
yarns outside these ranges (15 to 1800 denier).
4.2 Two optional procedures are included. Option 1 is based
NOTE 1—For coefficient of friction, yarn to metal, see Test Method
on theTwisted Strand Method, using a wrap angle of 15.71 rad
D3108.
(900°). Option 2 is based on the Capstan Method, using a wrap
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
angle of 3.14 radians (180°).
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
information only.
NOTE 2—Editions of Test Method D3412 prior to the 1986 revision
incorrectly stated the wrap angle for Option 1 to be 18.85 rad. This is
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
incorrect, since 3 turns of the swivel pulley do not result in a wrap angle
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of18.85radians.Thishasnowbeencorrectedto15.71rad.Thisshouldbe
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
taken into account in comparing with earlier results.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents 5.1 This test method for testing yarn-to-yarn friction is
2
being used, but is not recommended, for acceptance testing of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
commercial shipments since between-laboratory precision is
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
known to be poor.
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
5.1.1 In some cases, the purchaser and supplier may have to
D1907 Test Method for Linear Density of Yarn (Yarn Num-
test a commercial shipment of one or more specific materials
ber) by the Skein Method
by the best available method even though the method has not
D2258 Practice for Sampling Yarn for Testing
been recommended for acceptance testing of commercial
D3108 Test Method for Coefficient of Friction,Yarn to Solid
shipments. In case of a dispute arising from differences in
Material
reported test results when using Test Method D3412 for
D4849 Terminology Related to Yarns and Fibers
acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and
3. Terminology
the supplier should conduct comparative tests to determine if
there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.58, Yarns and
statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of
Fibers, refer to Terminology D4849.
bias.As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test
3.2 For all other terminology related to textiles, refer to
specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are
Terminology D123.
from a lot of material of the type in question. The test
specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
to each laboratory for testing.The average results from the two
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.58 on Yarns and Fibers.
laboratories should be compared using Student’s t-test for
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2007. Published January 2007. Originally
unpaireddataandanacceptableprobabilitylevelchosenbythe
approved in 1975T. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D3412 – 01. DOI:
10.1520/D3412-07.
two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consid-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. eration to the known bias.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.