ASTM D5968-19ae1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Corrosiveness of Diesel Engine Oil at 121 °C
Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Corrosiveness of Diesel Engine Oil at 121 °C
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is intended to simulate the corrosion process of non-ferrous metals in diesel lubricants. The corrosion process under investigation is that believed to be induced primarily by inappropriate lubricant chemistry rather than lubricant degradation or contamination. This test method has been found to correlate with an extensive fleet database containing corrosion-induced cam and bearing failures.
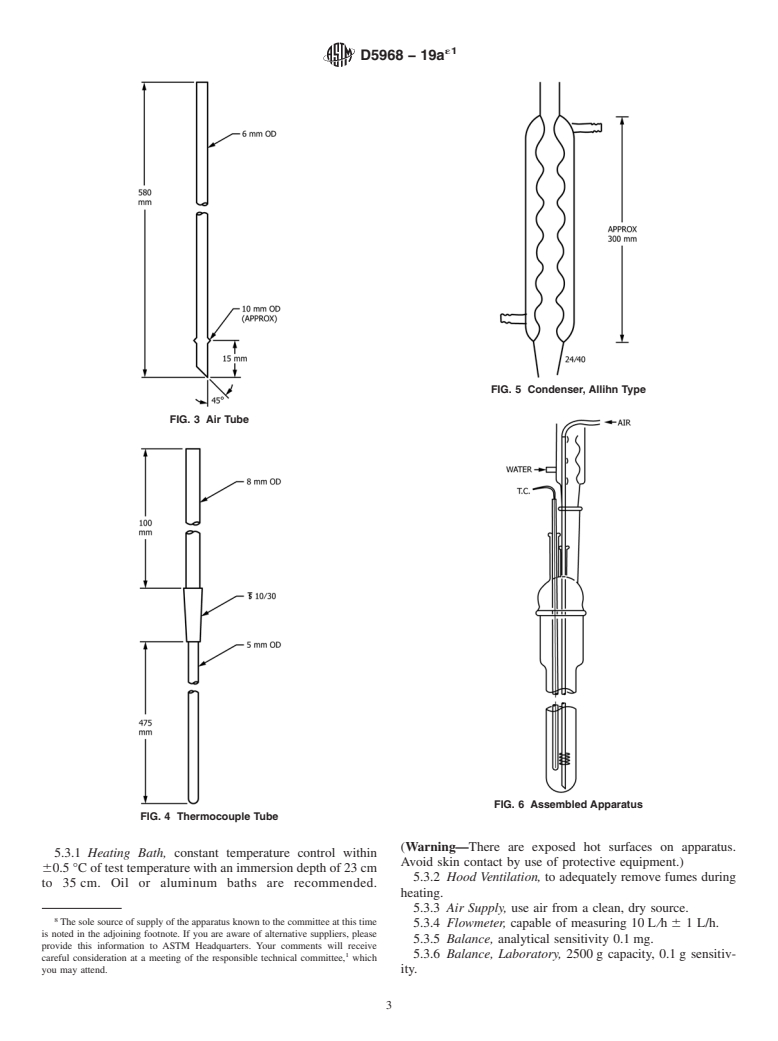
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used to test diesel engine lubricants to determine their tendency to corrode various metals, specifically alloys of lead and copper commonly used in cam followers and bearings. Correlation with field experience has been established.4
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in 5.3.1, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, 6.9, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, and 7.1.5.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: D5968 − 19a
Standard Test Method for
1
Evaluation of Corrosiveness of Diesel Engine Oil at 121 °C
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5968; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially updated TMC governance information in June 2022.
INTRODUCTION
The method described in this test method is based on the gas turbine lubricant corrosion and
oxidation test described in FederalTest Method Standard 791, Method 5308. Because this test method
relates to corrosion in diesel engines rather than in gas turbines, temperatures, metal coupons, and
certain parts of the test procedure were modified to be more appropriate for heavy duty diesel engines.
The method described in this test method can be used by any properly equipped laboratory, without
2
outside assistance. However, the ASTM Test Monitoring Center (TMC) provides reference oils and
an assessment of the test results obtained on those oils by the laboratory (see Annex A1). By these
means, the laboratory will know whether their use of the test method gives results statistically similar
to those obtained by other laboratories. Furthermore, various agencies require that a laboratory utilize
the TMC services in seeking qualification of oils against specifications. For example, the U.S. Army
imposes such a requirement in connection with several Army engine lubricating oil specifications.
Accordingly, this test method is written for use by laboratories that utilize the TMC services.
Laboratories that choose not to use those services may simply ignore those portions of the test method
that refer to the TMC.
This test method may be modified by means of Information Letters issued by theTMC. In addition,
the TMC may issue supplementary memoranda related to the method (see Annex A1). For other
3
information, refer to the research report on the Cummins Bench Corrosion Test.
1. Scope* 1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1.1 This test method is used to test diesel engine lubricants
standard.
to determine their tendency to corrode various metals, specifi-
cally alloys of lead and copper commonly used in cam
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
followers and bearings. Correlation with field experience has
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4
been established.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of
Specific hazard statements are given in 5.3.1, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 6.8,
Subcommittee D02.B0.02 on Heavy Duty Engine Oils.
6.9, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, and 7.1.5.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D5968 – 19. DOI:
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
10.1520/D5968-19AE01.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2
ASTM Test Monitoring Center, 203 Armstrong Drive, Freeport, PA 16229.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
(http://www.astmtmc.org)
3
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D02-1322. The research report and
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
this test method are supplemented by Information Letters and Memoranda issued by
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
theASTM Test Monitoring Center. This edition incorporates revisions contained in
all information letters through No. 19-1. Users of this test method shall contact the
ASTM Test Monitoring Center to obtain the most recent of these.
4
Wang, J. C., and Cusano, C. M., “Development ofABench Test to Detect Oils
Corrosive to Engine Components,” SAE Technical Paper No. 940790, 1994.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D5968 − 19a
2. Referenced Documents
5
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D130 Test Method f
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.