ASTM E1488-12
(Guide)Standard Guide for Statistical Procedures to Use in Developing and Applying Test Methods
Standard Guide for Statistical Procedures to Use in Developing and Applying Test Methods
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The creation of a standardized test method generally follows a series of steps from inception to approval and ongoing use. In all such stages there are questions of how well the test method performs.
4.1.1 Assessments of a new or existing test method generally involve statistical planning and analysis. This standard recommends what approaches may be taken and indicates which standards may be used to perform such assessments.
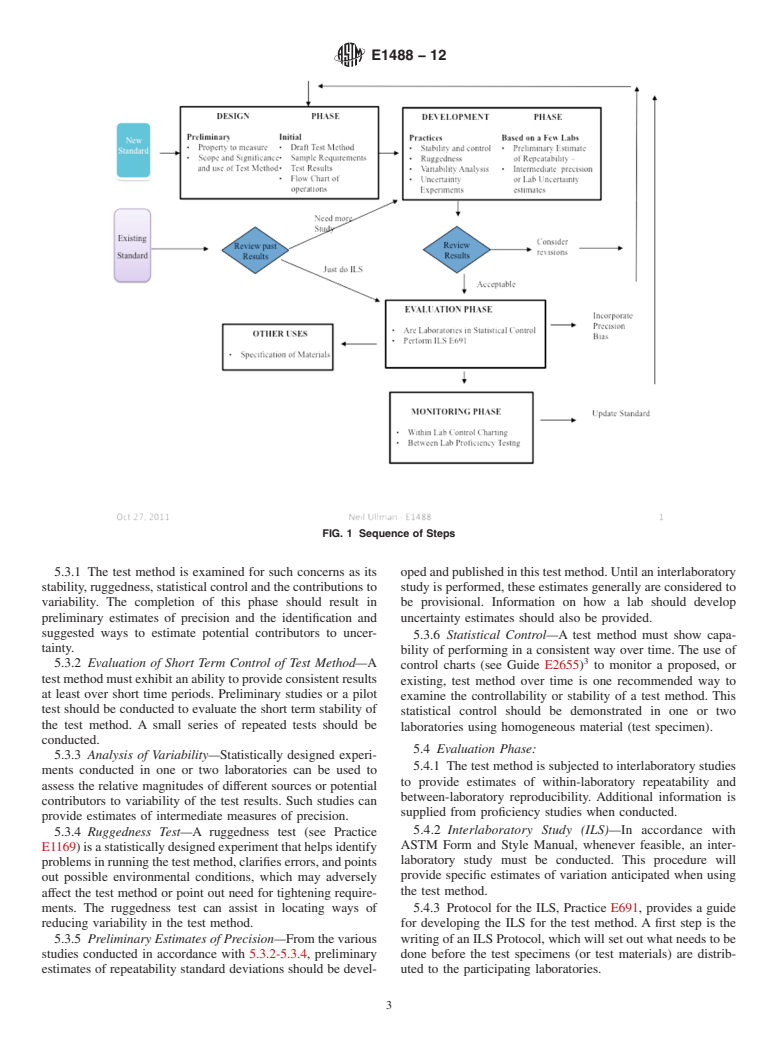
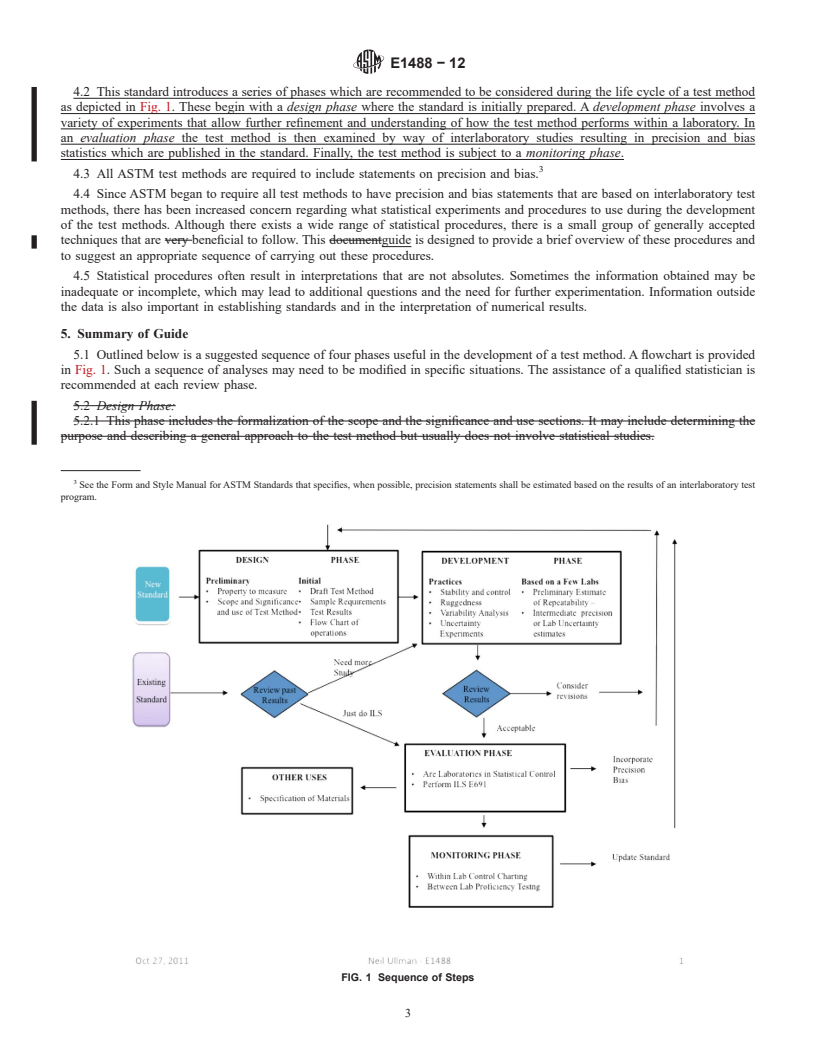
4.2 This standard introduces a series of phases which are recommended to be considered during the life cycle of a test method as depicted in Fig. 1. These begin with a design phase where the standard is initially prepared. A development phase involves a variety of experiments that allow further refinement and understanding of how the test method performs within a laboratory. In an evaluation phase the test method is then examined by way of interlaboratory studies resulting in precision and bias statistics which are published in the standard. Finally, the test method is subject to a monitoring phase.
4.3 All ASTM test methods are required to include statements on precision and bias.3
4.4 Since ASTM began to require all test methods to have precision and bias statements that are based on interlaboratory test methods, there has been increased concern regarding what statistical experiments and procedures to use during the development of the test methods. Although there exists a wide range of statistical procedures, there is a small group of generally accepted techniques that are beneficial to follow. This guide is designed to provide a brief overview of these procedures and to suggest an appropriate sequence of carrying out these procedures.
4.5 Statistical procedures often result in interpretations that are not absolutes. Sometimes the information obtained may be inadequate or incomplete, which may lead to additional questions and the need for further experimentation. Information outside the data is also important in establishing...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide identifies statistical procedures for use in developing new test methods or revising or evaluating existing test methods, or both.
1.2 This guide also cites statistical procedures especially useful in the application of test methods.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1488 − 12 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Guide for
Statistical Procedures to Use in Developing and Applying
1
Test Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 bias, n—the difference between the expectation of the
test results and an accepted reference value. E177
1.1 This guide identifies statistical procedures for use in
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Statistical procedures include the sam-
developing new test methods or revising or evaluating existing
plingconsiderationsortheexperimentdesignforthecollection
test methods, or both.
of data, or both, and the numerical and graphical approaches to
1.2 This guide also cites statistical procedures especially
summarize and analyze the collected data.
useful in the application of test methods.
3.1.2 coeffıcient of variation, CV, n—for a nonnegative
2. Referenced Documents
characteristic, the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: for a population or sample. E2586
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
3.1.3 component of variance, n—a part of a total variance
ASTM Test Methods
identified with a specified source of variability.
E178 Practice for Dealing With Outlying Observations
3.1.4 control chart, n—chart on which are plotted a statis-
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to ticalmeasureofasubgroupversustimeofsamplingalongwith
Determine the Precision of a Test Method limits based on the statistical distribution of that measure so as
E1169 Practice for Conducting Ruggedness Tests to indicate how much common, or chance, cause variation is
E1402 Guide for Sampling Design inherent in the process or product. E2587
E2282 Guide for Defining the Test Result of a Test Method
3.1.5 observation, n—the process of obtaining information
E2489 Practice for Statistical Analysis of One-Sample and
regarding the presence or absence of an attribute of a test
Two-SampleInterlaboratoryProficiencyTestingPrograms
specimen, or of making a reading on a characteristic or
E2554 Practice for Estimating and Monitoring the Uncer-
dimension of a test specimen. E2282
tainty of Test Results of a Test Method in a Single
3.1.6 observed value, n—the value obtained by making an
Laboratory Using a Control Sample Program
E2586 Practice for Calculating and Using Basic Statistics observation. E2282
E2587 Practice for Use of Control Charts in Statistical
3.1.7 precision, n—the closeness of agreement between
Process Control
independent test results obtained under stipulated conditions.
E2655 Guide for Reporting Uncertainty of Test Results and
E177
Use of the Term Measurement Uncertainty inASTM Test
3.1.8 proficiency testing, n—determination of laboratory
Methods
testing performance by means of interlaboratory comparisons.
3. Terminology
E2489
3.1 Definitions—For a more extensive list of terms in E11
3.1.9 repeatability, n—precision under repeatability condi-
standards, see Terminology E456.
tions. E177
3.1.10 repeatability conditions, n—conditions where inde-
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E11 on Quality and
pendent test results are obtained with the same method on
Statistics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E11.20 on Test Method
Evaluation and Quality Control. identical test items in the same laboratory by the same operator
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2012. Published September 2012. Originally
using the same equipment within short intervals of time. E177
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E1488 – 09. DOI:
10.1520/E1488-12.
3.1.11 repeatability limit r, n—the value below which the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
absolutedifferencebetweentwoindividualtestresultsobtained
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
under repeatability conditions may be expected to occur with a
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. probability of approximately 0.95 (95 %). E177
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1488 − 12
3.1.12 repeatability standard deviation, s,n— the standard recommends what approaches may be taken and indicates
r
deviation of test results obtained under repeatability condi- which standards may be used to perform such assessments.
tions. E177
4.2 This standard
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1488 − 09 E1488 − 12 An American National Standard
Standard Guide for
Statistical Procedures to Use in Developing and Applying
1
Test Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon («) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide identifies statistical procedures for use in developing new test methods or revising or evaluating existing test
methods, or both.
1.2 This guide also cites statistical procedures especially useful in the application of test methods.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E178 Practice for Dealing With Outlying Observations
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1169 Practice for Conducting Ruggedness Tests
E1402 Guide for Sampling Design
E2282 Guide for Defining the Test Result of a Test Method
E2489 Practice for Statistical Analysis of One-Sample and Two-Sample Interlaboratory Proficiency Testing Programs
E2554 Practice for Estimating and Monitoring the Uncertainty of Test Results of a Test Method in a Single Laboratory Using
a Control Sample Program
E2586 Practice for Calculating and Using Basic Statistics
E2587 Practice for Use of Control Charts in Statistical Process Control
E2655 Guide for Reporting Uncertainty of Test Results and Use of the Term Measurement Uncertainty in ASTM Test Methods
2.2 ISO Standards:
3
ISO 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories
3
ISO Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:Definitions—For a more extensive list of terms in E11 standards, see Terminology E456.
3.1.1 bias, n—the difference between the expectation of the test results and an accepted reference value. E177
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E11 on Quality and Statistics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E11.20 on Test Method Evaluation
and Quality Control.
Current edition approved May 15, 2009Aug. 1, 2012. Published July 2009 September 2012. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20082009
as E1488 – 08a.E1488 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/E1488-09.10.1520/E1488-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
Statistical procedures include the sampling considerations or the experiment design for the collection of data, or both, and the
numerical and graphical approaches to summarize and analyze the collected data.
3.1.2 coeffıcient of variation, CV, n—for a nonnegative characteristic, the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean for a
population or sample. E2586
3.1.3 component of variance, n—a part of a total variance identified with a specified source of variability.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1488 − 12
3.1.4 control chart, n—chart on which are plotted a statistical measure of a subgroup versus time of sampling along with limits
based on the statistical distribution of that measure so as to indicate how much common, or chance, cause variation is inherent in
the process or product. E2587
3.1.5 observation, n—the process of obtaining information regarding the presence or absence of an attribute of a test specimen,
or of making a reading on a characteristic or dimension of a test specimen. E2282
3.1.6 observed value, n—the value obtained by making an observation. E2282
3.1.7 precision, n—the closeness of agreement between independent test results obtained under stipulated conditions. E177
3.1.8 proficiency testing, n—determination of laboratory testing performance by means of interlaboratory comparisons. E2489
3.1.9 repeatability, n—precision under repeatability conditions. E177
3.1.10 repeatability conditions, n—conditions where independent test results are obtained with the same method on identical test
items in the same laboratory by the same operator using the
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.